Categories: Blockchain
Bitcoin Blockchain Technology: The Decentralized Revolution in Finance
Bitcoin blockchain technology is a decentralized ledger that enables secure, transparent transactions without intermediaries. It uses a Proof of Work consensus mechanism to validate transactions, ensuring network integrity and resilience while powering the first cryptocurrency.
Have you ever imagined a world where currency is not controlled by any government or financial organization? A world where transactions occur directly between individuals, swiftly, securely, and transparently? That is the vision that Bitcoin, with its groundbreaking blockchain technology, is gradually bringing to life. Let's explore Bitcoin's blockchain - the decentralized revolution shaking up the traditional financial world.
Table of Contents
- What is bitcoin blockchain technology?
- Short story of Bitcoin blockchain technology
- What is the operational mechanism of the Bitcoin blockchain technology?
- Difference between blockchain and banks
- What are the essential requirements for the functionality of the Bitcoin blockchain technology?
- Applications of Bitcoin Blockchain Technology
- The Future of Bitcoin Blockchain Technology
.jpg)
What is bitcoin blockchain technology?
The Bitcoin blockchain refers to the data stored in “blocks” of information that are then linked together in a permanent “chain.” A block is a collection of Bitcoin transactions from a specific period. Stacks of blocks are stockpiled on top of each other, with each new block relying on the previous ones. As a result, a chain of blocks is formed, giving rise to the word “blockchain.”
Short story of Bitcoin blockchain technology
The concept of blockchain technology was first introduced in 1991 by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta in their paper "How to Time-Stamp a Digital Document." They proposed a method using a continuous chain of timestamps to securely record information.
Bitcoin, initially created to facilitate cryptocurrency transactions, quickly revealed broader potential. Its blockchain was designed not only to track token movements but also to store diverse data securely.
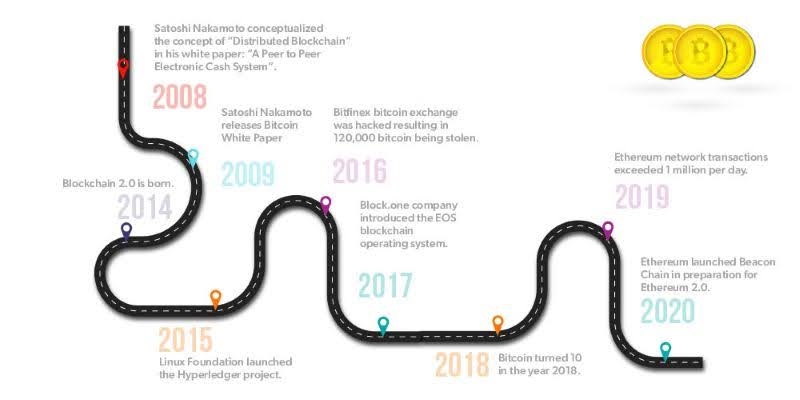
Operating on a peer-to-peer (P2P) basis, Bitcoin enables direct online payments between parties without intermediaries like banks. This decentralized approach distributes network functions across thousands of equal nodes, collectively maintaining the blockchain's integrity.
The P2P network thrives on user participation, where each node shares responsibility for network services. This setup ensures robustness and reliability in Bitcoin transactions, facilitated by the protocol governing the blockchain's creation and security.
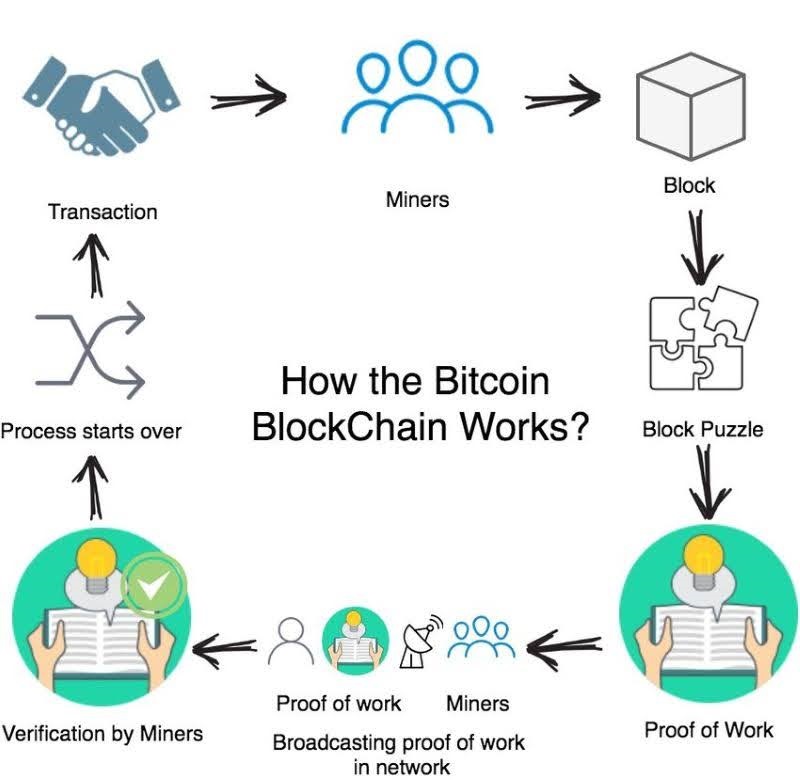
What is the operational mechanism of the Bitcoin blockchain technology?
