The blockchain technology world is evolving at a staggering pace, and decentralized applications (DApps) are gradually becoming an integral part of everyday life. However, for DApps to truly thrive and reach their maximum potential, we need to overcome current limitations in scalability, security, and interoperability. This is where advanced blockchain development techniques come into play. Let's explore how these groundbreaking technologies are shaping the future of DApps, from Zero-Knowledge Proofs safeguarding privacy to Sharding scaling solutions and Interoperability Protocols connecting diverse blockchains.
Table of Contents
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): The Shield of Blockchain Privacy
Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) are a revolutionary cryptographic technique pivotal in advanced blockchain development techniques, offering robust solutions for privacy, scalability, and security. These proofs allow one party (the prover) to demonstrate the validity of a statement to another party (the verifier) without revealing any additional information beyond the statement itself.
There are two primary types of ZKPs utilized in blockchain technology: zk-SNARKs (zero-knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge) and zk-STARKs (zero-knowledge Scalable Transparent Argument of Knowledge). Both types offer similar functionalities but differ in their cryptographic structures and trade-offs concerning proof size, verification time, and setup requirements.
.jpg)
ZKPs find diverse applications in blockchain:
- Privacy-Preserving Transactions: ZKPs enable the creation of privacy coins like Zcash, where transaction details remain confidential while remaining verifiable by the network.
- Scalable Layer 2 Solutions: ZK-roll ups such as Polygon zkEVM use ZKPs to bundle and authenticate transactions off-chain, substantially enhancing transaction throughput and reducing fees on the Ethereum network.
- Identity Verification: ZKPs can verify the legitimacy of credentials or identity information without disclosing underlying data, bolstering privacy and security in digital identity systems.
Sharding: Breaking Down Barriers to Scalability
Sharding is an advanced blockchain development technique designed to alleviate scalability challenges by partitioning the blockchain network into smaller, manageable segments known as shards. Each shard can process transactions independently, thereby increasing overall network throughput.
However, sharding introduces its own set of challenges, particularly concerning cross-shard communication and data availability. Ensuring secure and efficient communication among shards and maintaining data integrity across the network are critical considerations for successful sharding implementations.
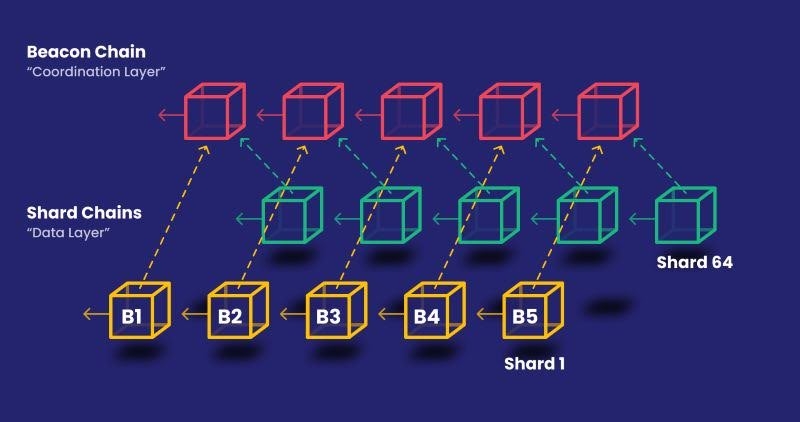
Ethereum's ongoing transition to a sharded architecture, known as Ethereum 2.0 or "Serenity," underscores the growing significance of sharding as a viable scaling solution. By embracing sharding, Ethereum aims to achieve substantially higher transaction throughput and support a broader range of decentralized applications.
Interoperability Protocols: Building Bridges Between Blockchains
As the blockchain landscape diversifies with numerous independent networks emerging, achieving interoperability has become paramount. Interoperability protocols facilitate communication and asset transfer between different blockchains, fostering a connected and collaborative ecosystem.
Various approaches to achieving interoperability include:
- Cross-chain Bridges: Protocols enabling asset and data transfers between multiple blockchains.
- Sidechains: Independent blockchains connected to a main blockchain, facilitating asset and data movement.
- Relay Chains: Blockchains serving as intermediaries, enhancing communication and interoperability among multiple parachains.
Projects like Cosmos and Polkadot lead in developing advanced interoperability protocols, aiming to establish a fully interconnected "Internet of Blockchains."
Smart Contract Security Best Practices: Safeguarding the Code
Smart contracts form the backbone of numerous blockchain applications, but their immutable nature makes them susceptible to exploits if not meticulously designed and implemented. Ensuring smart contract security is crucial for upholding the integrity and reliability of decentralized applications (dApps).
.jpg)
Advanced techniques for smart contract security encompass:
- Formal Verification: Mathematically proving the correctness of smart contract code to ensure it operates as intended under all conditions.
- Auditing: Thorough code reviews by security experts to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
- Secure Development Frameworks: Providing developers with tools and best practices for writing secure smart contracts, reducing the risk of errors and vulnerabilities.
Emerging Trends in Blockchain
While scalability remains a critical concern, the blockchain landscape continues to evolve, introducing new trends poised to redefine our interaction with decentralized technologies.
Web3 - The Decentralized Web: Web3 represents the next evolution of the internet, aiming for a decentralized, user-centric online experience. Blockchain technology serves as a foundational pillar, empowering decentralized applications (dApps), self-sovereign identity systems, and token-based economies. Key to Web3's infrastructure are advanced blockchain development techniques, including interoperability protocols and decentralized storage solutions.
Metaverse - The Virtual Frontier: The Metaverse, a digital universe where users engage with each other and virtual assets, is rapidly gaining prominence. Blockchain technology underpins the Metaverse economy, facilitating the creation and ownership of unique digital assets (NFTs) and virtual properties. Essential for shaping a secure and immersive Metaverse are advanced blockchain development tools such as smart contracts and decentralized identity systems.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) - Shaping the Future of Finance: DeFi is transforming the financial sector by offering decentralized alternatives to traditional financial services. Powered by smart contracts and blockchain technology, DeFi platforms provide services like lending, borrowing, trading, and asset management without intermediaries. Innovations in DeFi are driven by advanced blockchain development techniques such as yield farming protocols and decentralized exchanges.
Advanced blockchain development techniques are not just abstract concepts; they are gradually realizing a promising decentralized future. By addressing current challenges and unlocking new possibilities, these technologies are revolutionizing how we interact with the digital world. With the continuous evolution of blockchain technology, we can expect a future where DApps are not only stronger and more secure but also more widely adopted and accessible than ever before. Major projects like U2U Network are actively demonstrating their commitment to developing these advanced technologies, promising groundbreaking DApp experiences and contributing to the construction of a thriving Web3 ecosystem.


.png)


