Distributed ledger technology is paving the way for a more secure and transparent future. Explore how DLT can revolutionize your business operations and enhance data integrity.
Table of Contents
- What is distributed ledger technology (DLT)?
- Types of Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs)
- How do distributed ledgers work?
- What industries use distributed ledger technology (DLT)?
- Examples of distributed ledger technology (DLT)
- Why DLT is important?
- Challenges of Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs)
What is distributed ledger technology (DLT)?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a digital system designed for recording asset transactions simultaneously across multiple locations. Unlike traditional databases, DLT operates without a central data store or administrator.
DLT encompasses the infrastructure and protocols facilitating concurrent access, validation, and updating of records within a network spanning various entities or nodes. Each node independently processes and verifies transactions, generating an immutable record and achieving consensus on data integrity. This technology supports both static data, such as registries, and dynamic data, including financial transactions. Blockchain, exemplified by Bitcoin, illustrates a prominent DLT application.
.jpg)
DLT gained prominence following Bitcoin's 2009 launch, proving its scalability and security capabilities. Industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chain management quickly adopted DLT for enterprise processes.
Historically, organizations maintained decentralized data on paper or in disparate software systems, consolidating information periodically into centralized databases. DLT significantly enhances efficiency by automating data reconciliation across distributed networks, ensuring real-time access to accurate information.
Types of Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs)
Public Blockchain
A public blockchain is an open, decentralized network that anyone can join and participate in. It is fully transparent, with all transactions visible to the public. This type of blockchain is highly secure due to its decentralized nature and the consensus mechanisms used, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). Notable examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum. Public blockchains are ideal for applications where trust and transparency are paramount, such as in cryptocurrency and decentralized finance (DeFi).
Private Blockchain
A private blockchain, also known as a permissioned blockchain, restricts access to specific participants. These participants are usually pre-approved by a central authority or consortium. Private blockchains offer more control over the network, faster transaction speeds, and enhanced privacy. They are commonly used in enterprise settings where data confidentiality and operational efficiency are critical. Examples include Hyperledger Fabric and R3 Corda. Private blockchains are suitable for applications like supply chain management, internal audits, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
Consortium Blockchain
A consortium blockchain, or federated blockchain, is a hybrid of public and private blockchains. It is governed by a group of organizations rather than a single entity. This type of blockchain provides a balanced approach by combining the transparency and decentralization of public blockchains with the control and efficiency of private blockchains. Consortium blockchains are often used in industries where multiple organizations need to collaborate and share information securely. Examples include Energy Web Foundation and Quorum. They are ideal for applications in finance, healthcare, and cross-industry collaborations.
How do distributed ledgers work?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) operates on principles of decentralization, contrasting with traditional centralized databases. In a DLT system, multiple nodes within a peer-to-peer network store, validate, and update the ledger concurrently, eliminating the reliance on a central authority and reducing the risk of a single point of failure.
Here’s how DLT works: Digital data is replicated across all nodes in the network, ensuring each node maintains an identical copy of the ledger. Nodes independently process new transactions and use a consensus algorithm to agree on the correct version of the ledger. Once consensus is achieved, the updated ledger is synchronized across all nodes, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
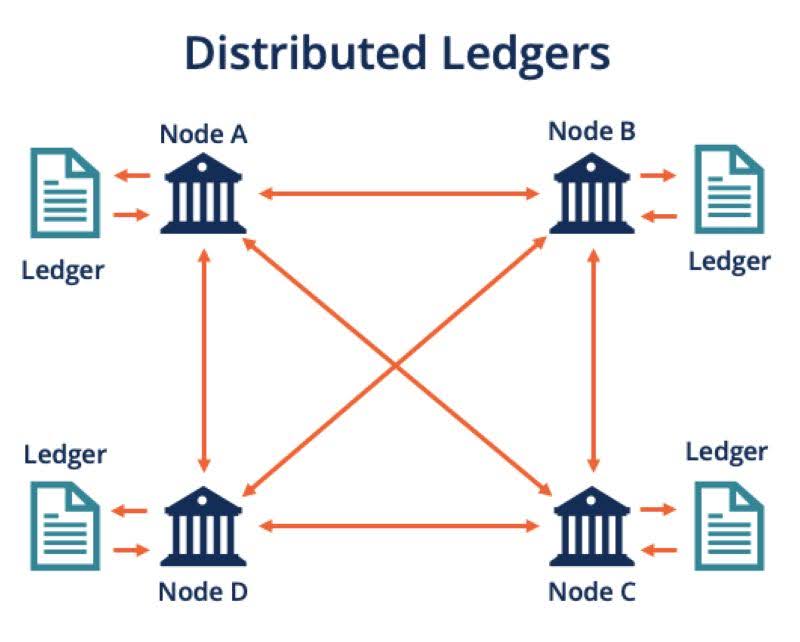
DLT employs cryptography to secure data storage and uses cryptographic signatures and keys to control access, allowing only authorized users to interact with the ledger. The technology ensures immutability by permanently recording all updates, preventing data deletion and providing a historical record of changes.
