Blockchain technology, the secure and transparent distributed ledger system behind Bitcoin, promises to revolutionize industries by eliminating fraud, inefficiencies, and lack of trust. Discover the diverse benefits of blockchain technology as it transforms finance, supply chain management, healthcare, government services, and beyond.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Benefits of Blockchain Technology
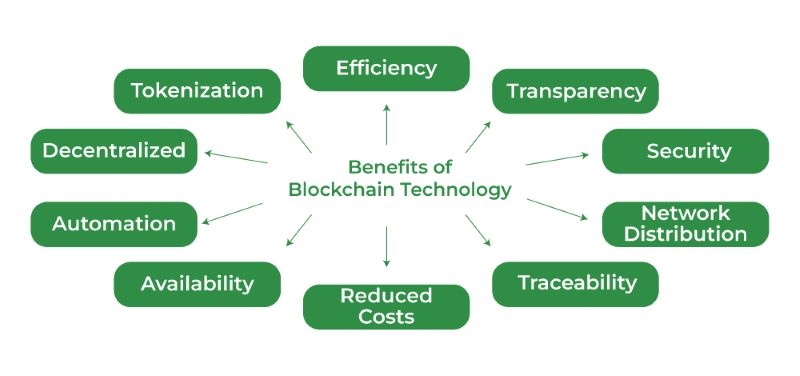
Blockchain technology offers a multitude of benefits across various industries, revolutionizing how we handle data and transactions. By leveraging its unique features, blockchain is poised to create a more secure, transparent, and efficient future.
Unbreakable Security
The decentralized nature of blockchain makes it incredibly resilient to hacking and fraud. Unlike traditional systems where data is stored in a central location, blockchain distributes data across a network of computers, eliminating a single point of failure. Additionally, cryptographic algorithms ensure that data is encrypted and tamper-proof, safeguarding it from unauthorized access or modification. This robust security framework instills trust and confidence in the system, making it ideal for storing sensitive information and conducting valuable transactions.
Crystal-Clear Transparency
Transparency is a cornerstone of blockchain technology. Every transaction or data entry is recorded on a public ledger, creating an immutable and verifiable history. This transparency ensures accountability, as all participants can view and verify the authenticity of information. By fostering trust and eliminating the need for intermediaries, blockchain promotes a more open and honest ecosystem where all parties can access the same information in real-time.
Streamlined Efficiency
Blockchain technology streamlines processes and eliminates the need for intermediaries, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and cost reduction. By automating tasks and reducing manual intervention, blockchain reduces the risk of errors and delays, making transactions faster and more cost-effective. This is particularly beneficial in industries like finance and supply chain management, where complex processes can be simplified and optimized through smart contracts.
Decentralized Trust
Traditional systems often rely on trust in central authorities or intermediaries to verify and validate transactions. Blockchain, on the other hand, establishes trust through its decentralized consensus mechanism. Transactions are verified by the network of nodes, eliminating the need for trust in a single entity. This decentralized trust model creates a more secure and equitable environment where all participants have equal power and can verify the legitimacy of transactions independently.
Blockchain technology Applications
Finance
In the financial sector, blockchain is driving a paradigm shift through the rise of cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi). Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin offer a decentralized alternative to traditional currencies, while DeFi platforms enable peer-to-peer lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements on the blockchain, automate financial processes, reducing costs and minimizing the risk of errors or fraud.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain is reshaping supply chain management by providing an immutable and transparent record of every step in a product's journey. This enhanced traceability helps combat counterfeiting, ensuring product authenticity and origin. By streamlining processes and reducing reliance on intermediaries, blockchain improves efficiency, reduces costs, and builds trust among stakeholders.
Healthcare
In healthcare, blockchain offers a secure and decentralized platform for storing and sharing sensitive patient data, ensuring privacy and compliance with regulations like HIPAA. Smart contracts can automate processes such as insurance claims and consent management, improving efficiency and reducing administrative burdens. Blockchain also has the potential to streamline clinical trials, track pharmaceuticals, and enhance overall healthcare delivery.
