Categories: Blockchain
High Throughput Blockchain Solutions for Modern Demands
A high throughput blockchain delivers exceptional transaction speeds and scalability, making it ideal for extensive applications and industries. By efficiently processing a high volume of transactions, it revolutionizes how blockchain technology is used in finance, supply chains, and beyond.
In the realm of blockchain technology, high throughput blockchain solutions are crucial for addressing scalability challenges. Traditional blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum face limitations in transaction speed and volume, hindering their ability to support widespread adoption of decentralized applications (dApps).
Table of Contents
Innovative high throughput solutions aim to enhance transaction processing capabilities, reduce latency, and lower costs per transaction. These advancements are essential for unlocking blockchain's full potential and enabling broader applications across various sectors.
Understanding High Throughput Blockchain
High Throughput Blockchain, also known as high-throughput blockchain, is a type of blockchain designed to handle a large number of transactions in a short period. Unlike first-generation blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, which are limited by slow processing speeds and high transaction costs, High Throughput Blockchain leverages advanced technologies and architectures to enhance scalability, enabling the processing of thousands or even hundreds of thousands of transactions per second (TPS).
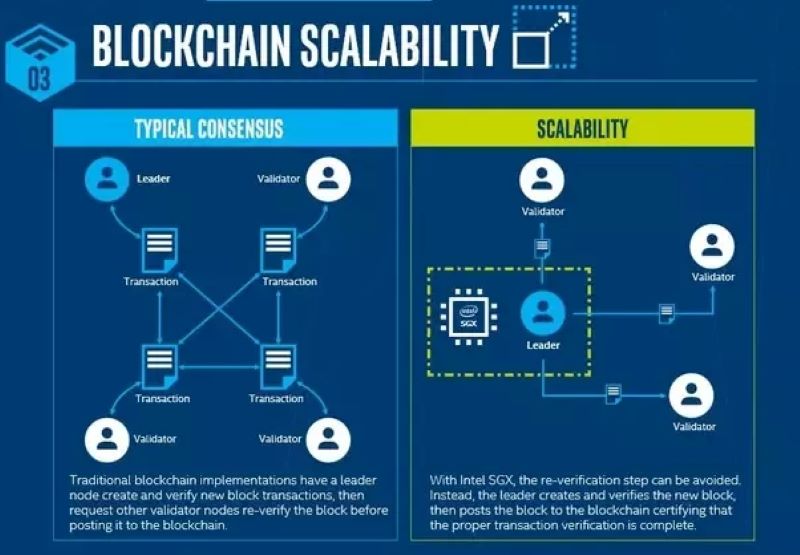
The Importance of High Throughput Blockchain
The development of decentralized applications (dApps) in areas such as decentralized finance (DeFi), blockchain gaming (GameFi), and Web3 has created a growing demand for highly scalable blockchains. Traditional blockchains cannot meet this demand due to network congestion and increased transaction costs during traffic spikes.
High Throughput Blockchain addresses this issue by providing a robust and efficient platform for processing transactions, allowing dApps to operate smoothly and meet user demands. This is particularly crucial for applications that require fast transaction speeds and low costs, such as financial transactions, online payments, and blockchain gaming.
Technologies Behind High Throughput Blockchain
To achieve high throughput, these blockchains utilize a variety of technologies and approaches, including:
New Consensus Mechanisms: Instead of Proof of Work (PoW), High Throughput Blockchains often use consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Stake (PoS) or Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), which help reduce energy consumption and increase transaction confirmation speeds.
Sharding: Dividing the blockchain network into smaller segments (shards), where each shard processes a subset of transactions, significantly increases the overall processing capacity of the network.
New Data Structures: Utilizing advanced data structures like Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) to enable parallel processing of transactions, thereby increasing speed and throughput.
Hardware Optimization: Employing specialized hardware to accelerate blockchain computations, improving performance and reducing latency.
Layer-1 Scaling Solutions
Blockchain is evolving rapidly, but its scalability remains a significant challenge. Layer-1 solutions have emerged to address this issue by directly improving the underlying blockchain protocol, providing superior performance and scalability benefits.
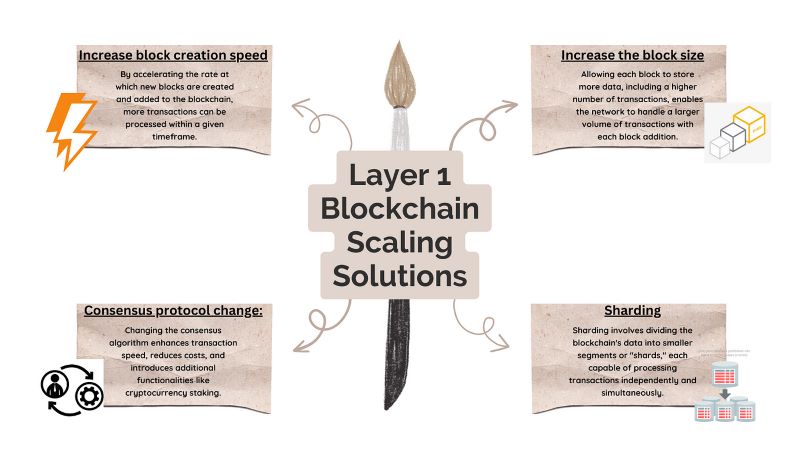
New Consensus Mechanisms
Proof of Stake (PoS): Instead of using energy-intensive computational power like Proof of Work (PoW), PoS allows users to "stake" their cryptocurrency to validate transactions, saving energy, increasing speed, and reducing centralization risks. Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Users elect delegates to validate transactions on their behalf, enhancing the democratic nature and efficiency of the consensus process.
