Categories: Blockchain
Blockchain for IoT Security: Enhancing Cybersecurity in the Internet of Things
Blockchain for IoT security enhances device protection through decentralized, immutable ledgers. It ensures data integrity, prevents unauthorized access, and improves transparency, creating a more secure and reliable IoT ecosystem.
Is your Internet of Things vulnerable to cyberattacks? Unlock the power of Blockchain for IoT Security to safeguard your connected devices and sensitive data. Discover how this revolutionary technology is transforming IoT security.
Table of Contents
Challenge Blockchain for IoT Security
The rapid growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) has brought about unprecedented convenience and connectivity, but it has also exposed a glaring vulnerability: the inherent security risks associated with these interconnected devices. IoT devices, ranging from smart home appliances to industrial sensors, are often plagued by weak default passwords, inadequate encryption protocols, and susceptibility to hacking and malware attacks.
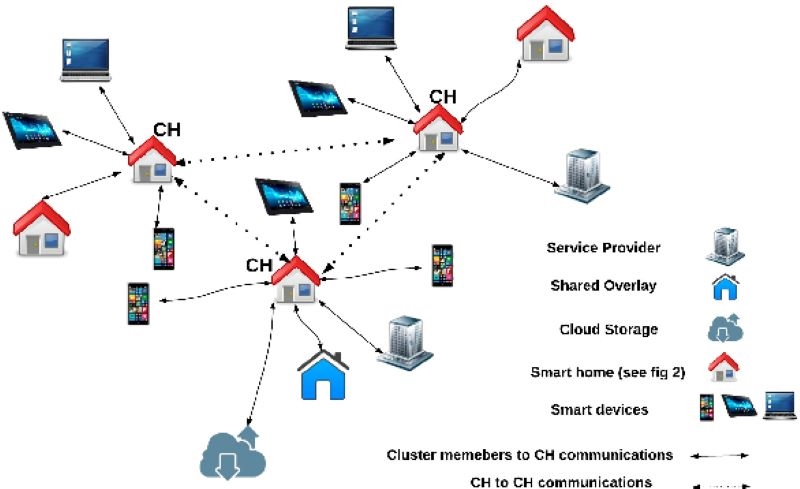
These vulnerabilities pose a significant threat to data privacy. IoT devices collect vast amounts of data, including personal information, sensitive data, and even real-time location tracking. In the wrong hands, this data can be exploited for malicious purposes, such as identity theft, surveillance, or targeted attacks.
Moreover, the centralized architecture of many IoT networks creates a single point of failure. If a central server or hub is compromised, the entire network becomes vulnerable, potentially leading to widespread disruption and data breaches. This centralized model also raises concerns about data ownership and control, as users often have limited say over how their data is collected, stored, and used.
The proliferation of IoT security risks has become a pressing concern for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Addressing these vulnerabilities and ensuring the security and privacy of IoT data are crucial for the continued growth and adoption of this transformative technology.
How Blockchain Enhances IoT Security
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing IoT security by addressing the inherent vulnerabilities of centralized systems and enhancing data protection through its unique features.
Decentralization (decentralized IoT)
Unlike traditional centralized IoT architectures, blockchain distributes data across a network of nodes, eliminating single points of failure. This means that even if one node is compromised, the entire network remains secure, making it significantly more difficult for hackers to launch widespread attacks.
Immutability (blockchain immutability)
Blockchain's tamper-proof ledger ensures the integrity and authenticity of IoT data. Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without leaving a trace, providing an auditable history of all interactions. This immutability safeguards against unauthorized modifications and ensures the trustworthiness of IoT data.
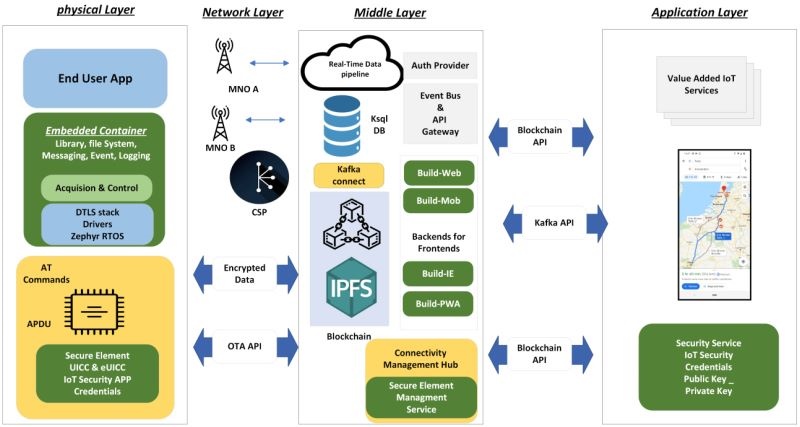
Encryption (IoT data encryption)
Blockchain employs advanced cryptographic techniques to secure data transmission and storage. Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest, making it nearly impossible for unauthorized parties to access or decipher sensitive information. This robust encryption protects IoT devices and data from cyberattacks and ensures the privacy of users.
Smart Contracts
Blockchain-based smart contracts offer a powerful tool for automating security processes in IoT networks. These self-executing contracts can enforce access control policies, monitor device behavior for anomalies, and trigger automated responses to potential threats. This proactive approach to security enhances the overall protection of IoT devices and data, minimizing the risk of vulnerabilities and breaches.
Benefits of Using Blockchain for IoT Security
The convergence of blockchain and IoT technologies offers a robust solution for addressing the security challenges inherent in interconnected devices.
