Categories: Blockchain
Best Practices for Blockchain Security: Strengthening the Chain
"Best Practices for Blockchain Security" offers essential guidelines to protect your blockchain applications. Learn how to implement robust security measures, mitigate risks, and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of your data in decentralized systems.
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and immutable nature, is transformative but brings unique security challenges. Smart contract vulnerabilities, 51% attacks, phishing scams, and private key compromises are significant risks. Understanding and implementing Best Practices for Blockchain Security is crucial to protect your digital assets. This guide distills expert insights and real-world examples to help you navigate these complexities and secure your blockchain initiatives effectively.
Table of Contents
Understanding Blockchain Security Risks
Blockchain technology, while revolutionary, introduces significant security risks that must be addressed to safeguard assets and maintain system integrity.
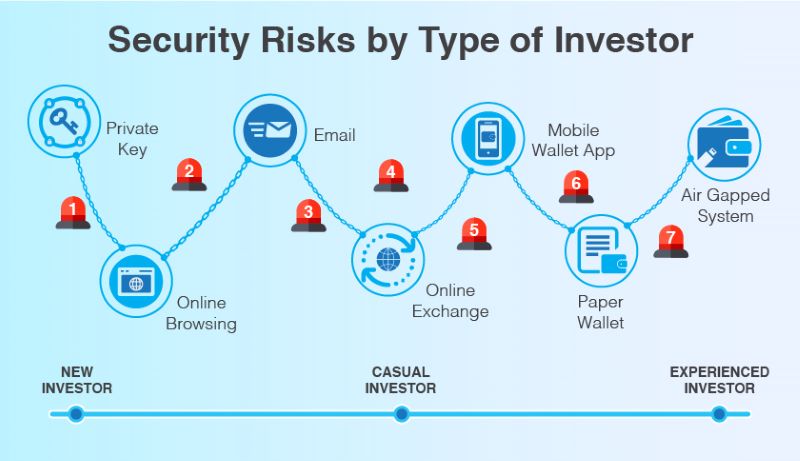
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Smart contracts, pivotal to many blockchain applications, are prone to exploitable flaws. These include re-entrancy attacks, where attackers repeatedly withdraw funds, integer overflow errors leading to unexpected calculations and fund loss, and logic errors that allow manipulation of contract behavior.
51% Attacks: In a 51% attack, malicious actors seize majority control of a blockchain's computing power. This enables them to manipulate transactions, execute double-spending, halt transaction confirmations, or prevent other miners from earning rewards.
Phishing Scams: Phishing remains a persistent threat in blockchain. Fraudsters deploy fake websites or emails to deceive users into divulging private keys or sensitive information. Compromised keys can be exploited for theft or unauthorized access.
Exchange Vulnerabilities: Cryptocurrency exchanges, holding substantial digital assets, are prime targets for hackers. Breaches, like the Mt. Gox incident in 2014, underscore the vulnerabilities of centralized exchanges and highlight the potential for significant user losses.
Private Key Security: Private keys, essential for transaction authorization, are susceptible to compromise through hacking, phishing, or device loss. Losing control of these keys equates to losing control of assets stored on the blockchain.
Real-World Examples: Incidents such as the DAO hack in 2016, which exploited a smart contract vulnerability to steal millions in Ether, and the Mt. Gox hack, resulting in the loss of 850,000 bitcoins, illustrate the severe consequences of security lapses in blockchain systems. These events emphasize the critical need for vigilance, robust security measures, and ongoing education to mitigate risks in the evolving blockchain landscape.
Best Practices for Blockchain Security
Blockchain technology, despite its decentralized and cryptographic foundations, requires a proactive approach to security to protect projects and digital assets effectively.
Secure Development Practices
Ensuring the security of your blockchain project begins with robust development practices. Conduct thorough code audits performed by experienced developers to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities early. Employ formal verification methods like mathematical proofs to validate the correctness of smart contracts. Adhere to secure coding standards tailored for blockchain to minimize risks such as re-entrancy attacks and integer overflow errors. Implementing bug bounty programs can further enhance security by encouraging community participation in identifying and reporting vulnerabilities.
Key Management
Protecting your private keys is paramount to securing your digital assets. Hardware wallets, also known as cold storage, offer the highest level of security by keeping keys offline and safe from online threats. Utilize multi-signature wallets that require multiple approvals for transactions, adding an extra layer of protection. Ensure strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) to secure blockchain accounts and prevent unauthorized access.
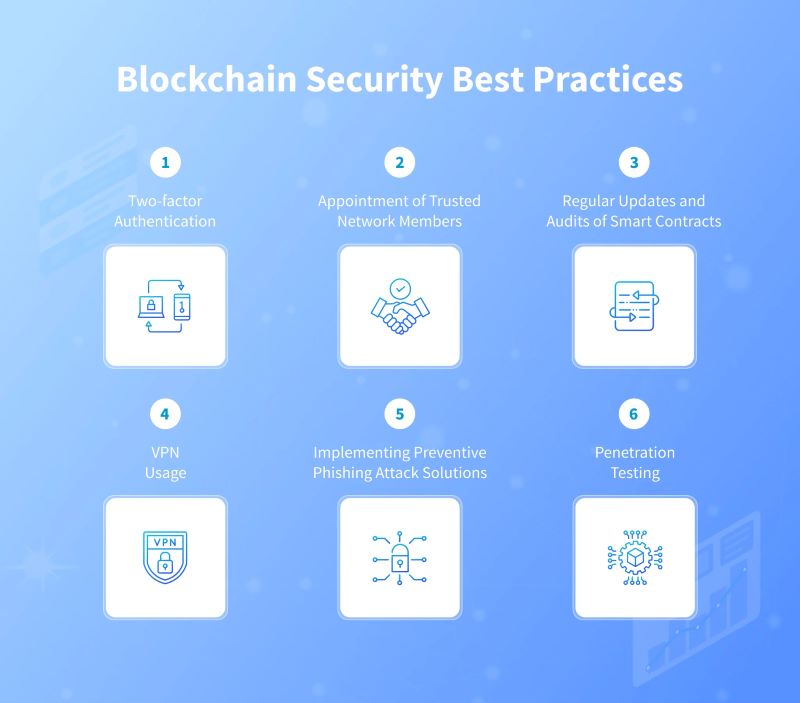
Network Security
Maintaining the security of your blockchain network is critical. Strengthen each node with robust security measures such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems to thwart unauthorized access and malicious activities. Implement secure communication protocols like encryption to safeguard data transmitted between nodes. Regularly update and patch systems to address newly discovered vulnerabilities and uphold network integrity.
