As the world becomes increasingly interconnected and reliant on technology, the need for robust and reliable infrastructure is becoming more critical than ever. However, traditional infrastructure models face numerous challenges, including high costs, limited scalability, and issues of centralized power. Amidst these difficulties, a promising new solution has emerged: Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network (DePIN). By combining blockchain technology with decentralized elements, DePIN is revolutionizing how we build, operate, and utilize infrastructure, ushering in a new era for sustainable and equitable development.
Table of Contents
Understanding Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN)
DePIN is short for Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network, a creative approach to managing and operating physical infrastructure systems. DePIN can be described as "a network utilizing crypto incentives to efficiently coordinate the construction and operation of critical infrastructure." This "infrastructure" could range from WiFi access points in wireless networks to solar-powered home batteries in energy grids.
DePIN is a recent concept that gained prominence. From Proof of Physical Work (PoPW) to Token Incentivized Physical Networks (TIPIN) and EdgeFi, it wasn't until November 5, 2022, that DePIN was officially named, ironically through a Twitter poll by Messari. Messari was also the first to refer to it as DePIN in a research paper, stating it "will be one of the most important areas of crypto investment in the decade ahead." Since then, DePIN is poised to become a breakout story in Web3 and arguably one of the most compelling use cases in cryptocurrency to date.
Types of DePINs
DePINs, or Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks, vary widely depending on the specific device and its intended function. Here are some common types:
Physical Resource Networks (PRNs)
- PRNs manage tangible, physical resources such as raw materials, equipment, transportation, and facilities. They aim to optimize the movement of physical resources through supply chains, manufacturing processes, and distribution networks.
- PRNs often involve logistics management, inventory control, production planning, and transportation optimization to ensure efficient utilization of physical resources.
- Examples include traditional manufacturing industries, transportation and logistics companies, and comprehensive supply chain management systems.
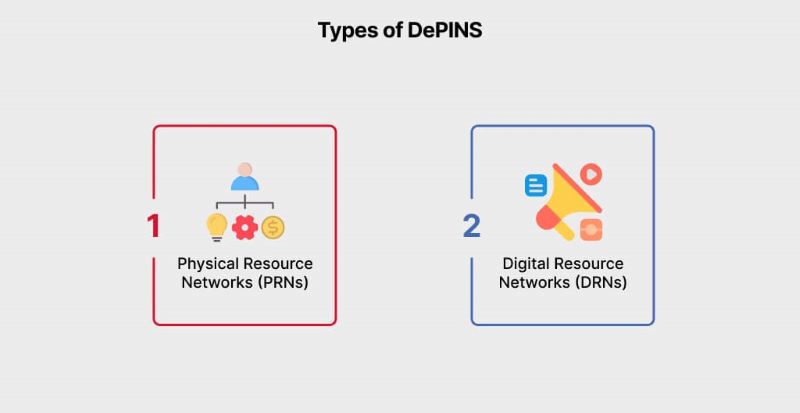
Digital Resource Networks (DRNs)
- DRNs handle intangible, digital resources such as data, information, software, and digital services. They focus on managing the flow of digital resources across digital platforms, networks, and systems.
- DRNs encompass processes such as data management, information sharing, digital collaboration, and software development.
- Examples include digital platforms like social media networks, cloud computing services, digital marketplaces, and online collaboration tools.
Core Principles of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks
DePINs, or Decentralized Public Infrastructure Networks, are pioneering infrastructure systems that are transforming traditional resource management models. Built upon principles of decentralization, blockchain technology, tokenization, and smart contracts, DePINs redefine how infrastructure is conceptualized, governed, and sustained. Let's explore the fundamental principles propelling the evolution of DePINs:
Decentralization
DePINs depart from centralized control structures by distributing authority across a diverse spectrum of stakeholders. This approach enhances resilience and inclusivity, empowering local communities, investors, and end-users. By fostering equitable decision-making, DePINs reduce reliance on singular entities and promote sustainable infrastructure development.
