Blockchain Technology refers to the database structure that includes the ownership of digital assets on a decentralized, distributed ledger. This disrupting solution promotes innovation and reshapes the digital economy thanks to its extraordinary characteristics, such as security, stability, and privacy. Since it is increasingly widely adopted, Blockchain also provides the impetus for many other symbiotic concepts such as Web3, metaverse, etc.
However, not every aspect of Blockchain is easy to understand for everyone, especially the architectural nature of this technology. This article aims to demystify the intricacies of blockchain architecture by breaking down its layers and their respective functionalities. Understanding "what is blockchain architecture" is crucial for blockchain developers and start-up entrepreneurs seeking to leverage blockchain technology effectively.
What is Blockchain architecture?
What is Blockchain Architecture? The blockchain architecture is designed as a peer-to-peer (P2P) network of computers structured by the components and subcomponents or layers that make up a complete blockchain system. Each component/layer has a unique role, such as storing data, maintaining network connectivity, ensuring consensus across the system, etc., to smoothly operate a larger ecosystem with that blockchain as the infrastructure.
This architecture focuses on constructing a decentralized distributed ledger (public or private) to record various kinds of transactions arranged into an encrypted database. This database is peer distributed to each participant (called node) as identical copies and can not altered without the consensus of the whole network (each separate computer).

The Key Characteristics of Blockchain Architecture
- Cryptography: The database must be encrypted by cryptography before being recorded in the ledger. Decrypting this database requires a private key.
- Immutability: Once recorded in the blockchain, the database cannot be arbitrarily changed. Any change requires the approval of the entire P2P network following the established consensus protocol.
- Decentralized: In blockchain, central authorities do not exist. The database, instead, is distributed to a network of independent computers through peer-to-peer consensus.
- Anonymity: In blockchain, each participant doesn't need to share their personal identifying but share the public key and use the addresses with corresponding private keys to act on the blockchain.
- Transparency: Although the anonymity of blockchain, the users' actions are recorded on a shared public ledger. They can share with others their activities, and it is easy to audit and verify accuracy.
The Types of Blockchain Architecture
Public Blockchain
The public blockchain allows anyone can set up a node and become part of the P2P network without seeking permission. This blockchain design enables involvement, using the network, and obtaining information - totally freely.
While anonymity is still open, the public blockchain architecture incentivizes stakeholders to act honestly through mining or staking rewards and opportunity costs.
Advantages:
- Decentralization: This means that no central authority controls the network. This makes the network more resilient to attacks and censorship.
- Transparency: Anyone can view all the transactions on the network. This makes it easier to verify the authenticity of transactions and reduces the risk of fraud.
- No permission required: Anyone can join a public blockchain network, which makes it more inclusive and accessible to everyone.
- Immutability: Any data in a public blockchain cannot be altered or deleted. This ensures the integrity of the network and reduces the risk of fraud.
Disadvantages:
- Scalability: Public blockchains can only handle a limited number of transactions per second, leading to slow transaction processing times and high fees during peak usage.
- Low privacy: Too transparent leads to this, specifically for users who want to keep their transactions private.
- Energy consumption: Public blockchains require a lot of computational power to maintain their security and integrity. This leads to high energy consumption, which can concern environmentalists.
Private blockchain
A private blockchain is designed to be used by an organization based on some specific goals. This blockchain provides greater control and privacy to the network's owners since only authorized parties can participate in it. These networks are faster than public blockchains because they don't require solving complex algorithms before adding new transactions.
Advantage
- Privacy: Only authorized users can access the network, and transactions can be kept private.
- Scalability: As the number of users is limited, it leads to faster transaction processing times and lower fees.
- Control: The network can be customized to meet the organization's needs.
Disadvantage
- Centralization: Because of controlled by a select group of users, it leads to concerns about the integrity and security of the network.
- Limited inclusivity: This can limit the users' inclusivity and accessibility.
- Cost: Private blockchains can be more expensive to set up and maintain than public ones.