User Education and Awareness
Educating users about potential risks and best practices is essential for a secure blockchain ecosystem. Raise awareness about phishing scams and educate users on securely creating and managing wallets. Provide guidance on verifying transactions before confirmation to prevent errors or fraud. Empowering users with knowledge enhances community resilience and fosters a safer blockchain environment.
Blockchain Security Best Practices for Specific Use Cases
Based on your previous requests and content, here are some detailed insights and suggestions to enhance your content without relying heavily on listing:
Blockchain Technology and Its Applications: Focus on discussing how blockchain extends beyond cryptocurrencies, exploring its impact on sectors like finance, supply chain, healthcare, voting systems, real estate, digital identity, intellectual property, and energy trading. Highlight specific use cases and transformative potential rather than listing them.
Blockchain Security: Instead of listing security threats and practices, delve into each vulnerability with detailed explanations and real-world examples. Discuss smart contract flaws, 51% attacks, phishing scams, exchange hacks, and private key compromises in depth, linking each to broader implications and preventive measures.
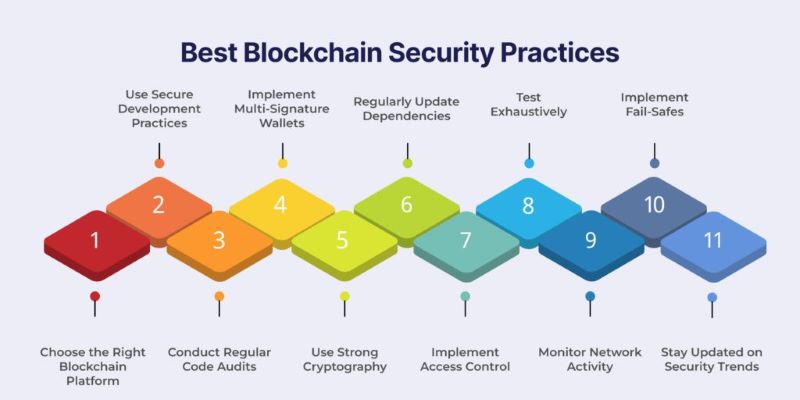
Getting Started with Blockchain: Create a comprehensive guide that emphasizes foundational knowledge acquisition through online courses, books, articles, and reputable blogs. Describe different types of wallets (hardware vs. software) and security measures (2FA, password management) concisely, with practical implementation tips.
Blockchain Development and Deployment: Explore secure development practices, emphasizing rigorous code audits, formal verification techniques, and the role of bug bounty programs. Discuss key management strategies, network security measures, and the importance of user education in maintaining a secure blockchain ecosystem.
DeFi and NFTs: Provide insights into auditing smart contracts, managing risks associated with DeFi platforms (impermanent loss, rug pulls), and securely engaging with NFTs (authenticity verification, secure storage solutions). Highlight the evolving nature of these technologies and associated security challenges.
Overall Approach: Maintain a narrative flow by connecting concepts logically, providing context for each topic, and offering practical advice backed by industry insights. Incorporate expert perspectives, case studies, and recent developments to enrich your content with authoritative information.
Additional Security Measures
To enhance the security of your blockchain projects beyond foundational practices, consider implementing these advanced measures:
Staying Informed: Your Best Defense In the dynamic world of blockchain, staying informed about evolving security threats and best practices is crucial. Regularly follow reputable news sources, engage in community forums, and participate in security-focused conferences or webinars. This ongoing education empowers you to proactively identify emerging risks and vulnerabilities, allowing you to implement preemptive security measures.
Security Audits: A Proactive Approach Regular security audits are essential for identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in your blockchain projects. Conduct comprehensive reviews of your code, infrastructure, and operational processes. Engage reputable security firms to perform audits, ensuring thorough evaluations that uncover potential flaws. By addressing vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, you demonstrate a commitment to robust security practices, fostering trust among users and stakeholders.
Incident Response Plan: Be Prepared Despite preventive measures, security incidents can still occur. Having a well-defined incident response plan is critical for minimizing the impact of breaches and ensuring swift recovery. Your plan should include protocols for detecting, containing, eradicating, and recovering from security breaches. Assign roles and responsibilities, establish communication channels, and conduct regular drills to ensure readiness. A well-executed incident response plan enables you to respond promptly and effectively, mitigating financial and reputational damage.
In the ever-evolving landscape of blockchain technology, security remains paramount. By adhering to Best Practices for Blockchain Security, individuals and organizations can fortify digital assets, protect sensitive information, and maintain the integrity of the blockchain network. Adopting a proactive and comprehensive security approach is not just a recommendation but a necessity for confidently navigating the blockchain world and safeguarding its future. Remember, the strength of blockchain lies in its security. By implementing these best practices, we can collectively build a resilient and trustworthy blockchain ecosystem, unlocking its full potential for innovation and progress. Follow U2U Network to update the latest information about Blockchain
.png)