Categories: Blockchain
Beginners Guide to Understanding Blockchain: Key Concepts and Applications
The "Beginners Guide to Understanding Blockchain" is your essential resource for grasping the basics of blockchain technology. Learn about its principles, benefits, and applications, and discover how this revolutionary technology is transforming industries and shaping the future of digital transactions.
Are you ready to understand the technology that's shaping the future of finance, supply chains, and even how we vote? This beginners guide to understanding blockchain will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate this exciting new landscape. We'll cover everything from the basics of how blockchain works to its real-world applications, empowering you to grasp the potential of this transformative technology.
Table of Contents
What is Blockchain?
At its core, blockchain is a revolutionary technology that integrates several key components to create a secure, transparent, and decentralized system for recording and verifying data. Often described as a digital ledger, blockchain differs from traditional ledgers in that it isn't controlled by a single entity or stored in a central location. Instead, it is distributed across a network of computers, eliminating any single point of failure and enhancing security and resilience.
Core Components of Blockchain
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): The foundation of blockchain, DLT, is a decentralized database where data is stored across multiple nodes (computers) rather than in a single location. This distribution enhances security and resilience, as the data is replicated and verified across the entire network.
- Blocks and Chains: Data on a blockchain is organized into blocks, which are like pages in a ledger. Each block contains a set of transactions and is linked to the previous block using cryptography, forming a chain. This chaining mechanism ensures data integrity and prevents tampering.

- Cryptography: Blockchain relies heavily on cryptography for security. Hashing functions create unique fingerprints for each block, while digital signatures are used to verify the authenticity of transactions.
- Decentralization: Perhaps the most defining feature of blockchain, decentralization means that no single entity has control over the network. Decisions are made collectively by the network participants, making blockchain resistant to censorship and manipulation.
Analogy: The Digital Ledger That Can't Be Erased
Imagine a shared Google document that records every transaction ever made. This document is not stored on one computer but replicated across thousands worldwide. Every time a new transaction occurs, it's added to the document, creating a new "block" of information. Each block is then linked to the previous block, forming a chain that's virtually impossible to tamper with. This is the essence of blockchain: a digital ledger that's constantly updated, verified by the network, and resistant to change.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Step-by-Step Explanation
Blockchain technology may seem complex, but its fundamental operation is surprisingly straightforward. Let's take a step-by-step journey through the process:
Transactions
Blockchain records various types of transactions, such as sending cryptocurrency, transferring ownership of digital assets, or executing smart contracts. These transactions are grouped together, forming a list ready to be added to the blockchain.
Verification and Validation by Nodes
A blockchain network consists of many computers, or "nodes," working together to maintain the blockchain's integrity. When a new transaction is initiated, it's broadcast to the network. Each node independently verifies the transaction's validity by checking if the sender has sufficient funds and if the digital signature is correct.
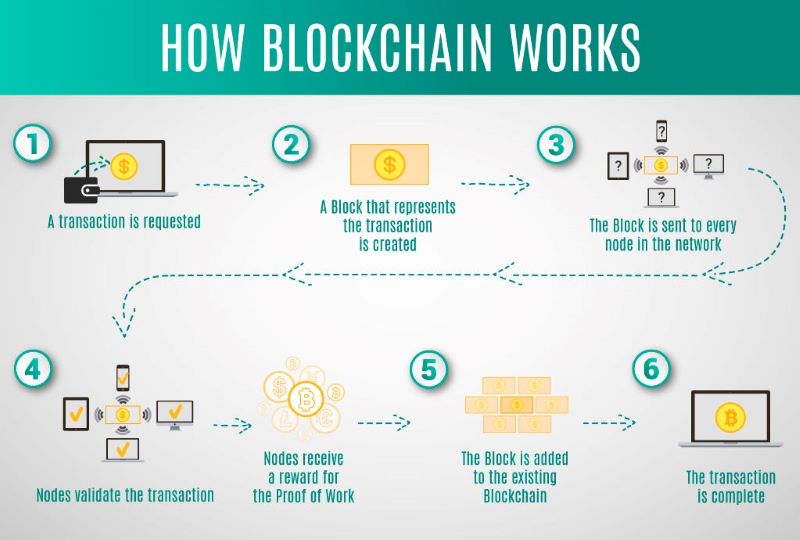
Block Creation
Once verified, the transactions are grouped into a "block" of data. Each block includes:
- A unique identifier (a hash) generated from the block's contents.
