Categories: Blockchain
How Sharding Technology is Transforming Data Processing
Sharding technology revolutionizes blockchain scalability by partitioning data into smaller, manageable shards. This method enhances transaction speeds, reduces network congestion, and increases efficiency, making it a pivotal innovation for large-scale blockchain applications.
In today's digital age, data is becoming increasingly important and plays a huge role for businesses. With data collection and storage increasing day by day, handling huge volumes of data effectively is a major challenge for businesses. Traditional database systems struggle to meet the required speed, scalability, and reliability needs. This is when Sharding technology appears, providing the optimal solution to this problem.
Table of Contents
What is Sharding?
Sharding is an important technology in processing big data today. This is a smart and effective data fragmentation technique, making data processing faster and more efficient. Sharding has become an important part of the database systems of many businesses today and is widely used in web, mobile, server applications and many other technology fields.
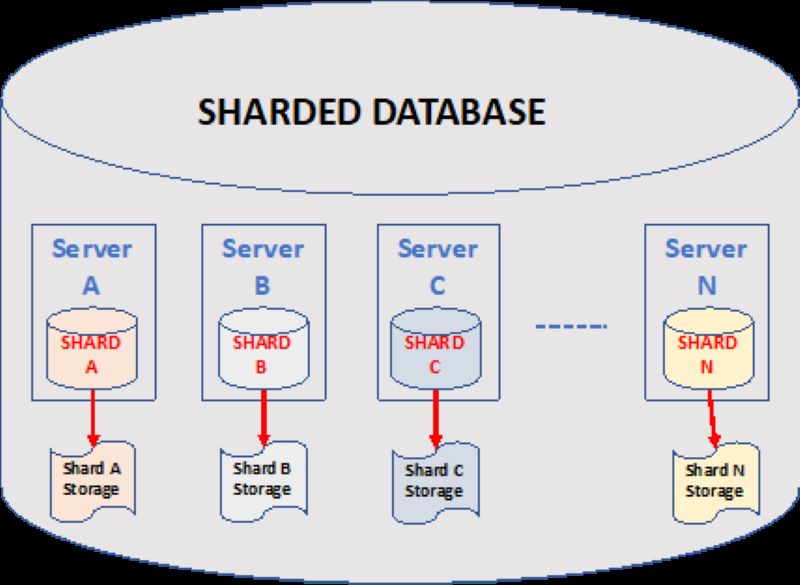
Examples of Sharding usage
Sharding is applied in many different fields, and some typical examples are as follows:
Social network
Social networks are one of the fields with the largest amount of data today. With millions of users and billions of posts, data management and processing becomes extremely complex. Sharding helps social networks process large amounts of data more quickly and efficiently. For example, Facebook used sharding to fragment their data into about 1000 shards, making data management and processing easier.
Ecommerce
E-commerce sites are also one of the typical examples of using sharding. Data fragmentation helps websites process thousands of orders and transactions quickly, while minimizing system overload. Sharding also makes product searching and information retrieval faster.
Video games
With the development of technology, video games are increasingly popular and attract many players. And to manage the number of users and data in the game, sharding is an optimal solution. For example, the famous game Minecraft has applied sharding to fragment data into many different shards, making game play smoother.
How does Sharding work?
To understand how sharding works in a blockchain network, it's important to grasp how blockchain data is typically stored and processed. There are various ways to handle data. We'll look at sequential and parallel processing.
Usually, each blockchain node is responsible for processing the entire volume of transactions in the network. This type of data processing is commonly referred to as sequential processing. This means every node must maintain and store all crucial information, such as account balances and transaction histories. Essentially, each node must handle all activities, data, and transactions of the network.
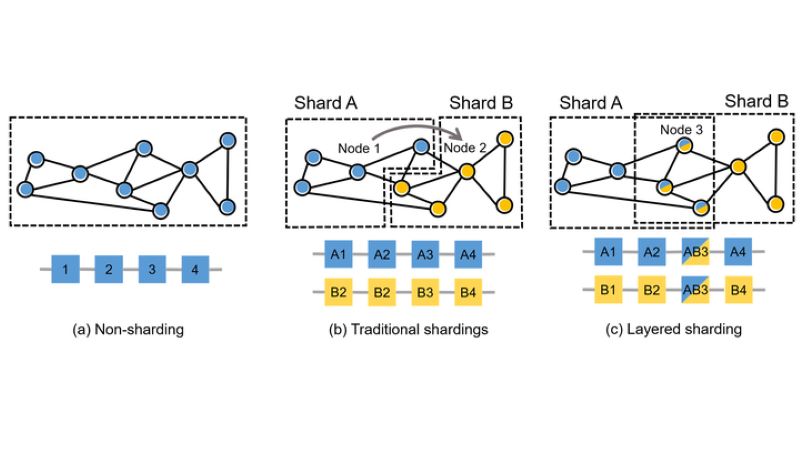
While this model enhances the security of the blockchain by recording every transaction on all nodes, it significantly slows down the data processing. This is where parallel data processing comes into play, as it allows multiple operations to be executed simultaneously.