Blockchain Technology
At the core of DePINs is blockchain integration—a distributed ledger system renowned for its transparency and security. Blockchain enables DePINs to establish immutable records of transactions, thereby enhancing trust and accountability among participants. This foundational technology ensures the integrity of collaborative efforts within DePIN ecosystems, facilitating efficient resource management and operational transparency.

Tokenization
Central to DePINs is the incentivization of participation through token economies. Tokens, serving as digital assets, encourage contributions to infrastructure projects and grant stakeholders access to network resources. Whether representing ownership stakes or enabling service provision, tokens foster engagement and align interests within DePIN ecosystems, driving collective investment in infrastructure sustainability.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts automate governance and operational processes within DePIN networks. These self-executing agreements encode contractual terms into executable code, enabling seamless coordination and reducing dependency on intermediaries. By optimizing resource allocation and enhancing operational efficiency, smart contracts play a pivotal role in the sustainable development and management of DePIN infrastructure.
How DePINs Operate
DePIN is based on two fundamental concepts of cryptocurrencies: decentralization and tokenomics - foundational principles shared across most other cryptocurrency domains: from Decentralized Finance (DeFi) to GameFi or SocialFi. Thanks to the nature of blockchain and cryptocurrencies, we have innovated and surprisingly changed the operations of many different models indefinitely. By using cryptocurrencies as the primary incentive for economic systems, we have been able to redistribute most of the power and ownership rights to users, in ways never seen before.
Traditionally, the deployment and management of physical infrastructure such as wireless networks, cloud services, mobile networks, and power grids have been dominated by large corporations due to high capital requirements and operational challenges associated with these large-scale projects. Consequently, these centralized entities have almost monopolized pricing and service provision to end-users, leading to a lack of competition and innovation. Previously, there was a middle ground between entirely centralized and decentralized infrastructure (like DePIN). This concept is referred to as the "Sharing Economy."
The Sharing Economy is a socio-economic system built around resource sharing. This model is supported by technology and peer-to-peer interactions, often leveraging digital platforms to connect users. Essentially, the sharing economy involves companies leveraging contributions from individuals (and their assets) to provide valuable goods and services, rather than relying on a traditional business model of owning and maintaining a centralized inventory. This approach allows for more efficient use of resources and promotes community participation.
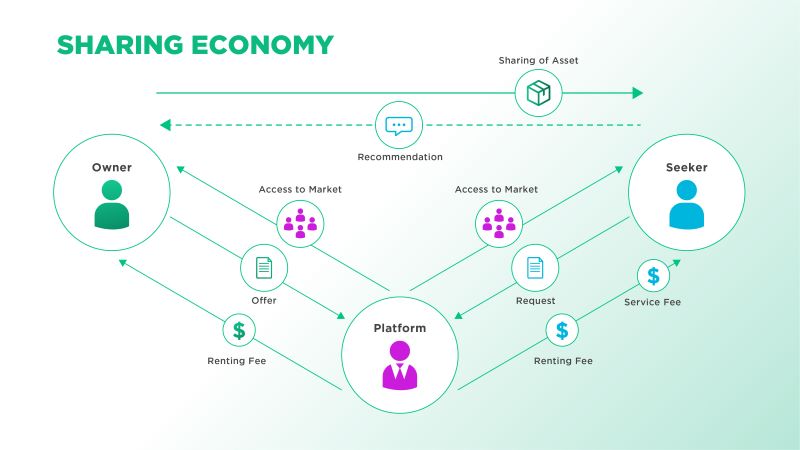
Uber is a prime example of the sharing economy. It's a service that connects drivers with their own vehicles to people needing rides. This setup means Uber doesn't own the cars; instead, Uber uses an app to facilitate these connections. This idea has transformed the traditional taxi service model, making it easier for drivers to work when they want to and providing passengers with more convenient rides. Uber demonstrates how leveraging existing resources like cars can be more efficient for everyone involved.