- A reference (hash) to the previous block, linking the blocks together in a chronological chain.
Adding Blocks to the Chain (Consensus)
Not every node can add a new block to the chain. This process is governed by consensus mechanisms, ensuring all nodes agree on the valid state of the blockchain.
Consensus Mechanisms
Proof of Work (PoW): In this mechanism, nodes compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first node to solve the puzzle gets to add the next block to the chain and is rewarded with cryptocurrency. This process is often referred to as "mining."
Proof of Stake (PoS): In this mechanism, nodes are chosen to add blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they "stake" or lock up as collateral. The more a node stakes, the higher its chance of being selected to create a new block.
Other Mechanisms: There are other consensus algorithms like Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA), each with its own advantages and drawbacks.
Key Benefi.jpg) ts of Blockchain
ts of Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers a range of transformative benefits:
Unparalleled Security: Blockchain's immutability ensures data integrity, making it tamper-proof. Its cryptographic protection and decentralized nature make it highly resistant to fraud and malicious attacks.
Radical Transparency: All transactions on a public blockchain are visible and verifiable, fostering trust and accountability. This creates an auditable history that enhances accountability and reduces corruption.
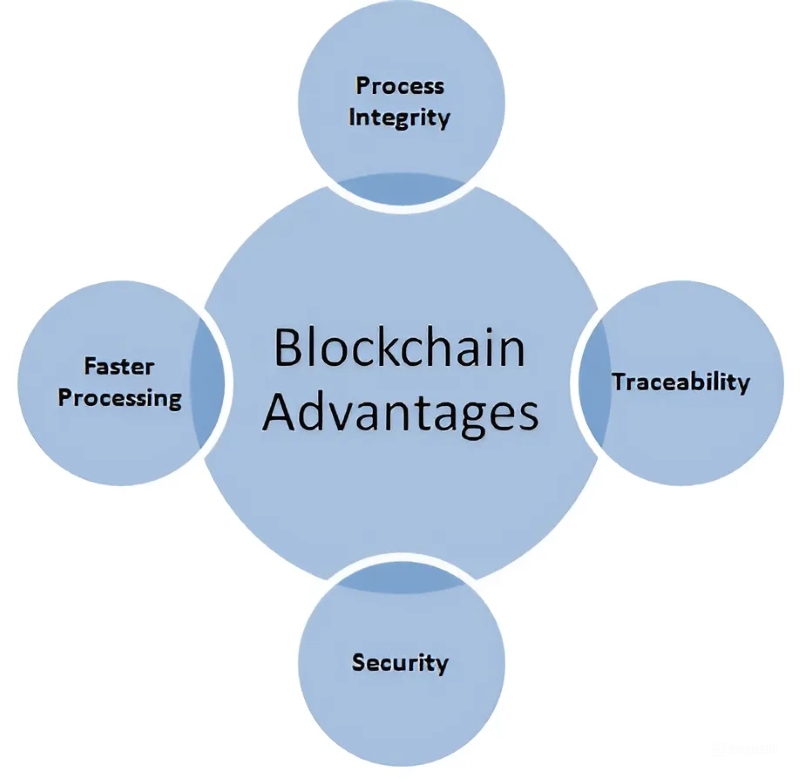
Decentralized Empowerment: With no single point of control, blockchain distributes power across the network, increasing resilience and eliminating the risk of centralized failure. Community governance mechanisms give users a voice in decision-making, and its decentralized nature resists censorship.