Bitcoin blockchain technology operates through several key steps:
- Transactions are initiated by users within the Bitcoin network.
- These transactions are broadcasted to all nodes (computers) on the network.
- Miners collect these transactions into blocks.
- Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles (proof-of-work) to validate and add blocks to the blockchain.
- Once a block is added, it is distributed across the network and becomes part of the permanent, immutable blockchain record.
- Consensus among nodes ensures agreement on the valid blockchain, maintaining the integrity and security of the network.
This process ensures transparent and decentralized management of transactions within the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Difference between blockchain and banks
Blockchain technology and traditional banks differ significantly in their operational principles and functionalities. Here’s a comparison outlining their key differences:
Aspect | Blockchain | Banks |
Decentralization | Fully decentralized; relies on thousands of computers (nodes) to verify transactions. | Centralized; operates through financial institutions that manage transactions and data. |
Operational Hours | Operates 24/7, every day of the year. | Operates during business hours; may have limited availability on weekends and holidays. |
Transparency | Offers transparency as a public ledger records every transaction in the network. | Transparency may vary; banks provide account statements but details of transactions may not be publicly accessible. |
Transaction Speed | Transaction confirmation time varies (15 minutes to over an hour) depending on network congestion. | Card payments and check deposits may take 24 to 72 hours to process. |
Transaction Fees | Variable fees (typically $0 to $50) based on network conditions and transaction size. | Fixed fees or percentage-based fees on transactions, potentially higher for international transfers |
Access Requirements | Requires only an internet connection to make transactions; no account or specific device needed. | Requires an account with the bank, along with access to a mobile phone or computer to perform transactions. |
Flexibility and Innovation | Enables decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts, fostering innovation beyond financial transactions. | Limited flexibility; adoption of new technologies may be slower due to regulatory compliance and infrastructure limitations. |
Blockchain technology disrupts traditional finance by offering tamper-proof, decentralized transaction networks that enhance transparency and potentially reduce costs for users. In contrast, banks provide centralized financial services with regulated access and transaction processing, catering to a wide range of financial needs but operating within established regulatory frameworks.
What are the essential requirements for the functionality of the Bitcoin blockchain technology?
What makes the Bitcoin blockchain function is its role as a digital, trustless form of currency and its aim to decentralize financial services. Before Bitcoin, reliance on a trusted third party was necessary to maintain a ledger, recording financial data ownership. With Bitcoin, this ledger is distributed across the entire network, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
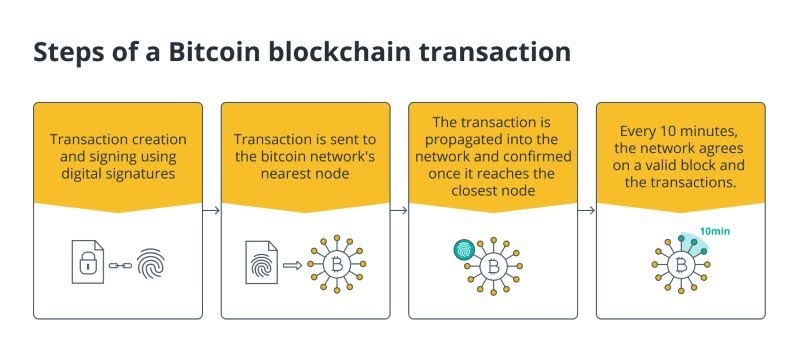
Transactions within the Bitcoin blockchain occur in a digital space where mining and hash power generation take place. Hashing power, the computational capability used by computers or hardware, is employed to solve hashing algorithms, essential for cryptocurrency creation and trading—a process known as mining.
Typically, Bitcoin holders acquire their cryptocurrency through a cryptocurrency exchange, a platform facilitating transactions for Bitcoin and other digital currencies. The blockchain's decentralized ledger underpins this network, illustrating Bitcoin as software with participants engaging in various roles.
A blockchain functions as a digital ledger where duplicated transactions are spread across a network of computers. Each block in the chain contains multiple transactions, and any new transaction is appended to every participant's ledger.
