Categories: Blockchain
The Role of Blockchain Transaction Protocols in Decentralized Systems
Understanding "Blockchain Transaction Protocols" is key to leveraging blockchain technology effectively. These protocols define how transactions are securely processed and verified, ensuring efficiency, transparency, and integrity in decentralized networks, which are crucial for various applications in finance, supply chain, and more.
Dive into the critical role of blockchain transaction protocols in decentralized systems. Explore how they enable secure, transparent, and efficient transactions, with insights from the U2U Network's innovative approach.
Table of Contents
What are Blockchain Transaction Protocols?
Blockchain transaction protocols are the essential set of rules that dictate how transactions are created, verified, and recorded on a blockchain network. These protocols ensure the integrity, security, and immutability of the blockchain, making it a trusted and reliable system for recording and transferring digital assets. Key Components:
Transaction Structure
- Inputs: References to previous transactions that are being spent.
- Outputs: Specify the recipients and amounts of the cryptocurrency being transferred.
- Signatures: Cryptographic proofs that authorize the transaction, usually generated using the sender's private key.
Validation Rules
- Transaction Validity: Ensure that transactions are legitimate and comply with the blockchain's specific requirements.
- Double-Spending Prevention: A critical rule that prevents a single unit of cryptocurrency from being spent more than once.
- Other Rules: May include transaction size limits, fee requirements, and script validation for more complex transactions.

Consensus Mechanisms
Role: Determine how the network reaches an agreement on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are added to the blockchain.
Common Mechanisms:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add blocks to the chain.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and "stake" as collateral.
- Other Mechanisms: Include Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (pBFT), and more.
The U2U Network is an innovative blockchain project focused on advancing blockchain protocols. U2U aims to create a more scalable, secure, and efficient blockchain ecosystem by exploring and implementing cutting-edge technologies in transaction protocols, consensus mechanisms, and other critical areas. This forward-thinking approach positions U2U at the forefront of blockchain innovation, driving the development of robust and sustainable blockchain solutions.
How Blockchain Transaction Protocols Work
Transaction Request: A user initiates a transaction on the blockchain network. This could involve transferring cryptocurrency, executing a smart contract, or any other action supported by the specific blockchain protocol.
Block Creation: The initiated transaction is verified and grouped together with other pending transactions into a new block. The blockchain protocol ensures the integrity of this block by maintaining accurate transaction data and preventing unauthorized modifications.
Block Propagation: The newly created block is then broadcasted to all nodes (computers or servers) participating in the blockchain network. The protocol facilitates this distribution process, ensuring that all nodes receive the latest information and maintain a synchronized copy of the blockchain.
Validation and Incentive: Each node in the network independently verifies the validity of the block and the transactions it contains. This verification process involves checking the accuracy of transaction data, ensuring compliance with the protocol's rules, and confirming the authenticity of digital signatures. Nodes that successfully validate the block are rewarded with incentives, typically in the form of cryptocurrency, as per the protocol's design.
Database Update: Once a block is validated by a sufficient number of nodes, it is added to the blockchain, forming a permanent and unalterable record of transactions. The databases of all nodes are updated to reflect the latest state of the blockchain, ensuring consistency across the entire network. The protocol ensures that this update process is synchronized and consistent
across all nodes.
Transaction Finalization: With the block added to the blockchain and the databases updated, the transaction is considered finalized and immutable. This means that the transaction details cannot be altered or reversed, providing a high degree of security and trust in the blockchain system.
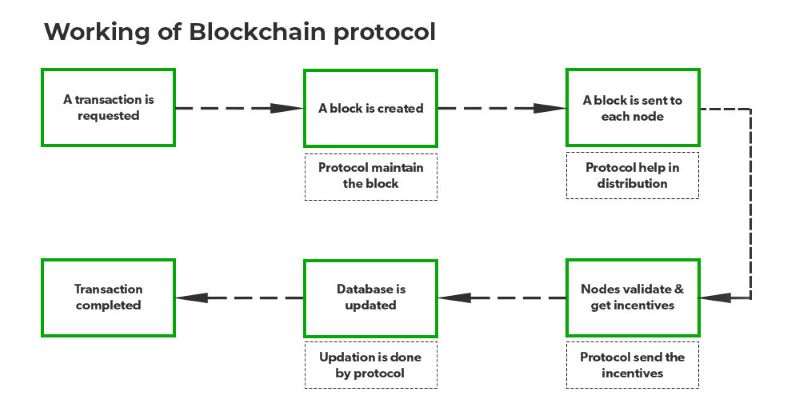
The blockchain transaction protocol orchestrates the entire transaction process, ensuring security, transparency, and immutability. It establishes a decentralized and trustless environment where transactions can be conducted securely without the need for intermediaries. The protocol's incentive mechanism encourages participation from nodes, contributing to the overall health and growth of the blockchain network.
The Impact of Blockchain Transaction Protocols on Decentralized Systems
Blockchain transaction protocols significantly influence decentralized systems, bringing transformative changes in several critical areas.
