Categories: Blockchain
Diving into decentralized applications (DApps): The New Era of DApps (nháp)
Decentralized applications (dApps) are innovative software programs running on blockchain networks, ensuring transparency, security, and resilience. Unlike traditional apps, dApps operate without a central authority, offering greater user control and data privacy. The benefits of decentralized applications include enhanced trust, reduced censorship, and improved efficiency across various sectors such as finance, gaming, and supply chain management.
Tired of Big Tech controlling your data and online experience? Dive into the decentralized applications revolution with dApps – the future of user-centric applications. Unlock a world of enhanced security, transparency, and ownership, where your data is truly yours.
Table of Contents
What are decentralized applications (DApps)?
A decentralized application (DApp) is a type of distributed, open-source software that operates on a peer-to-peer (P2P) blockchain network instead of a single computer. DApps function similarly to other software applications found on websites or mobile devices, but they rely on P2P support. They are part of Web3, the current evolution of the World Wide Web.
Due to the decentralized nature of DApps, once a developer releases a DApp's codebase, others can build upon it, and the app is not governed by a single authority. This approach to development results in a variety of applications, including those for decentralized finance, web browsing, gaming, and social media.

Built on decentralized networks supported by blockchain distributed ledgers, DApps can process data through distributed networks and execute transactions. They are often developed using the Ethereum platform. Technologies like the Ethereum blockchain have significantly contributed to the popularity of DApps. The primary advantages of DApps include constant accessibility and the absence of a single point of failure.
How decentralized applications (dapps) operate?
Decentralized applications (DApps) operate based on three key attributes:
Open Source: The codebase is accessible to all users for evaluation, and any changes require consensus from the majority of users.
Decentralized Storage: Data is stored on decentralized blocks, ensuring no single point of control or failure.
Cryptographic Support: The decentralized data blocks are validated and authenticated through cryptographic methods.
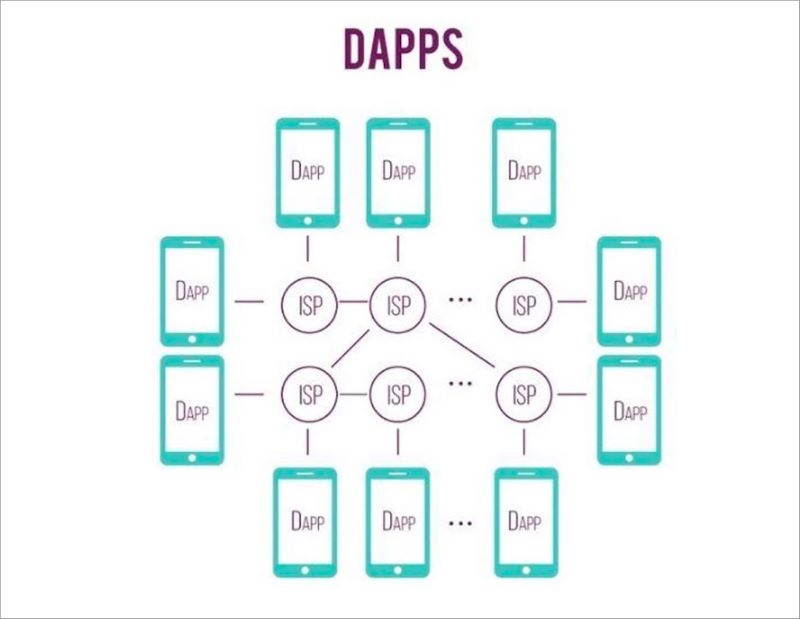
DApps are stored and executed on a blockchain system, often utilizing the Ethereum network. Access to these apps requires validation through cryptographic tokens.
While DApps resemble conventional apps in their front-end code used for rendering web pages, their back-end code runs on a decentralized peer network, removing control from any single authority. Traditional applications rely on centralized servers and databases, whereas DApps are supported by smart contracts stored on a blockchain.
Ethereum is the most popular blockchain for running smart contracts, which enforce rules defined in the code and mediate transactions. A smart contract comprises the back end and typically forms just a small part of the entire DApp. Developing a decentralized app on a smart contract system involves combining several smart contracts and utilizing third-party systems for the front end.
The blockchain on which a smart contract operates is a ledger of data records stored in blocks distributed across various locations. These data blocks are interconnected and governed by cryptographic validation within the ecosystem.
Not all DApps are compatible with standard web browsers; some may require customized code to function on specific websites.
Benefits and Drawbacks of decentralized applications
Benefits of Decentralized Applications | Drawbacks of Decentralized Applications |
Fault Tolerance: If a single network is operational, a decentralized platform remains available, although performance might be hampered. Hackers would find it difficult to target enough nodes to take down a DApp. | Maintenance: Fixes require a consensus mechanism to ensure agreement among all peers in the blockchain network, complicating maintenance, debugging, and updates. |
Data Integrity: Data stored on a blockchain is immutable and secure, as blockchain consensus algorithms ensure the data is resistant to changes. | Scale: Decentralized networks are harder to scale than centralized ones. |
Flexible Platform: The flexibility of the Ethereum blockchain allows for quick development of DApps for various industries. | Network Congestion: If a DApp uses too many resources, it can slow down the entire network. |
User Privacy: Users do not need to submit personal information to DApps to use app-specific functionalities. | User Experience: Developers may find it challenging to create a user-friendly experience for DApp end users. Users need a public and private key to log in, unlike a traditional app where a username and password are sufficient. |
Popular Types of Decentralized applications (dapps)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Lending and Borrowing: DeFi dApps enable users to lend their cryptocurrencies in exchange for interest or borrow assets using their crypto holdings as collateral. This eliminates the need for traditional intermediaries like banks and allows for more accessible lending options.
Trading Platforms: Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) facilitate peer-to-peer trading of cryptocurrencies without the need for a central authority. Users retain control of their funds throughout the trading process, enhancing security and reducing counterparty risk.
Tokenization: Assets can be tokenized on blockchain platforms, enabling fractional ownership and trading of real-world assets like real estate or commodities.
.jpg)
Gaming
Player-Owned Assets: dApps in gaming allow players to truly own in-game assets as non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on blockchain platforms. This ownership can facilitate trading of virtual items across games and platforms.
Decentralized Economies: Games built on blockchain can have decentralized economies where in-game currencies and assets are controlled by smart contracts, enabling transparent and fair distribution of rewards and incentives.