However, because Uber is a centralized entity, power over the network, drivers, and business still lies with Uber. The concept of DePIN aims to develop the sharing economy, as exemplified by companies like Uber, into a more equitable and comprehensive model. While Uber's centralized structure concentrates control and decision-making within the company, DePIN advocates for a completely decentralized approach.
This model empowers individuals and businesses to contribute to the network, giving them a fair share in the value they create. By distributing power and benefits evenly among contributors, DePIN seeks to create a network that is not only shared but also supportive and beneficial to its participants. Such distribution wouldn't be feasible without tokenomics and decentralized governance provided by blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies, explaining why DePIN is a recent phenomenon.
Role of U2U Network in DePIN
Unicorn Ultra Network (U2U Network) plays a pioneering role in innovating DePIN, leveraging blockchain technology for what we term as "real-world applications." This vision is deeply integrated into our technological advancements and strategic initiatives.
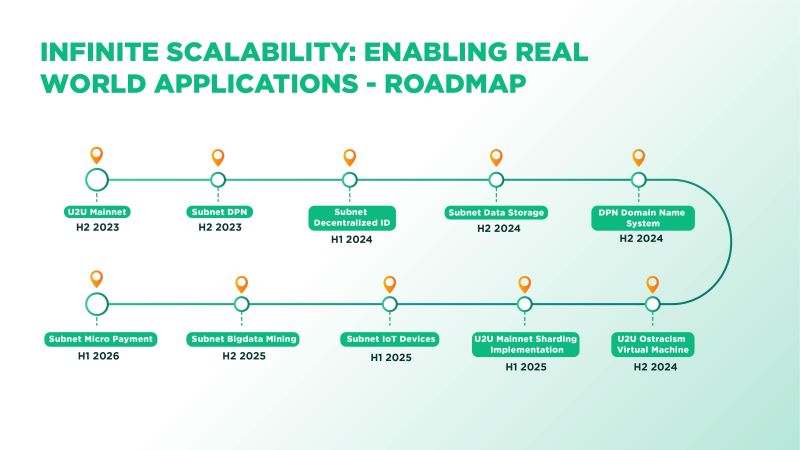
Central to achieving this vision is our focus on developing U2U Subnets. U2U Subnets are a critical component of U2U Network's blockchain infrastructure, designed to address specific needs and challenges of DePIN. These Subnets are essentially layers built on the main blockchain, allowing the U2U Network to handle large volumes of transactions and operations without compromising speed or security. This capability is particularly crucial for DePIN applications, which often require rapid processing and secure management of vast amounts of data.
The essence of U2U Network's approach is bridging the gap between the potential of blockchain technology and its practical applications in daily life. In the context of DePIN, this involves using blockchain to efficiently and equitably manage and operate physical infrastructure systems.
Moreover, we prioritize community-centric approaches, believing that DePIN represents one of the best ways to redistribute power and ownership to contributors. In doing so, Unicorn Ultra Network aims to revolutionize how people think about and interact with critical infrastructure, starting with our initial efforts in U2 DPN - a decentralized private network empowering absolute privacy for the world's first Mobile Nodes.
With this mindset, U2U Network has strategically positioned itself for significant growth and the increasing demand for DePIN in the coming years, with a lineup of DePIN products: from decentralized data storage and decentralized IDs to Matchmaking Tools, Search Tools, Micro-Payment solutions, and more.
Use Cases of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePINs)
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePINs) are revolutionizing various sectors by leveraging decentralized principles and blockchain technology. Here are some compelling applications of DePINs across different industries:
Energy Distribution
DePINs enable decentralized energy distribution where participants can contribute excess energy to the network in exchange for tokens. For example, households with solar panels can sell surplus energy directly to neighbors, reducing transmission losses and dependency on centralized utilities. Token rewards incentivize participation and foster sustainable energy practices.