Enhanced Security and Privacy (IoT security solutions)
Blockchain's decentralized architecture, cryptographic encryption, and immutable ledger create a fortified environment for IoT devices and data. By distributing data across a network of nodes, blockchain eliminates single points of failure, making it difficult for hackers to compromise the entire system. Encryption ensures that data remains confidential and tamper-proof, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Increased Trust and Transparency
Blockchain's transparent and auditable ledger fosters trust among stakeholders in the IoT ecosystem. By recording every transaction and interaction, it creates a verifiable history that promotes accountability and ensures data integrity. This transparency allows for greater trust in the authenticity and reliability of IoT data, building confidence in the entire system.
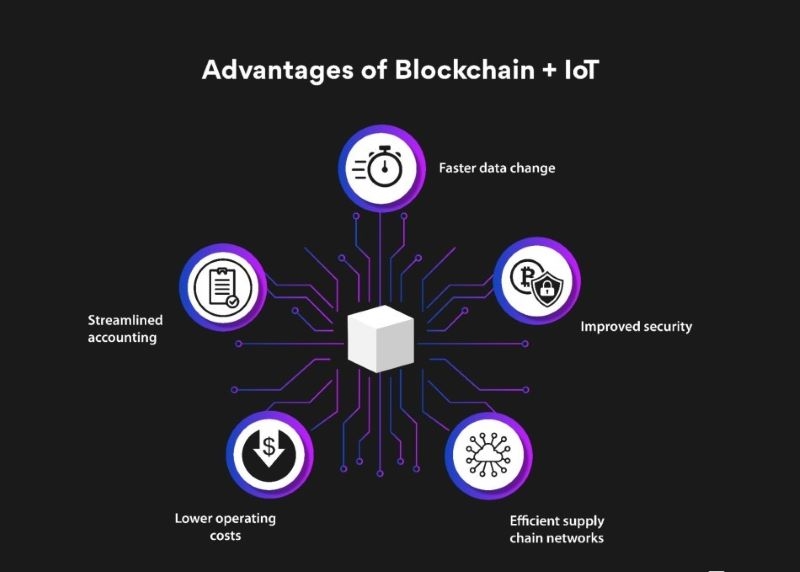
Improved Efficiency and Automation (blockchain and IoT applications)
Blockchain technology streamlines various processes within IoT networks. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements on the blockchain, automate tasks such as access control, authentication, and data sharing, reducing the need for manual intervention. This automation not only improves efficiency but also minimizes the risk of human error, enhancing the overall security and reliability of the network.
New Business Models
Blockchain unlocks new business models in the IoT space, creating opportunities for innovation and growth. For example, blockchain-based platforms can enable peer-to-peer data sharing, where individuals and businesses can directly exchange data without intermediaries. Micropayments for device usage can also be facilitated through blockchain, allowing for a more granular and flexible pricing model for IoT services.
Some challenges and limitations
Scalability: Public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum often face scalability limitations, meaning they can only process a certain number of transactions within a given time frame. This could be a significant issue for IoT networks, where millions of devices need to communicate and share data continuously.
Energy Consumption: Consensus algorithms such as Proof of Work (PoW), used in many blockchains, require substantial computational energy to validate transactions and maintain network security. This could pose a major barrier for IoT devices, which typically have limited energy sources and need to operate efficiently.
Cost: Deploying and maintaining a blockchain system can be expensive, especially for small businesses and startup projects. Costs include hardware, software, energy, and other resources needed to operate and upkeep the blockchain network.
IoT blockchain applications
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology revolutionizes supply chain management by providing an immutable and transparent record of a product's journey from origin to consumer. Each step is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring authenticity and preventing counterfeiting. This traceability allows businesses and consumers to verify the legitimacy of products, enhancing trust and confidence in the supply chain.
Smart Homes and Cities
Blockchain enhances the security of smart home devices by decentralizing control and encrypting data. This prevents unauthorized access and protects sensitive information. In smart cities, blockchain can secure critical infrastructure like traffic management systems and energy grids, mitigating vulnerabilities and ensuring the smooth functioning of urban environments.
Healthcare (blockchain for healthcare IoT)
Blockchain's immutable ledger ensures the integrity of medical records and IoT device data, protecting patient privacy and enabling secure data sharing between healthcare providers. Smart contracts on the blockchain can automate processes like verifying medical device authenticity and managing consent for data access, improving the overall quality and security of healthcare delivery.
Energy
Blockchain plays a crucial role in securing smart grids by providing a tamper-proof record of energy generation, distribution, and consumption. This transparency helps identify anomalies, prevent fraud, and optimize energy usage. Additionally, blockchain enables peer-to-peer energy trading, where individuals can buy and sell excess energy directly, promoting renewable energy adoption and decentralizing the energy market.
The integration of blockchain and IoT is not just a technological trend but also a significant step forward in addressing critical security challenges. Blockchain provides a comprehensive solution, from protecting sensitive data and ensuring data integrity to creating effective automated security systems.
Projects like U2U Network, envisioning a decentralized physical infrastructure network, demonstrate the immense potential of integrating blockchain into IoT. By leveraging blockchain technology, U2U Network and similar initiatives can build a secure, transparent, and reliable IoT ecosystem.
Despite ongoing challenges, the potential of blockchain for IoT security is undeniable. With continuous technological advancements and collaboration among stakeholders, we can expect a future where IoT devices are more securely and reliably protected, laying a solid foundation for the development of a connected, intelligent, and safe world.
.png)