Sharding can be a powerful solution to this issue because it divides or 'partitions' the transaction workload across the entire blockchain network. This means not all nodes need to manage or process the entire load of the blockchain.
Instead, sharding splits the workload through horizontal partitioning. In this process, data is divided into horizontal subsets, with each shard acting as an independent database capable of processing transactions separately from other shards.
Introducing to Sharding technology
Definition of Sharding technology
Sharding, also known as data fragmentation, is a technique of dividing large databases into smaller parts called shards. Each shard is stored on a separate and independent server, helping to disperse the data load and improve system performance. This makes data processing more efficient and reduces processing time.
Types of Sharding technology
Currently, there are two main types of sharding: Horizontal Sharding and Vertical Sharding.
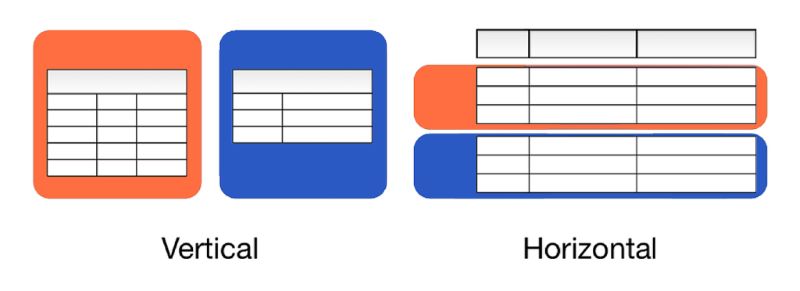
Horizontal Sharding
Horizontal Sharding is a technique for dividing data based on rows or lines. In this way, data will be divided into shards according to each row or row in the table. For example, a customer data table can be divided into shards corresponding to different geographical areas, such as shards for customers in Hanoi, shards for customers in Ho Chi Minh City, and shards for customers in Ho Chi Minh City, and shards for customers in Hanoi. for customers in Da Nang. Queries will only be performed on the corresponding shard, helping to reduce query time and increase system performance.
Vertical Sharding
Vertical Sharding is a technique for dividing data based on columns. In this way, data columns will be divided into shards, and each shard will contain data columns corresponding to a certain group of attributes. For example, in a product data table, columns can be divided into shards corresponding to product attributes such as product name, price, description, image, etc. Queries will be performed only on the corresponding shard, helping to minimize query time and increase system performance.
Benefits of Sharding technology
Sharding brings many significant benefits to data processing, including:
Increasing productivity
By spreading the data load, sharding helps reduce system response time, improve query processing and data synchronization. When data is divided into multiple shards, each shard will contain a smaller amount of data than the original database. This makes querying and processing data faster and more efficient.
Ability of extension
Sharding allows you to easily add new shards to the system to handle growing amounts of data. This helps the system to expand flexibly according to needs and accommodate large amounts of data without affecting system performance.
Easy to manage
When data is divided into multiple shards, system management and maintenance becomes simpler. You can focus on each shard separately, making bug fixes and system upgrades easier.
The future of sharding technology
Sharding technology is not just a passing trend but a fundamental shift in how we process and manage data. As the world becomes increasingly data-driven, the demand for scalable, efficient, and reliable data solutions will only grow. Sharding, with its proven ability to address these challenges, is well-positioned to play a central role in shaping the future of data management.
Expanding New Horizons
One of the most promising aspects of sharding's future lies in its scalability potential. As data volumes continue to explode, sharding will become an essential tool for managing and processing this vast information landscape. We can anticipate the emergence of even more sophisticated sharding techniques and algorithms capable of handling increasingly complex data structures and relationships.
Hybrid Solutions and Cross-Shard Communication
The future of sharding will likely involve developing approaches that combine different types of sharding to optimize data processing for specific applications. For example, a system might use horizontal sharding for user data and vertical sharding for transaction data. Moreover, advancements in cross-shard communication protocols will be crucial to ensuring seamless data exchange and consistency across multiple shards.
The Blockchain Revolution
In the field of blockchain technology, sharding is set to revolutionize scalability and transaction throughput. As major blockchain platforms like Ethereum implement sharding, we can expect a significant increase in the number of transactions that can be processed per second, making blockchain more viable for real-world applications.

Beyond Databases
While sharding is primarily associated with databases, its potential applications extend far beyond that. Sharding principles can be applied to various distributed systems, such as cloud storage, content delivery networks, and even machine learning algorithms
Sharding technology is not just a temporary solution but a turning point in how we process and manage data. As data becomes increasingly important, the demand for scalable, efficient, and reliable data solutions will continue to rise. Sharding, with its proven ability to address these challenges, is well-positioned to play a central role in shaping the future of data management.
Projects like U2U Network, utilizing Helios technology—a unique consensus mechanism with many similarities to sharding—are contributing to the overall development of distributed ledger technology. By leveraging the advantages of Helios, U2U aims to build a robust, secure, and highly scalable Web3 ecosystem that meets the growing needs of users and businesses. As we move towards a more decentralized and data-centric world, sharding will undoubtedly be a crucial factor enabling the advancement of this technology.
.png)