.jpg)
Government and Public Sector
Blockchain technology is poised to transform the public sector by enhancing transparency and accountability in government operations. Secure voting systems, digital identity management, and land registration are just a few examples of how blockchain can improve efficiency and reduce fraud in government services.
Other Industries
The potential applications of blockchain extend to various other industries. In energy, it can facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading and optimize energy distribution. In real estate, blockchain can streamline property transactions and secure ownership records. In education, it can verify credentials and create tamper-proof academic records. These examples illustrate how blockchain is poised to disrupt and revolutionize traditional processes across different sectors.
Real-World Examples of Blockchain
Bitcoin (Bitcoin blockchain)
Bitcoin, the first and most widely known cryptocurrency, leverages blockchain technology to enable secure, peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks. Its decentralized nature ensures that no single entity controls the network, making it resistant to censorship and manipulation. Bitcoin's blockchain serves as a public ledger, recording every transaction transparently and immutably, providing a high level of trust and security for its users.
Ethereum (Ethereum blockchain)
Ethereum takes blockchain technology a step further by introducing smart contracts, self-executing agreements with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This innovation has opened up a world of possibilities for decentralized applications (dApps) that can automate processes, eliminate intermediaries, and create new economic models. DeFi platforms, NFT marketplaces, and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) are just a few examples of the diverse applications built on the Ethereum blockchain.
Other Notable Blockchain Projects
- Ripple: Focused on facilitating fast and efficient cross-border payments for financial institutions.
- Chainlink: Provides decentralized oracle networks that connect smart contracts with real-world data.
- IBM Food Trust: A blockchain-based platform that enhances traceability and transparency in the food supply chain.
- Hyperledger Fabric: An open-source blockchain framework designed for enterprise use cases.
- Stellar: A decentralized protocol for facilitating low-cost, cross-border transactions.
Navigating the Challenges and Envisioning the Future of Blockchain Technology
While blockchain technology holds immense promise, it faces several hurdles on its path to widespread adoption and mainstream integration.
Scalability
Scalability is a critical challenge for blockchain networks as user and transaction numbers increase, causing congestion, slower speeds, and higher fees, especially in public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Solutions like sharding and layer-2 protocols are being innovated to enable parallel transaction processing and alleviate these limitations.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for blockchain is dynamic, as governments and financial institutions work to classify and regulate cryptocurrencies and other blockchain assets. Uncertainty poses barriers to adoption and investment, navigating complex legal frameworks. As understanding improves, clearer guidelines are anticipated, supporting innovation and growth in a stable regulatory environment.

Energy Consumption
The energy consumption of some blockchain networks, notably those using Proof of Work (PoW), has sparked concerns due to its environmental impact. Mining in PoW blockchains requires substantial computational power, consuming significant electricity. Efforts are underway within the industry to adopt more sustainable alternatives like Proof of Stake (PoS) and other energy-efficient consensus mechanisms. Furthermore, initiatives promoting renewable energy sources and carbon offset programs are gaining momentum, showcasing the blockchain community's dedication to mitigating environmental issues.
Public Perception
Despite its potential advantages, blockchain technology encounters skepticism and misunderstanding among the general public due to its association with cryptocurrencies, their volatility, and concerns about security and complexity. Education and awareness initiatives are essential to clarify blockchain's practical applications beyond cryptocurrency, build trust, and foster wider adoption. This is crucial for realizing blockchain's transformative potential across diverse industries.
Harnessing the benefits of blockchain technology, U2U Network exemplifies transparency, security, and efficiency in revolutionizing industries. As a decentralized social platform, U2U embodies these principles, fostering trust and empowering communities. While U2U focuses on specific blockchain applications, it contributes significantly to advancing a decentralized and fair digital landscape. By showcasing blockchain's power to connect and empower individuals, U2U Network plays a pivotal role in driving adoption and shaping the technology's future evolution.



.png)