This decentralized architecture revolutionizes information management by distributing record-keeping responsibilities among network participants. It promotes transparency, enabling all parties to view transaction history and modifications, thereby fostering trust and minimizing the risk of fraudulent activities.
By eliminating the need for a trusted central authority or third-party intermediaries, DLT enhances security, efficiency, and trust in data management and transaction processes.
What industries use distributed ledger technology (DLT)?
Financial Services: DLT is widely adopted in financial services for applications such as cross-border payments, trade finance, securities trading, and regulatory reporting. It enables faster transactions, reduces costs, and enhances transparency and auditability.
Supply Chain Management: DLT enhances supply chain transparency by tracking goods through every stage of the supply chain, from manufacturing to delivery. It improves traceability, reduces fraud, and ensures authenticity and compliance.
Healthcare: In healthcare, DLT is used for managing medical records, tracking pharmaceuticals through the supply chain, clinical trials management, and ensuring patient data security and interoperability among healthcare providers.
Government and Public Sector: Governments are exploring DLT for applications such as identity management, voting systems, land registry management, and public service delivery. It enhances transparency, reduces bureaucracy, and improves citizen trust.
Insurance: DLT is transforming insurance operations by streamlining claims processing, reducing fraud through transparent records, and improving underwriting processes by securely sharing data among insurers and reinsurers.
Real Estate: DLT is used in real estate for property title management, land registries, and smart contracts for rental agreements and property sales. It increases transparency in property transactions and reduces the risk of fraud.
Energy and Utilities: In the energy sector, DLT facilitates peer-to-peer energy trading, metering, and billing processes. It enables decentralized energy grids, improves grid efficiency, and supports renewable energy transactions.
Logistics and Transportation: DLT optimizes logistics and transportation by improving tracking and tracing of goods, optimizing supply chain operations, and reducing administrative costs associated with documentation and compliance.
Legal: DLT is utilized in the legal industry for managing contracts, intellectual property rights, and legal documents. It improves transparency in legal transactions, reduces disputes, and automates contract execution through smart contracts.
Education: DLT applications in education include digital credentialing, secure student records management, and transparent certification processes. It enhances the security and authenticity of educational credentials.
Examples of distributed ledger technology (DLT)
Hyperledger Fabric: Developed by the Linux Foundation, Hyperledger Fabric is used for enterprise blockchain solutions. It supports modular architecture and private channels, making it suitable for permissioned networks in industries like finance, supply chain, and healthcare.
RippleNet: Ripple uses its consensus ledger and payment protocol to facilitate real-time, cross-border payment settlements between financial institutions. It aims to enhance the efficiency and reduce the cost of international transfers.
IOTA Tangle: Unlike traditional blockchains, IOTA utilizes a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) called the Tangle. It aims to facilitate the Internet of Things (IoT) by enabling feeless micro-transactions and secure data transfer between machines.
Why DLT is important?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is crucial due to its transformative impact on record-keeping practices. Unlike traditional centralized systems, DLT enhances transparency and efficiency by enabling real-time data sharing among multiple nodes. This approach eliminates the need for a centralized authority, reducing costs and potential points of failure.
DLT ensures data accuracy through consensus mechanisms across the network, enhancing security and minimizing fraud risks. While DLT can streamline transactions and lower costs, its decentralized nature requires substantial computing resources, impacting performance in certain environments compared to centralized ledgers.
Challenges of Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLTs)
Scalability
Scalability remains a significant challenge for DLTs, particularly public blockchains. As these networks grow in size and transaction volume, they face limitations in processing speed and throughput. The consensus mechanisms used to validate transactions, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), can become slower and more energy-intensive as the network scales. Solutions like sharding and layer 2 scaling are being explored to improve scalability without compromising decentralization.
Energy Consumption
DLTs like Bitcoin and Ethereum have been criticized for their high energy consumption, primarily due to the computational power required for consensus algorithms like PoW. This issue has raised concerns about environmental sustainability and the carbon footprint of blockchain networks. Efforts are underway to develop more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS) and Proof of Authority (PoA), which require less computational power.
Legal and Regulatory Issues
The legal and regulatory landscape surrounding DLTs is still evolving and varies significantly across jurisdictions. Issues such as data privacy, intellectual property rights, and compliance with financial regulations pose challenges for the adoption of blockchain technology. Regulatory uncertainty can hinder investment and innovation in blockchain projects, especially in sectors like finance and healthcare where stringent regulations apply.
Interoperability
Interoperability between different blockchain networks and legacy systems is another challenge. Each blockchain platform may use its own protocols and standards, making it difficult for them to communicate and exchange data seamlessly. Bridging the gap between disparate systems is crucial for achieving widespread adoption and realizing the full potential of blockchain technology in interconnected ecosystems.
U2U Network, enhancing direct peer-to-peer communication, plays a crucial role in distributed ledger technology (DLT). By eliminating intermediaries, U2U Networks boost the decentralization, privacy, and security of blockchain systems. This integration improves scalability, transaction speeds, and reliability, aligning with the core principles of DLT. The synergy between U2U Networks and DLT paves the way for a more secure, efficient, and decentralized digital future.





.png)
