Blockchain technology has been making headlines for its potential to revolutionize a variety of industries, from finance to healthcare and beyond. In this beginner's guide, we'll take a closer look at what blockchain protocols are, how they work, and why they are so important in today's digital landscape. We'll explore the different types of blockchain protocols, including public and private blockchains, and discuss their unique strengths and weaknesses. Additionally, we'll examine some of the most popular blockchain protocols in use today, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Ripple.
Table of Contents
- What are Blockchain Protocols?
- Why Does Blockchain Need a Protocol?
- Why is blockchain protocol important to crypto?
- How Does Blockchain Protocol Work?
- Main Types of Blockchain Protocols
- Advantages and disadvantages of Blockchain Protocol
- How is a blockchain protocol different from a platform?
- The Future of Blockchain Protocol
What are Blockchain Protocols?
Blockchain protocols are a set of rules and regulations that govern the functioning of a blockchain network. These protocols define the interface of the network, interactions between computers, incentives for users, and the type of data that can be stored on the network. The primary goal of these protocols is to ensure that the blockchain network adheres to the four fundamental principles: security, decentralization, consistency, and scalability.
Security is a crucial aspect of any blockchain network as it involves the transfer of valuable assets such as cryptocurrencies. The protocols define the structure of the data and implement various security measures to protect the network from malicious users.
Decentralization is a defining characteristic of a blockchain network, as it eliminates the need for any central authority to manage the network. The protocols authorize the network and ensure that it functions autonomously.
Consistency is vital to the integrity of the blockchain network. Whenever a transaction occurs, the protocols update the entire database to ensure that all users have access to the latest information and the network remains consistent.
Scalability refers to the ability of the network to handle an increasing number of transactions and nodes. Initially, scalability was a significant challenge for blockchain networks, but modern protocols have addressed this issue by implementing various techniques to handle the increasing traffic on the network.
Every transaction that occurs on the blockchain network is verified by the developers and stored on the network, providing a transparent ledger that any individual can access. The protocols play a crucial role in maintaining this transparency by ensuring that every transaction is accurately recorded and stored.
.jpg)
Why Does Blockchain Need a Protocol?
A blockchain is a complex network that consists of blocks, each of which stores valuable information, and each block is linked to a unique hash address. This distributed and decentralized system serves as a public ledger, containing a wealth of data, including transactions that are openly shared across all the nodes that form part of the network. The ledger, in this context, is the primary source of information that stores all transaction records. The fact that each machine is connected to one another is what makes this a distributed ledger, and there is no need for any central authority or middlemen to be involved. This fundamental characteristic of decentralization ensures the security and transparency of the system.
In order to maintain the security of data transfer across the network, it is crucial to implement a set of protocols that facilitate secure communication between nodes. Since blockchains are primarily utilized for transactions, protocols play an essential role in regulating data sharing and maintaining the integrity and security of the cryptocurrency network.
Why is blockchain protocol important to crypto?
Blockchain protocols are the fundamental building blocks that underpin the functioning of cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrency is essentially a digital asset that has some monetary value and is secured by encryption. The role of protocols in ensuring the secure transfer of data is crucial. In the context of the blockchain, there is no central authority or government involved in the transfer of funds. Therefore, a set of rules and regulations is required to govern the network.
Blockchain protocols play a key role in establishing the entire structure of the blockchain network, ensuring that digital currency is exchanged securely. They enable users to manage their data and are responsible for handling services such as transactions and payments for all services. The use of blockchain protocols also enables individuals to make financial transactions without the involvement of banks, allowing for greater financial autonomy and independence.
One of the most important features of blockchain protocols is their ability to prevent double-spending, ensuring that funds are only spent once and not duplicated. With the rapid evolution of blockchain technology, protocols are also evolving at a fast pace, with many sectors such as supply chain, healthcare, finance, and more adopting protocol-based blockchain solutions to enhance security and efficiency.
In summary, blockchain protocols are critical components that enable the secure transfer of digital assets and facilitate financial transactions without the need for intermediaries. They play a pivotal role in establishing the entire structure of blockchain networks and continue to evolve with the technology itself.