Healthcare Innovations
In healthcare, DePINs support decentralized infrastructure for patient data management and telemedicine. Users contribute resources to a decentralized network and receive tokens for accessing services like remote patient monitoring and medical consultations. This setup ensures secure data storage and facilitates global medical collaboration.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
DePINs provide essential infrastructure for DAOs by offering distributed computing resources and decentralized data storage. This supports DAO operations across sectors like banking, government, and entertainment, ensuring transparent and efficient governance without centralized control.
Educational Access
DePINs enhance educational access by providing decentralized platforms for e-learning resources and virtual classrooms. Students in underserved areas can access educational materials and interact with educators globally, fostering knowledge sharing and lifelong learning opportunities.
Data Sovereignty
By storing personal data on decentralized platforms, DePINs empower individuals with data sovereignty. Users control access to their data and can monetize it through transparent transactions, such as medical research or targeted advertising, ensuring privacy and fair compensation.
Supply Chain Optimization
Decentralized supply chain networks powered by DePINs enable real-time tracking, secure transactions, and efficient logistics management. Companies benefit from enhanced transparency and reduced fraud, ensuring seamless operations across global supply chains.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DePINs facilitate decentralized finance applications like collateralized loans using digital assets. Users can borrow funds by pledging tokens as collateral, secured through smart contracts. This decentralized approach to finance promotes financial inclusion and reduces reliance on traditional banking systems.
Infrastructure Finance and Funding
Tokenization in DePINs allows crowdfunding for infrastructure projects, where investors purchase tokens representing ownership in revenue-generating assets like bridges or utilities. Token holders receive dividends, democratizing infrastructure investment beyond traditional funding sources.
Telecommunications
In telecommunications, DePINs enable decentralized peer-to-peer communication networks. Communities lacking traditional infrastructure can establish communication channels using DePINs, enhancing connectivity and self-sufficiency in remote areas.
Development of Smart Cities
DePINs support smart city development by decentralizing essential services like energy, water management, and transportation. Real-time data from decentralized sensors optimize resource allocation and automate city operations, enhancing resilience and sustainability.
Benefits of DePINs
DePINs represent a transformative approach to infrastructure management, offering significant advantages across various sectors:
Resilience and Reliability DePINs' decentralized structure ensures resilience by distributing control across multiple nodes. This redundancy minimizes disruptions and enhances reliability, even during crises like natural disasters or cyberattacks.
Accessibility and Democratization By leveraging local resources and community participation, DePINs bridge the digital divide, bringing essential services like internet access and energy to underserved areas. They empower communities by democratizing access to infrastructure.
Affordability and Efficiency Eliminating intermediaries reduces costs for services such as energy and telecommunications. Shared resources and optimized utilization further enhance affordability, making essential services more accessible to all participants.
Empowerment and Data Sovereignty DePINs empower individuals and communities with greater control over infrastructure decisions and data ownership. They prioritize privacy and data sovereignty, ensuring that users retain ownership and control over their personal information.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their benefits, successful implementation of DePINs requires addressing several challenges:
Scalability and Technological Innovation Ensuring DePINs can scale to accommodate growing user bases and diverse applications while maintaining performance and security requires ongoing technological innovation.
Security and Data Integrity Protecting DePINs from cybersecurity threats and ensuring the integrity of data stored on the blockchain are critical considerations for maintaining trust and reliability.
Regulatory Frameworks Navigating evolving regulatory landscapes is essential for DePINs to operate compliantly and sustainably. Balancing innovation with regulatory compliance is crucial for fostering growth and ensuring consumer protection.
The pioneering role of U2U Network in the Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Network sector not only signifies a paradigm shift in applying blockchain technology to practical use but also heralds a new era in infrastructure management. Through the development of U2U Subnets and a comprehensive decentralized service suite, U2U Network addresses not only the inherent technical challenges of DePIN but also enhances efficiency, empowers the community, and ensures fair distribution of resources and control. As DePIN continues to evolve and reshape industries, U2U Network leads the way, fostering innovation and setting a course for a decentralized, sustainable, and interconnected future.



.png)