Security: Blockchain transaction protocols utilize cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms to prevent double-spending, ensuring that a single unit of cryptocurrency cannot be spent more than once. This feature is crucial in maintaining the system's integrity and preventing fraudulent activities. Additionally, once transactions are recorded on the blockchain, they are virtually immutable, guaranteeing data integrity and providing a secure, reliable historical record of all transactions. Transactions are further secured through cryptographic signatures and verification processes, making it highly challenging for unauthorized parties to intercept or manipulate asset transfers.
Transparency: The transparent nature of blockchain transactions ensures that all transactions are publicly accessible, fostering transparency and accountability. Anyone can verify the validity of a transaction and trace the movement of assets. This transparency facilitates easy auditing, allowing organizations to track and verify financial records, supply chains, and other data-driven processes, promoting trust and efficiency within the ecosystem.
Decentralization: Consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) distribute decision-making power across the network, eliminating the need for a central authority and reducing the risk of single points of failure. This decentralization makes blockchain networks resistant to censorship and manipulation, ensuring a more democratic and secure system. The absence of a single controlling entity further enhances the resilience and reliability of the network.
Efficiency: Smart contracts, integral to many blockchain protocols, automate complex processes, reducing the need for manual intervention and streamlining operations. This automation leads to increased efficiency and reliability. Additionally, blockchain systems can eliminate the need for intermediaries such as banks or clearinghouses, cutting down transaction costs and speeding up processes, making transactions more efficient and cost-effective.
Challenges and Future Developments in Blockchain Transaction Protocols
Blockchain transaction protocols have significantly advanced decentralized systems, but they still face several challenges that need to be addressed for their full potential to be realized. One major issue is scalability, particularly in networks using Proof of Work (PoW). These networks often struggle with transaction throughput and confirmation times, limiting their ability to handle large volumes of transactions efficiently. This scalability problem hampers their adoption for applications requiring quick and high-volume transactions. To tackle this, ongoing efforts focus on enhancing scalability through methods like Layer 2 solutions, sharding, and new consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Stake (PoS), which offers faster transaction times and lower energy consumption.
Another challenge is interoperability. The blockchain ecosystem is fragmented, with numerous independent blockchains operating without interconnection. This lack of interoperability restricts the potential for cross-chain communication and asset transfer. Addressing this, interoperability protocols are crucial, enabling seamless communication and asset exchange between different blockchains, thus fostering a more interconnected and collaborative blockchain ecosystem.
Privacy concerns also arise from the transparent nature of blockchain transactions. While transparency ensures accountability and security, it may not be ideal for users who prefer their financial activities to remain private. Privacy-enhancing protocols like zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) are being developed to allow transaction verification without disclosing sensitive information. These advancements aim to balance transparency with privacy, ensuring both security and confidentiality on blockchain networks.
Future developments in blockchain transaction protocols will focus on overcoming these challenges through continuous innovation. Enhancements in consensus mechanisms, interoperability protocols, and privacy-preserving techniques are essential for driving the evolution of blockchain networks. As these technologies mature, they will pave the way for more robust, efficient, and widely adopted decentralized systems. In summary, addressing the challenges of scalability, interoperability, and privacy is crucial for the continued growth and potential realization of blockchain technology.
The U2U Network: Pioneering Blockchain Protocols
The U2U Network has established itself as a trailblazer in the blockchain industry, driven by a steadfast commitment to developing innovative blockchain protocols. This dedication to advancing technology is evident in several critical areas:
Research into New Consensus Mechanisms: U2U recognizes the scalability and energy efficiency limitations of traditional consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). To address these challenges, they are actively researching and developing novel consensus algorithms. One notable innovation is the "Helios Consensus," which is powered by U2U Chain and U2U Subnet. This groundbreaking mechanism can handle up to 500,000 transactions per second (TPS) with a transaction finality time of just 650 milliseconds.
Development of Interoperability Solutions: Understanding the crucial role of interoperability in maximizing blockchain technology's potential, U2U is focused on creating solutions that enable seamless communication and asset transfer between different blockchains. Their "Universal Messages Verification" (UMV) technology is a significant development in this area, designed to establish a common language for various blockchains to interact with each other, fostering a more interconnected and collaborative ecosystem.

Focus on Privacy-Preserving Protocols: With growing concerns over privacy in the blockchain space, U2U is dedicated to exploring privacy-enhancing technologies. They are investing in the development of zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) and other advanced cryptographic techniques. These efforts aim to protect user data while ensuring the transparency and security that are fundamental to blockchain technology.
U2U Network, with its unwavering commitment to innovation, is reshaping the future of blockchain technology through the development of advanced transaction protocols. By addressing challenges related to scalability, interoperability, and privacy, U2U not only enhances the efficiency and security of its network but also contributes to the overall advancement of the blockchain ecosystem.
Blockchain transaction protocols play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety, transparency, and effectiveness of decentralized systems. They serve as the foundation for the development of blockchain applications across various sectors, from finance and supply chain management to identity management and beyond.
Through continuous research and development efforts, U2U Network is proving to be a pioneer in shaping the future of blockchain technology. By implementing innovative solutions such as Helios Consensus and Universal Messages Verification (UMV), U2U tackles current blockchain challenges while opening new opportunities for real-world applications.
.png)