Increased Efficiency and Cost Savings: Blockchain automates processes through smart contracts and removes intermediaries, reducing transaction time and costs. It creates a single source of truth and improves operational efficiency across various industries.
Blockchain Use Cases Beyond Cryptocurrency
While blockchain technology initially gained recognition as the foundation for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, its applications extend far beyond digital money. Here's a glimpse into how blockchain is poised to transform various sectors:
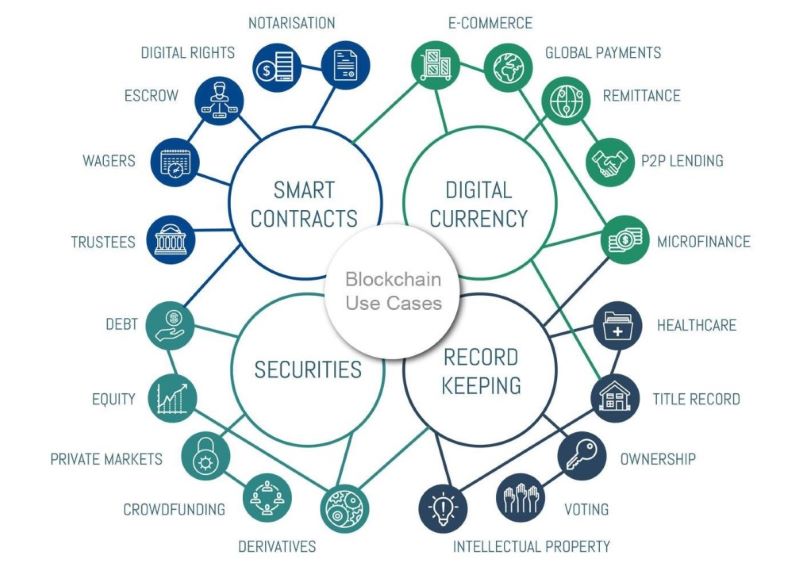
Finance
Blockchain's smart contracts, self-executing agreements with predefined conditions, automate financial processes, reduce the need for intermediaries, and minimize fraud risk. Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms are emerging, offering services like lending, borrowing, and trading without traditional financial institutions. Additionally, blockchain enables faster and cheaper cross-border payments, eliminating multiple intermediaries and reducing transaction fees.
Supply Chain
Blockchain's transparency and immutability are ideal for supply chain management. By tracking products from origin to consumer, blockchain ensures the authenticity and provenance of goods, combats counterfeiting, and enhances transparency throughout the logistics process. This has significant implications for industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and luxury goods, where trust and traceability are paramount.
Healthcare
Blockchain can revolutionize healthcare by providing a secure and tamper-proof way to store and share medical records. Patient data can be accessed and updated by authorized parties in real-time, improving care coordination and reducing errors. Additionally, blockchain can enhance the integrity of clinical trials by securely recording data and ensuring transparency throughout the research process.
Beyond These Industries
Blockchain's potential is vast, extending to diverse sectors. Secure and transparent voting systems can be built on blockchain, ensuring the integrity of elections and preventing fraud. In real estate, blockchain can streamline property transactions, automate record-keeping, and enhance transparency in ownership. Digital identities can be securely stored on blockchain, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud. Intellectual property rights can be protected through transparent and immutable records on the blockchain. Even energy trading is being disrupted, with blockchain enabling peer-to-peer energy transactions and incentivizing the use of renewable energy sources.
Beginners guide to understanding blockchain
Embarking on your blockchain journey can seem daunting, but with the right resources and approach, you can confidently navigate this exciting landscape. Here's your roadmap to get started:
Fuel Your Knowledge
Before diving into the practical aspects, equip yourself with a solid understanding of blockchain fundamentals. Here's where to begin:
Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and edX offer a wealth of blockchain courses, from introductory overviews to specialized topics like smart contract development and decentralized finance (DeFi). Look for courses with high ratings and positive reviews, taught by experienced instructors from reputable institutions.