New Data Structures:
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG): Unlike traditional blockchain, DAG uses a directed acyclic graph structure, enabling simultaneous processing of multiple transactions, thereby increasing network speed and throughput.
Block-lattice: Allows multiple parallel chains of the blockchain to exist concurrently, enhancing scalability and reducing congestion. 3. Sharding:
Sharding
Divides the blockchain network into smaller segments (shards), where each shard processes a subset of transactions, significantly increasing the overall processing capacity without compromising security and decentralization. Dynamic Sharding: Automatically adjusts the size and number of shards to accommodate network demand.
Increasing Block Size
Allows more transactions per block, enhancing transaction throughput. However, this approach requires careful consideration of hardware resource requirements and network decentralization.
Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
Layer-2 scaling solutions are pivotal innovations designed to enhance the scalability and efficiency of blockchain networks, particularly addressing the limitations of on-chain transactions. These solutions operate alongside the main blockchain, utilizing different mechanisms to process transactions faster and more cost-effectively.
State channels represent one such solution, enabling participants to conduct numerous transactions off-chain. These transactions are recorded and settled on the main blockchain only when necessary, minimizing congestion and costs while maintaining security through cryptographic proofs.
Sidechains function as autonomous blockchains connected to the mainchain. They facilitate faster transaction processing by handling transactions off the mainchain, leveraging their independent consensus mechanisms. This setup reduces the burden on the mainchain, allowing for increased throughput and lower fees.
.jpg)
Plasma introduces a hierarchical framework where multiple child chains, or Plasma chains, can execute transactions independently. These chains periodically submit a summary of their transactions to the mainchain, enhancing scalability by processing a large number of transactions off-chain while maintaining security through periodic anchoring.
Rollups are emerging as effective scaling solutions for Ethereum. Optimistic rollups bundle transactions off-chain and post their results on-chain, assuming validity unless proven otherwise. Zero-knowledge rollups, on the other hand, use zero-knowledge proofs to ensure the validity of transactions, offering a balance between scalability and security.
Examples of layer-2 scaling solutions include the Lightning Network, which enables fast and inexpensive Bitcoin transactions by conducting them off-chain and settling them periodically on the Bitcoin blockchain. Polygon (formerly Matic Network) provides a framework for Ethereum scaling through sidechains, enhancing transaction throughput and efficiency. Arbitrum utilizes optimistic rollups to increase Ethereum's transaction capacity while maintaining compatibility with existing smart contracts.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
Emerging technologies and innovations are continuously reshaping the landscape of blockchain scalability and efficiency. These advancements aim to address the inherent limitations of traditional blockchain architectures, paving the way for more scalable and robust decentralized systems.

Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) represent a paradigm shift from traditional blockchain structures. Unlike linear chains where each block follows the previous one, DAG-based blockchains like Hashgraph and IOTA use a graph-like structure where transactions are arranged in a directed acyclic graph. This approach allows for parallel processing of transactions, potentially increasing throughput and reducing latency compared to linear blockchains.
Sharding with Cross-Shard Communication is another innovative approach to scaling blockchain networks. Sharding involves partitioning the blockchain into smaller shards, each handling a subset of transactions. However, ensuring seamless communication between shards poses significant challenges. Solutions such as cross-shard communication protocols and consensus mechanisms are being explored to facilitate interoperability and maintain the integrity of the entire blockchain network.
Hardware acceleration plays a crucial role in enhancing blockchain performance. Specialized hardware such as Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) and Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are designed to execute blockchain-specific computations more efficiently than general-purpose processors. ASICs, for instance, are tailored for specific blockchain algorithms, significantly improving processing speeds and reducing energy consumption.
Example of High Throughput Blockchain
The blockchain world is witnessing the rise of numerous High Throughput Blockchain (HTB) projects featuring unique technologies and impressive scalability. Here are some notable examples:
Solana: Known for its extremely fast transaction speeds, Solana uses the Proof of History (PoH) consensus mechanism combined with Proof of Stake (PoS) to achieve throughput of up to 65,000 TPS. PoH acts as a global clock, organizing transactions in chronological order and accelerating confirmation times.
Avalanche: With its unique subnet architecture, Avalanche allows the creation of multiple customizable subnets, each capable of using its own consensus mechanism. This enables Avalanche to achieve high scalability and flexibility, supporting a wide range of applications.
Algorand: Utilizing the unique Pure Proof of Stake (PPoS) consensus mechanism, Algorand ensures high decentralization and good scalability. PPoS allows all users to participate in the consensus process, enhancing security and minimizing centralization risks.
