Decentralized applications, or Dapps, are a hot topic in the world of blockchain and cryptocurrency. What is a Dapp, and how does it differ from a traditional app? In essence, Dapps are applications that run on a decentralized network, rather than a centralized server. This allows for greater security, transparency, and flexibility, as well as a variety of other benefits.
Table of Contents
What is a dApp?
What is a dApp? A Dapp, short for Decentralized Application, is a software application that operates on a decentralized network, typically utilizing blockchain technology. Unlike traditional apps that run on centralized servers, Dapps use decentralized peer-to-peer networks, making them more transparent, secure, and resistant to censorship.
Dapps usually have smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions that automatically execute when certain criteria are met. These smart contracts facilitate the functioning of the Dapp without the need for intermediaries.
Users interact with Dapps through web browsers or specialized software, just like traditional apps. However, the underlying technology and architecture of Dapps make them distinct from their centralized counterparts, offering unique advantages in terms of trust, data ownership, and control.
DApps are designed to run on decentralized peer-to-peer networks. An early report suggested that DApps possess the following characteristics:
- Open-source: The source code of DApps is publicly available, meaning that anyone can inspect, utilize, copy, and modify them. There is no single entity controlling the majority of its coins or tokens, and users can propose and vote on changes to the DApp.
- Decentralized and cryptographically secure: To ensure data safety, all information of the DApp is securely cryptographically stored on a public, decentralized blockchain maintained by multiple nodes.
- Tokenized system: DApps can be accessed with a cryptographic token, which can be a cryptocurrency like ETH or a native token generated using a consensus algorithm like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). The token can be used to reward contributors like miners and stalkers.
Under this comprehensive definition, the Bitcoin blockchain can be regarded as a DApp and arguably the first DApp ever. It's open-source, has all data live on its decentralized blockchain, relies on a crypto token, and uses the PoW consensus algorithm. Other blockchains that exhibit the above features can also be defined as DApps.
However, nowadays, the term "DApps" typically refers to all applications that have smart contract functionalities and operate on blockchain networks. Since the Bitcoin blockchain does not support smart contracts, most people would not classify it as a DApp.
As of June 2022, most DApps operate on the Ethereum network, which offers a solid infrastructure for DApp developers to extend their current use cases. As DApps mature, developers have begun building them on other blockchains, including BNB Smart Chain (BSC), Solana (SOL), Polygon (MATIC), Avalanche (AVAX), and EOS.

How does a dApp work?
Decentralized applications (dApps), or Dapps, possess unique characteristics that distinguish them from conventional applications. Firstly, What is a Dapp? dApps are open source, meaning that any changes made to the application must be decided by a consensus of a significant number of users. This ensures that the codebase of the application is transparent and available for all users to evaluate. Additionally, dApps offer decentralized storage, using blocks on a decentralized network to store data.
dApps are stored on a blockchain system, typically Ethereum, and are validated using cryptographic tokens. Access to these applications requires the possession of such tokens.
Although decentralization sets dApps apart from conventional apps, they share some commonalities in their functionality. Like traditional applications, dApps use front-end codes to create a web page. However, their back-end codes are different, relying on the decentralized peer-to-peer network to operate. This characteristic makes dApps impossible to be controlled by a single authority.
Smart contracts are another unique aspect of dApps, unlike traditional apps that rely on centralized servers and databases. These contracts enforce rules for transactions and are stored on a blockchain. A small contract is only a small part of the entire application and is essentially a set of back-end codes. Therefore, a combination of several smart contracts along with third-party systems for the front end is necessary for a decentralized application to function.
Smart contracts run on a blockchain, which is a ledger of data records stored in blocks. These blocks are distributed across multiple locations, and cryptographic validations govern and link the data blocks.
Why Use a dApp?
Decentralized applications, also known as Dapps, offer several advantages over conventional applications, one of which is their decentralized nature. What is a Dapp, and how does it ensure that decision-making involves all stakeholders rather than being solely in the hands of a single authority? Another advantage of dApps is the absence of third-party intermediaries, as smart contracts are utilized instead.
One of the key benefits of using dApps is their ability to simplify complex processes. For example, traditional transaction applications may charge fees for transferring funds to a bank account and may take several days to complete the transfer. However, when using a decentralized app, transactions are instant and typically have little to no cost. This can save users both time and money, eliminating the need for unnecessary transaction fees.
Furthermore, because dApps are decentralized and do not rely on a physical device for operation, they are less vulnerable to cyber threats and attacks compared to centralized applications. As a result, these networks are more secure and have less downtime. Users can access decentralized applications at any time without worrying about security breaches or system failures.
Another advantage of dApps is their versatility, as they can be utilized in a variety of industries such as gaming, governance, finance, medicine, and file storage. This makes dApps an attractive option for businesses and individuals looking to streamline their operations and increase efficiency.
Despite the differences in their backend operations, the user experience of dApps is similar to that of conventional applications. This makes it easy for users to adopt and incorporate dApps into their daily routines without requiring extensive technical knowledge. With their numerous benefits, dApps are a compelling choice for those looking to enhance their online experience and take advantage of the decentralized future.
What are some differences between dApps and traditional apps?