Social Networks
Privacy and Data Ownership: dApps for social networks prioritize user privacy by storing data on decentralized networks where users control access to their information. This contrasts with traditional social networks where user data is centralized and often used for targeted advertising.
Censorship Resistance: Decentralized social networks are resistant to censorship, allowing for freedom of expression and content sharing without interference from centralized authorities.

Other Emerging Use Cases
Decentralized Prediction Markets: These dApps allow users to predict outcomes of events and trade shares based on their predictions. The aggregated information can provide valuable insights into future events and outcomes.
Decentralized Marketplaces:
- Peer-to-Peer Trading: Platforms exist where users can buy and sell goods or services directly with each other using cryptocurrencies. These marketplaces operate without intermediaries, reducing transaction costs and increasing efficiency.
- NFT (Non-Fungible Token) Marketplace: This is where users can buy, sell, and trade unique digital assets such as artworks, collectibles, virtual real estate, etc., in the form of NFTs on the blockchain.
The Future of dApps
Decentralized applications (dApps) are poised for significant growth and innovation in the coming years. Emerging trends in dApp development include enhanced interoperability between different blockchain networks, scalability solutions like layer-2 protocols, and integration with AI and IoT for smarter functionalities. These advancements are expected to broaden the scope of dApps beyond finance into sectors such as governance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
Factors driving wider adoption of dApps include improvements in scalability, regulatory clarity, and user-friendly interfaces. As scalability solutions mature, dApps can handle larger transaction volumes efficiently, attracting both individual users and institutional players seeking faster and cheaper alternatives to traditional systems. Additionally, clearer regulatory frameworks will provide confidence for widespread adoption in various industries.
Challenges facing the dApp ecosystem include scalability issues, regulatory uncertainties, and the need for enhanced security measures. Overcoming these challenges presents opportunities to innovate and expand dApp functionalities, thereby enhancing global accessibility to financial services, social networking, and other decentralized applications. By addressing these challenges and leveraging emerging trends, dApps have the potential to reshape industries and empower individuals worldwide.
Decentralized applications (DApps) are ushering in a new era for the digital world, where power and control are decentralized to users. With superior advantages in transparency, security, and censorship resistance, DApps promise to revolutionize various sectors, from finance and gaming to social networks and beyond.
Despite the challenges that remain, the development of blockchain platforms like Ethereum and the emergence of promising new blockchains like U2U Network are driving innovation and expanding the capabilities of DApps. With superior scalability, fast processing speeds, and low transaction costs, U2U Network is creating a favorable environment for the development of next-generation DApps, offering users better experiences and expanding the applications of blockchain technology into daily life.
The future of DApps is incredibly bright. As blockchain technology continues to evolve and become more widely adopted, we can expect DApps to become an integral part of our digital lives, ushering in a more decentralized, fair, and transparent world.
.png)