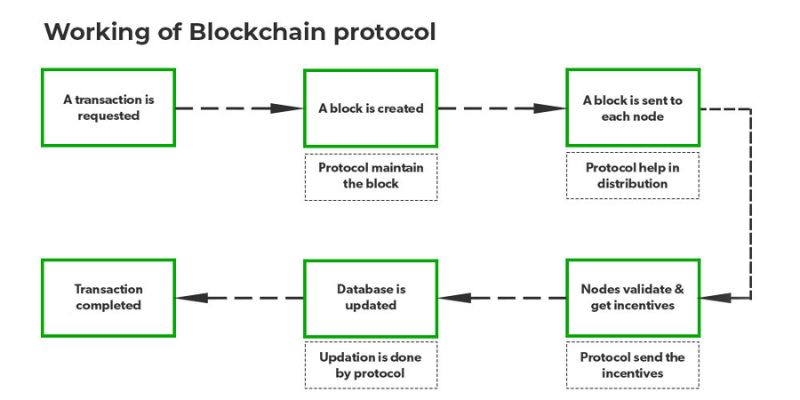
How Does Blockchain Protocol Work?
Suppose that two individuals, A and B, are involved in a transaction. To ensure the security and immutability of the transaction, a block for individual A is created by the blockchain protocol, which cannot be altered once created. The created block is then distributed to every user in the network using protocols, ensuring that the entire network has a copy of the block.
Nodes within the network then verify the transaction, after which each node is sent a reward, managed by the protocol. Once the transaction has been successfully verified, the block is added to the list and the protocols update the database. The updated database is also distributed across the network by the protocols, providing each user with access to the network's summary. Finally, after the completion of the above steps, the transaction is considered complete. At every step, the involvement of protocols ensures a secure and consistent crypto network that is scalable and trustworthy.
Main Types of Blockchain Protocols
Hyperledger
Hyperledger is an open-source project that has gained popularity due to its ability to support international business transactions and its rapid deployment tools for blockchain technology. The Linux Foundation, an avid supporter of Hyperledger, has contributed its expertise to accelerate the protocol's development. Hyperledger's libraries have been frequently used in blockchain software solutions to speed up development, and its compatibility with Linux makes it a good fit for the business world.
Multichain
Multichain, on the other hand, was created to assist non-profit organizations in constructing private blockchains that facilitate faster transactions. Multichain also helps to develop new applications for proof-of-work systems that blockchain-based technologies rely on. One of Multichain's distinguishing features is its ability to work with fiat currencies, physical stores of worth, and other digital currencies. As a private business, it can offer an API to assist blockchain developers and companies in accelerating deployment.
Enterprise Ethereum
Enterprise Ethereum, designed specifically for business use, allows businesses to quickly create large-scale applications for exchanging value. Businesses can create customized versions of Ethereum while still using the most up-to-date Ethereum code, which is a feature not easily available in ordinary circumstances due to Ethereum's license.
Corda
Corda is an enterprise protocol that primarily competes with Multichain in the finance and banking sector. Corda is open-source and uses consensus algorithms to maintain transparency and security. Corda's accreditation under the R3 banking consortium has made it a popular choice for blockchain solutions in the finance sector.
Quorum
Quorum has significant financial backing from J.P. Morgan Chase, which is a significant advantage. Quorum is an open-source project that anyone can use, and it has ties to Ethereum because it was created by modifying Ethereum code.
Advantages and disadvantages of Blockchain Protocol
Blockchain protocols offer several advantages and disadvantages, each affecting different aspects of their application and use cases. Let's explore some of the key advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages of Blockchain Protocols
-
Decentralization: One of the most significant advantages of blockchain protocols is their decentralized nature. They operate on a distributed network of nodes, eliminating the need for a central authority. This decentralization enhances security, transparency, and trust in the system.
-
Immutable and Tamper-Resistant: Data stored on a blockchain is immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or deleted once recorded. This feature ensures the integrity and authenticity of transactions and information, making the blockchain highly resistant to tampering and fraud.
-
Enhanced Security: Blockchain protocols employ cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms to secure data and transactions. The distributed nature of the network also reduces the risk of single points of failure and potential attacks.
-
Transparency: All transactions on a public blockchain are visible to all network participants, ensuring transparency and accountability. This transparency can build trust among users and stakeholders.
-
Efficiency and Cost Savings: Blockchain protocols can streamline processes, reduce intermediaries, and automate tasks, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings, especially in industries with complex supply chains or financial transactions.
-
Global Accessibility: Blockchain protocols are accessible to anyone with an internet connection, enabling participation and transactions across borders without the need for intermediaries or traditional financial institutions.
Disadvantages of Blockchain Protocols
-
Scalability: Scalability remains a significant challenge for many blockchain protocols, especially public ones like Bitcoin and Ethereum. As the number of users and transactions increases, the network can experience delays and higher transaction fees.