Books and Articles: Many well-regarded books and articles offer in-depth explanations of blockchain technology, its history, and its potential impact. Start with beginner-friendly guides like "Mastering Bitcoin" by Andreas Antonopoulos or "Blockchain Revolution" by Don and Alex Tapscott.
Reputable Blogs and Websites: Stay up-to-date with the latest developments and trends in the blockchain space by following reputable blogs and websites. Some popular choices include Coindesk, Decrypt, and CoinTelegraph.
Secure Your Assets
If you plan to acquire or trade cryptocurrencies, securing your assets is paramount. Here's what you need to know:
Wallets
Hot Wallets: These are connected to the internet and include software wallets (desktop or mobile apps) and web wallets (accessed through browsers). While convenient for frequent transactions, they are more susceptible to hacking.
Cold Wallets: These are offline wallets, including hardware wallets (physical devices) and paper wallets (printed QR codes). They offer superior security for long-term storage but are less convenient for regular transactions.
Exchanges
- Choose a reputable exchange with a proven track record, strong security measures, and a user-friendly interface.
- Look for features like two-factor authentication (2FA) and cold storage for added security.
- Compare fees and available cryptocurrencies before making your selection.
Embrace Security Best Practices
Protect your digital assets with these essential practices:
Secure Your Keys: Your private keys are crucial. Never share them with anyone and store them in a secure location (offline or in a password-protected manager).
Beware of Phishing: Be cautious of suspicious emails, links, or messages that could be phishing attempts to steal your information.
Use Strong Passwords: Create strong, unique passwords for your wallets and exchange accounts. Consider using a password manager to help you keep track.
Stay Informed: Blockchain security threats are constantly evolving. Keep up with the latest news and best practices to protect your assets.
For Developers: Dive Deeper
If you're a developer looking to build on the blockchain, consider these steps:
Tools: Explore platforms like Remix IDE for writing and testing smart contracts.
Languages: Learn Solidity, the primary language for Ethereum smart contracts, and understand its syntax and structure.
Frameworks: Utilize the Truffle Suite for comprehensive development, testing, and deployment of decentralized applications (dApps).
This is just the beginning. With dedication and curiosity, you can unlock the vast potential of blockchain. Whether you're interested in understanding the technology, investing in cryptocurrencies, or developing innovative applications, the blockchain world offers endless possibilities for exploration and growth.
Blockchain technology is undeniably poised to revolutionize industries across the globe, despite still being in its early stages of development. By grasping its fundamental principles through a beginners guide to understanding blockchain, exploring its diverse applications, and taking proactive steps to deepen your knowledge, you're positioning yourself at the forefront of a profound technological revolution. Whether you identify as an investor keen on emerging opportunities, a developer eager to innovate within decentralized ecosystems, or simply an enthusiast curious about the future possibilities, embracing blockchain means embracing the future of trust, transparency, and value exchange.
This technology offers novel solutions to age-old challenges, from enhancing security and reducing fraud to streamlining processes and fostering global collaboration. By staying informed and engaged, you're not just adapting to change but actively shaping it. Blockchain's potential to disrupt and innovate is immense, and those who embrace it now are poised to lead in shaping a more efficient, secure, and interconnected digital landscape.
So, whether you're ready to invest in the next wave of digital assets, dive into smart contract development, explore decentralized finance, or simply understand how blockchain can impact everyday life, now is the time to embark on this journey. The blockchain landscape is dynamic and ever-evolving, offering limitless possibilities for those bold enough to seize them. Embrace this transformative technology with a beginners guide to understanding blockchain and discover how it's shaping the future of industries worldwide. Follow U2U Network to update the latest information about Blockchain
.png)