Zero Knowledge Proofs in Blockchain represent a groundbreaking technology that ensures verifiable transactions without exposing sensitive data. This innovative approach enhances privacy and security across blockchain networks, making transactions confidential and scalable. Discover how Zero Knowledge Proofs in Blockchain are revolutionizing data security and trust.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Zero Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs)
Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) represent a revolutionary cryptographic concept that allows one party (the prover) to demonstrate to another party (the verifier) that a statement is true without revealing any additional information apart from the validity of the statement itself. This capability ensures that sensitive data remains private and undisclosed during the verification process, thereby preserving confidentiality.
Significance of ZKPs in the Blockchain Space
In the realm of blockchain technology, ZKPs play a pivotal role in addressing fundamental challenges such as privacy, scalability, and security:
Privacy Concerns: ZKPs enable transactions to be verified without revealing the identities or transaction details of the parties involved. This enhances user privacy, a critical requirement in decentralized and transparent blockchain networks.
Scalable Solutions: By reducing the computational burden associated with verifying transactions, ZKPs contribute to the scalability of blockchain networks. This is achieved by allowing complex computations to be verified efficiently and securely, thereby enabling networks to process a higher volume of transactions.
Enhanced Security: ZKPs bolster the security of blockchain networks by minimizing the risks of data breaches and unauthorized access. Through cryptographic protocols like ZK-SNARKs, ZK-STARKs, and Bulletproofs, blockchain platforms can validate transactions and smart contracts with mathematical certainty, mitigating the potential for fraudulent activities and vulnerabilities.
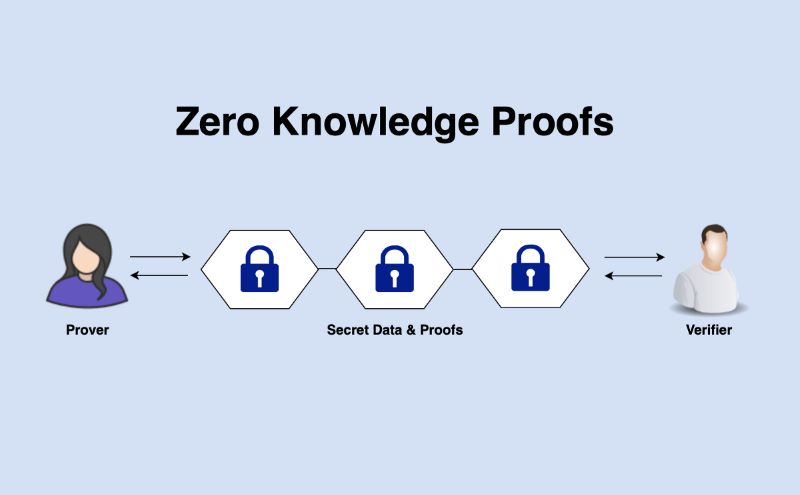
Overview of Different Types of Zero Knowledge Proofs in Blockchain
There are several types of zero-knowledge proofs, each offering unique advantages in terms of efficiency and applicability:
zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-interactive Argument of Knowledge): Known for their succinctness and efficiency, zk-SNARKs allow one party to prove possession of certain information without revealing the information itself. They are widely used in privacy-focused cryptocurrencies like Zcash.
zk-STARKs (Zero-Knowledge Scalable Transparent Arguments of Knowledge): Unlike zk-SNARKs, zk-STARKs are post-quantum secure and do not require a trusted setup phase. They offer transparency and scalability, making them suitable for verifying complex computations on public blockchains.
Bulletproofs: Bulletproofs are a type of zero-knowledge proof that enhances privacy and efficiency in blockchain transactions. They enable smaller and more efficient proofs compared to traditional approaches, reducing transaction size and computational overhead.
Types of Zero Knowledge Proofs in blockchain
Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) are cryptographic techniques that enable one party (the prover) to convince another party (the verifier) of the truth of a statement without revealing any additional information beyond the validity of the statement itself. This capability has profound implications for blockchain technology, offering enhanced privacy, scalability, and security. Here are the key types of ZKPs:
zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge): zk-SNARKs enable a prover to convince a verifier that a statement is true without revealing the underlying information. They achieve this by generating succinct proofs that are computationally efficient to verify. This efficiency makes zk-SNARKs suitable for applications requiring quick transaction verifications while maintaining confidentiality, such as in cryptocurrencies like Zcash.
zk-STARKs (Zero-Knowledge Scalable Transparent Arguments of Knowledge): Unlike zk-SNARKs, zk-STARKs do not require a trusted setup phase, eliminating concerns related to the security of setup parameters. They are characterized by their transparency and offer resilience against quantum computing attacks, making them a promising solution for future-proof cryptographic applications. zk-STARKs can potentially enhance scalability in blockchain networks by validating large batches of transactions off-chain and submitting succinct proofs for verification.