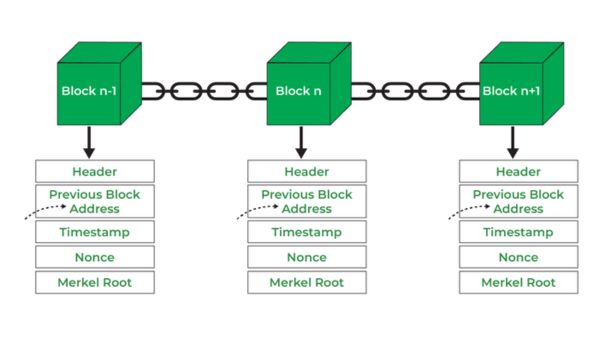
The Core Components of Blockchain Architecture
Node
A node refers to an independent computer on the peer-to-peer network. The number of nodes of a blockchain network corresponds to the number of computers participating in the P2P network. All are connected to the internet and installed with the core software, enabling it to collaborate with others on the network. Every node is algorithmically programmed to execute transactions based on a majority consensus.
Block
A block is a data structure within the blockchain database where every data transaction is permanently recorded. Once the data are validated, the block is closed. Then, a new block is created for new transactions to be entered into and validated.
For example, on the Bitcoin blockchain, all transactions initiated within about ten minutes are approved and recorded as a new block.
Chain
The chain is a combination of blocks that are linked from the first-ever (the genesis block) to the current one. Each block is linked to the previous one through unique metadata, creating a secure chain. The linking of blocks to create a chain is where the name blockchain comes from.
Transaction
Transaction could be a transfer of digital value like coins/tokens from one address to another or a state change in a smart contract.
Miners
In a blockchain network, "miner" is assigned to two components. First, it refers to a node that performs functions for the network - such as relaying data, approving transactions, and storing the shared ledger. Besides, "miner" also refers to the person who acquires, sets up, and runs a node to earn the reward that the protocol issues.
Consensus protocol
This is a set of rules that form a consensus on how transactions are processed and stored on a shared ledger or how smart contracts are executed. It is also the guideline to help each computer on the peer-to-peer network to interact.
Public vs. Private Keys
Once recorded to the blockchain, all data will be encrypted by cryptography to secure it on the shared ledger. The type of cryptography used on blockchain architectures is public-private key cryptography. It creates separate keys for encryption and decryption. The encrypting key is public, while the decrypting key is private.
The hashed version of the public key serves as the wallet address that someone shares to receive payment. Meanwhile, the private key becomes their password to access and spend the funds or authorize action in a smart contract.
What Is The Different Between Blockchain Architecture And Database?
Blockchain and traditional databases are two distinct technologies that store and manage data uniquely. Blockchain can be considered to be a type of database in that it can store information, but it is wrong to assume that it is like a regular database. The differences between a Blockchain and a database are very glaring, and their peculiarities enable them to suit different use cases.
The ultimate goal of a blockchain is to store information, which makes it a database. Blockchains only differ from other database types by the way they store data. While blockchains can be considered a database, a database is typically not a blockchain. Databases generally don't use signed blocks to store the data.
This table shows how difference between blockchain architecture and database:
|
Blockchain architecture |
Database |
|
Blockchain uses decentralized storage of data. |
The database uses centralized storage of data. |
|
There is no administrator in Blockchain. |
The database needs a Database admin or Database administrator to manage the stored data. |
|
Modifying data does not require permission. Users have a copy of data, and by modifying the copies does not affect the master copy of the data as Blockchain is irresistible to modification of data. |
Modifying data requires permission from the database admin. |
|
Blockchain keeps the present information as well as the past information that has been stored before. |
Centralized databases keep information that is up-to-date at a particular moment |
|
Blockchain is ideal for transaction platforms, but it slows down when used as a database, especially with large data collections. |
Centralized databases are used as databases for a really long time and have a good performance record but are slow for certain functionalities. |
Conclusion
As posed at the beginning, the complex structure of Blockchain and its architecture has never been really easy to grasp, especially with newbies. Within the limited scope of this blog post "what is blokchain architecture", it may not be able to provide more detail about blockchain architecture, but hopefully, the information above will be useful to those who are interested in this emerging technology. Follow U2U.xyz for more blockchain information!