U2U (Helios Consensus): U2U Chain, the blockchain platform of U2U Network, employs the Helios Consensus mechanism, an innovative combination of Proof of Stake (PoS) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS). Coupled with the Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) structure and the OstracismVM virtual machine, U2U Chain achieves impressive transaction throughput, reaching hundreds of thousands of TPS while ensuring high security and decentralization.

High Throughput Blockchain: Diverse Applications for Modern Life
The rapid and efficient transaction processing capabilities of High Throughput Blockchain (HTB) open up numerous application opportunities across various fields, offering significant improvements over traditional systems. Here are some specific applications:
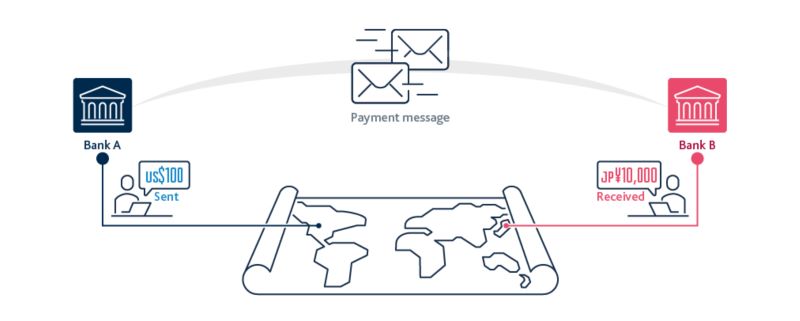
Cross-Border Payments:
HTB can revolutionize cross-border payments by significantly reducing transaction time and costs. International transactions often take several days to process and involve high fees due to multiple intermediaries. HTB eliminates these intermediaries, enabling near-instant payments at significantly lower costs.
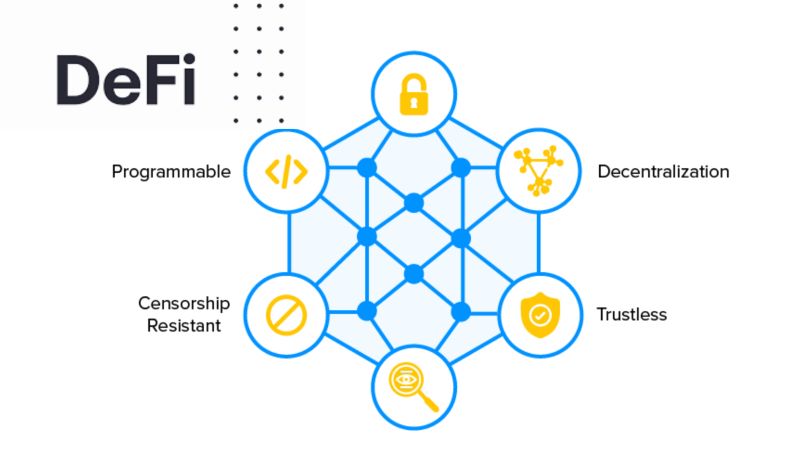
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Transactions:
HTB provides an ideal platform for DeFi applications such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), decentralized lending and borrowing, stablecoins, and derivatives. The scalability of HTB allows DeFi applications to handle large volumes of transactions, delivering smooth and efficient user experiences.
NFT Marketplaces:
The booming NFT market requires a platform that can handle a large number of NFT transactions. HTB provides the speed and throughput necessary to support the growth of this market, allowing users to buy, sell, and trade NFTs quickly and easily.

Online Gaming (GameFi):
HTB has the potential to revolutionize the gaming industry by enabling decentralized games where players can own and trade in-game assets as NFTs. The scalability of HTB allows these games to handle a large number of in-game transactions, creating a smoother and more engaging gaming experience.

Supply Chain Management:
HTB can be used to track and verify the provenance of products in the supply chain, from manufacturers to end consumers. This enhances transparency and traceability, reduces fraud, and ensures product quality.
Other Applications:
In addition to the above, HTB has potential applications in many other fields such as:
- Electronic voting
- Digital identity management
- Real estate
- Healthcare
- Education
The development of High Throughput Blockchain solutions has marked a significant milestone in addressing scalability challenges, opening the door to a new era of blockchain applications. From Layer-1 solutions like sharding and Proof of Stake (PoS) to Layer-2 solutions like state channels and rollups, blockchain technology is continuously advancing to meet the growing demands of decentralized applications.
Projects like Solana, Avalanche, Algorand, and notably U2U Network with its advanced Helios Consensus mechanism, have demonstrated the immense potential of High Throughput Blockchain in solving real-world issues across various sectors, including finance, supply chain, gaming, and entertainment. With fast transaction speeds, superior scalability, and low costs, High Throughput Blockchain is not just a technological solution but a driving force for the development of the digital economy in the future.
Although challenges such as decentralization and security remain to be addressed, the continuous progress in this field indicates a promising future for High Throughput Blockchain. With ongoing technological advancements and the increasing number of practical applications, High Throughput Blockchain is poised to become an integral part of our daily lives, delivering significant value to individuals, businesses, and society as a whole.
.png)