This distributed database is managed by multiple participants utilizing distributed ledger technology (DLT). Blockchain is a type of DLT where transactions are recorded using an unalterable cryptographic hash. Transactions are grouped into blocks, with each new block containing a hash of the preceding one, creating an interconnected chain—hence the term "blockchain."
Applications of Bitcoin Blockchain Technology
DeFi (Decentralized Finance)
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) represents a broad category of financial applications built on blockchain technologies aimed at disrupting traditional financial systems.
Lending and Borrowing Platforms: On DeFi platforms, users can lend their Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies to earn interest or borrow against their holdings. These platforms operate without intermediaries, using smart contracts to automate the processes.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): These allow users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with one another, using the blockchain to facilitate and record transactions. Unlike traditional exchanges, DEXs operate without a central authority, enhancing security and reducing fees.
Stablecoins: Cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets (like the US Dollar) can be built on Bitcoin's blockchain, providing a stable store of value and medium of exchange.
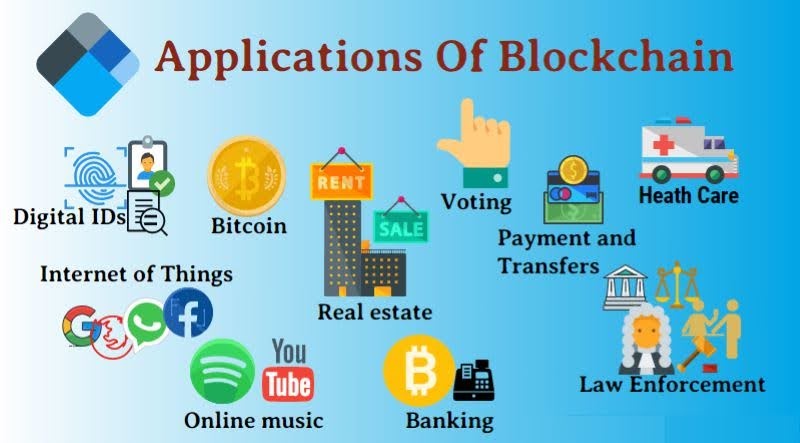
Smart contracts
On the Bitcoin blockchain, smart contracts can be created using technologies like Rootstock (RSK), a smart contract platform that is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) but secured by the Bitcoin network. This integration allows for complex financial instruments and applications to run on Bitcoin's secure and decentralized infrastructure.
- Automated Transactions: Smart contracts can facilitate automated payments when certain conditions are fulfilled, such as releasing funds when goods are delivered.
- Tokenization: Assets can be tokenized and traded on the blockchain, representing real-world assets like real estate, art, or stocks.
- Decentralized Applications (DApps): These applications run on the blockchain without central servers, providing services from gaming to financial services.
The Future of Bitcoin Blockchain Technology
Expansion and Growth of DeFi
DeFi has emerged as one of the fastest-growing sectors within the blockchain ecosystem. For Bitcoin, DeFi platforms can develop using networks like RSK (Rootstock) or layer-2 solutions such as the Lightning Network. Potential applications include lending, borrowing, decentralized derivatives, and other complex financial products.
Support for Traditional Financial Infrastructure
Bitcoin can support traditional financial infrastructure by providing fast, secure, and cost-effective payment solutions. Money transfer companies and banks can utilize Bitcoin blockchain to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Applications in Supply Chain Management and Internet of Things (IoT)
Bitcoin blockchain can enhance supply chain management by providing a transparent and traceable system. This can help track the origin of products, manage inventory, and reduce fraud and abuse.
Use in Elections and Electronic Voting Processes
Blockchain technology, including Bitcoin, can improve transparency and security in electoral processes. Implementing blockchain for electronic voting can reduce fraud and enhance voter participation.
Integration with IoT and Smart Device Connectivity
Bitcoin can integrate with IoT applications to create smart devices capable of autonomously executing transactions on the blockchain without human intervention. This opens new possibilities in areas such as smart homes, smart cities, and industrial automation.
Development of NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens)
Bitcoin blockchain can support the development of NFTs, particularly in the art, education, and entertainment sectors. NFTs can represent unique digital assets like artworks, videos, or 3D models.
Bitcoin blockchain technology has proven its immense potential in completely transforming how we perceive currency and finance. By eliminating intermediaries, enhancing security, and transparency, this technology is ushering in a new era for the global financial system. The emergence of layer-2 solutions like Lightning Network and promising projects such as U2U Network aims to leverage the power of Bitcoin blockchain to build a comprehensive decentralized financial ecosystem, further bolstering confidence in its bright future. Despite remaining challenges, it cannot be denied that Bitcoin blockchain technology has sparked a decentralized revolution, bringing forth significant opportunities and developmental potential for the future of finance.
.png)