Bulletproofs: Bulletproofs are a cryptographic construction that provides efficient range proofs and enhances transaction confidentiality. They allow users to prove that a secret value lies within a specified range without disclosing the exact value. This capability is crucial for ensuring the validity of transactions on public blockchains while protecting sensitive information such as transaction amounts and participant identities. Bulletproofs contribute to blockchain scalability by reducing the size of cryptographic proofs, thereby improving transaction verification efficiency.
Applications and Benefits of Zero Knowledge Proofs in Blockchain
Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) represent a transformative cryptographic tool with diverse applications in blockchain technology. Here’s how ZKPs are utilized and their benefits in various aspects of blockchain:
Privacy-Preserving Transactions
ZKPs enable confidential transactions on public blockchains by allowing parties to prove the validity of a transaction without disclosing sensitive information such as transaction amounts or participant identities. This is achieved through cryptographic protocols like zk-SNARKs and Bulletproofs, which generate succinct proofs of transaction validity. By shielding transaction details from prying eyes, ZKPs enhance privacy and confidentiality, making blockchain networks suitable for sensitive financial transactions and personal data management.
Scalability Solutions
In blockchain systems, scalability remains a critical challenge due to the computational overhead of verifying large amounts of data on-chain. ZKPs offer a solution by enabling the creation of succinct proofs that verify the correctness of off-chain computations or data. This approach, exemplified by zk-STARKs and Bulletproofs, allows blockchain networks to handle complex computations off-chain while maintaining the security and integrity of on-chain transactions. By reducing the burden on the blockchain, ZKPs contribute to scalability improvements, enabling networks to process more transactions efficiently.

Identity Verification
Decentralized identity systems can benefit greatly from ZKPs by enabling identity verification without exposing personal information. ZKPs allow users to prove ownership of certain attributes (e.g., age verification, credential issuance) without revealing the underlying data. This enhances privacy and security in identity management, mitigating risks associated with centralized databases and identity theft. Projects like uPort and Sovrin are leveraging ZKPs to build robust identity solutions that prioritize user privacy while maintaining interoperability with blockchain networks.
Smart Contracts
Integrating ZKPs into smart contracts enhances their functionality by enabling privacy-preserving computations and conditional execution. Smart contracts powered by ZKPs can verify complex conditions without disclosing the specifics of the conditions themselves, ensuring confidentiality while automating contract execution. This capability opens up new possibilities for applications in areas such as decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and voting systems, where privacy and verifiability are paramount.
Challenges and Future Directions for Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs)
Scalability and Efficiency
Ongoing research is focused on enhancing the scalability and efficiency of ZKPs to make them more viable for real-world applications. One significant challenge lies in optimizing the generation and verification of proofs, which can be computationally intensive. Improvements in algorithms and protocols aim to reduce the complexity of ZKPs, enabling faster verification times and lower computational costs. Moreover, advancements in hardware capabilities, such as the development of specialized processors for cryptographic operations, could further enhance the efficiency of ZKPs.
Trust Assumptions
A critical consideration in the adoption of ZKPs, particularly zk-SNARKs, is the trust assumptions associated with the setup phase. Traditional zk-SNARKs require a trusted setup where participants generate and destroy cryptographic keys to prevent collusion. The security of zk-SNARKs relies on the assumption that these setup parameters are securely generated and disposed of. Ongoing research seeks to eliminate or minimize these trust assumptions through techniques like transparent setups (as in zk-STARKs) or using multi-party computation (MPC) to distribute trust among multiple parties.
Adoption and Integration
Integrating ZKPs into existing blockchain platforms and applications presents both challenges and opportunities. One challenge is compatibility with different blockchain architectures and consensus mechanisms. Blockchain developers must adapt ZKP implementations to suit specific platform requirements while ensuring interoperability with existing protocols. Moreover, educating developers and stakeholders about the benefits and implementation details of ZKPs is crucial for widespread adoption. Addressing regulatory concerns and ensuring compliance with privacy laws are additional hurdles that need to be navigated for ZKPs to gain broader acceptance in various sectors, including finance, healthcare, and government services.
In conclusion, zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) represent a significant breakthrough in blockchain technology. Their ability to provide verifiable proof of information without revealing the underlying data has profound implications for privacy, scalability, and security. Zero-knowledge proofs in blockchain enable confidential transactions, facilitate scalable solutions, and enhance the security of various operations. As research and development in this field advance, we can anticipate a future where ZKPs play an even more pivotal role in the evolution of blockchain technology. Their integration into existing platforms, like U2U Network's innovative DAG-based blockchain, promises new levels of privacy, efficiency, and security for decentralized applications.



.png)