-
Energy Consumption: Some consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW), require significant computational power and consume a considerable amount of energy. This environmental impact has raised concerns about the sustainability of certain blockchain networks.
-
Regulatory Challenges: The decentralized and pseudonymous nature of blockchain can present regulatory challenges, especially in areas like finance and identity verification. Compliance with existing regulations and the need for new regulatory frameworks can be complex.
-
Data Privacy Concerns: Public blockchains store data openly, raising privacy concerns for certain applications. While private and permissioned blockchains address this issue, they sacrifice some of the benefits of decentralization.
-
User Experience: Interacting with blockchain protocols can be more complex and less user-friendly compared to traditional centralized systems. Transactions may require additional steps and familiarity with cryptographic concepts.
-
Finality of Transactions: While immutability is a key advantage, it can also be a disadvantage when errors occur in transactions. Irreversible transactions can lead to the loss of funds if sent to the wrong address or in cases of hacking.

How is a blockchain protocol different from a platform?
Although blockchain platforms utilize blockchain technology, they are not inherently blockchain-based entities. In fact, it is advantageous for such platforms to be "blockchain agnostic," meaning they are compatible with any protocol. Companies are often hesitant to adopt platforms that rely exclusively on a single protocol.
A prime illustration of a blockchain-agnostic platform is STAMP. STAMP is bolstered by blockchain technology, but it also utilizes other protocols and can function independently of blockchain. Users have the flexibility to choose which blockchain protocol they prefer or even choose not to use blockchain at all on STAMP.
The Future of Blockchain Protocol
The future of blockchain protocols holds immense potential and is expected to bring about significant transformations across various industries and sectors. Here are some key trends and possibilities that may shape the future of blockchain protocols:
- Scalability Solutions: Scaling remains a crucial challenge for blockchain protocols. In the future, we can expect the development and adoption of innovative scaling solutions like sharding, layer-2 solutions (e.g., Lightning Network), and improved consensus mechanisms to enhance the throughput and transaction speed of blockchain networks.
- Interoperability: Blockchain protocols are increasingly exploring interoperability solutions, enabling seamless communication and data exchange between different blockchains. Interoperability will foster a more connected and efficient blockchain ecosystem, enabling the creation of cross-chain applications and services.
- Privacy and Confidentiality: Advancements in privacy-enhancing technologies like zero-knowledge proofs, secure multi-party computation (SMPC), and confidential smart contracts will address data privacy concerns on public blockchains while maintaining transparency where required.
- Evolving Consensus Mechanisms: As blockchain protocols mature, we may witness the adoption of more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), and Proof of Authority (PoA).
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): DeFi applications have gained tremendous popularity, and the future of blockchain protocols will see further integration of decentralized finance services, providing users with more opportunities for borrowing, lending, trading, and yield farming.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs have gained mainstream attention, opening up new possibilities in areas like digital art, gaming, and virtual real estate. Future blockchain protocols will likely continue to support and enhance NFT standards and infrastructure.
- Enterprise Adoption: Enterprises are increasingly exploring blockchain solutions to improve efficiency, transparency, and security in supply chain management, identity verification, and financial services. As blockchain protocols mature, we can expect more widespread adoption by large corporations and industries.
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Many countries are exploring the concept of CBDCs, and blockchain protocols are at the forefront of this development. In the future, we may witness the integration of blockchain technology into national digital currency initiatives.
- Regulatory Clarity: As blockchain technology gains prominence, governments and regulators are working to establish clearer guidelines and regulations. A more favorable regulatory environment will foster innovation and investment in blockchain protocols.
- AI and Blockchain Integration: The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology will likely open up new possibilities in data analysis, consensus optimization, and autonomous decision-making.
- Environmental Sustainability: Blockchain protocols will continue to explore energy-efficient consensus mechanisms and environmentally friendly solutions to address concerns about the energy consumption associated with traditional Proof of Work (PoW) blockchains.
As the world becomes increasingly digital and interconnected, blockchain protocols are poised to play a crucial role in shaping the future of a wide range of industries. By providing a secure, decentralized framework for data management and transfer, blockchain protocols offer a level of transparency and trust that is sorely needed in today's digital landscape. As blockchain technology continues to evolve and mature, it will be exciting to see what new applications and use cases emerge, and how they will impact our world for years to come. Follow Uniultra.xyz for more blockchain information!