Decentralization
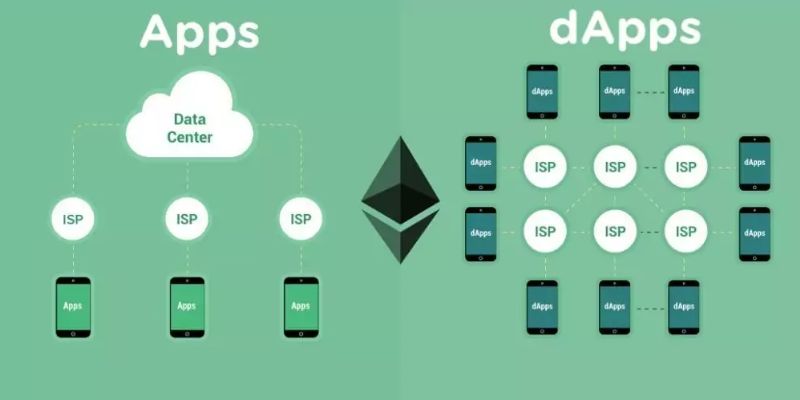
Decentralized applications, or dApps, differ from traditional applications in several ways. Firstly, dApps are hosted on public blockchain platforms which are decentralized, meaning that no one person or group has complete control over them. In contrast, traditional apps are usually hosted on centralized servers controlled by a single entity. Additionally, dApp code is often open-source, which means that it is available for anyone to view, audit, and verify.
Privacy
Another difference between dApps and traditional apps is privacy. Traditional apps typically require personal information, such as your name, email address, or phone number, and may track your data usage. However, dApps are accessed through a crypto wallet, so you don't need to use your real identity to interact with them. You control your information, which means that you can disconnect from a dApp at any time and stop sharing data.
Censorship resistant
Dapps are also censorship-resistant, as they do not require anyone's permission to use and no individual entity can stop you from connecting to an open blockchain network. In contrast, governments can coerce companies to block access to traditional apps that run on centralized servers.
Smart contracts
Smart contracts are another distinguishing feature of dApps. Smart contracts automatically execute when certain terms are met and do not require approval from intermediaries. The code in smart contracts is public and can be verified by anyone, which means that audited smart contracts operate in predictable ways without requiring trust. In contrast, traditional apps usually have a single group or entity that controls them, and their exact processes tend to be proprietary information. Transactions in traditional apps cannot be publicly audited or verified in the same way as they can on the blockchain.
Dapps can exist on a variety of smart-contract-compatible blockchains, including Ethereum, Solana, and Avalanche. Overall, dApps are changing the way we think about software development by offering a decentralized, transparent, and more secure alternative to traditional apps.
Benefits of dApps
Despite their similar interfaces, decentralized applications (DApps) offer several advantages over traditional centralized applications. Unlike web apps that store data on centralized servers, DApps operate on distributed networks that have no central authority. This means that a single compromised server cannot take down the entire network, rendering the app unusable. Additionally, centralized systems are prone to data breaches and theft, exposing companies and users to potential risks.
In contrast, DApps are more secure since they do not have a single point of failure, making it extremely difficult for malicious actors to attack or hijack the network. Furthermore, DApps are designed to work with minimal downtime, even if some parts of the network malfunction, thanks to their peer-to-peer (P2P) network architecture.
The decentralized nature of DApps also gives users more control over the information they share. Unlike traditional applications where users are required to provide personal information, DApps allow users to remain anonymous while using a crypto wallet to interact with the platform. This means that users have full control over the information they share, without the need for companies to control their personal data.
Developers can also benefit from DApps since they can easily integrate cryptocurrencies into their basic functionalities by leveraging smart contracts. For instance, DApps built on Ethereum can adopt ETH as payment without relying on third-party payment providers, making transactions more efficient and secure. Overall, the decentralized nature of DApps offers several advantages that make them an attractive alternative to traditional centralized applications.
Drawbacks of dApps
Decentralized applications (DApps) have the potential to play a significant role in a future that is free from censorship. However, as with most things, there are pros and cons to consider. While the benefits of DApps are apparent, the industry is still in the early stages of development, and there are several limitations that need to be addressed. For example, scalability remains a significant issue, as DApps require a significant amount of computing power to operate. This puts pressure on the networks they run on, leading to network congestion, inflated gas fees, and a low transaction per second (TPS) rate.
Another limitation of DApps is the difficulty of making modifications to their backend code once they are deployed on the blockchain. Enhancing user experience and security requires ongoing changes, including fixing bugs, updating the user interface, and adding new functionalities. However, gaining majority consensus from the network’s nodes to approve changes or improvements can take an extended period, leaving the DApp vulnerable to bugs and vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, standing out in the crowded DApp market is challenging. For a DApp to be effective, it needs to attract a large user base. The more users a DApp has, the more effective it is at providing services, making it more secure against hackers meddling with open-source code. However, attracting users can be difficult, particularly when there is fierce competition from other DApps.
Despite these challenges, DApps remains a promising technology. The industry is continuously working towards resolving the limitations, and as the technology matures, DApps are expected to become more accessible, scalable, and user-friendly. With continued innovation and investment, the potential of DApps to disrupt traditional industries and empower individuals and communities remains vast.

Examples of Decentralized Apps
As the blockchain space continues to grow at a rapid pace, the number of decentralized applications (dApps) is increasing significantly. Some of these dApps have already evolved into mature platforms with numerous advantages. Here are some examples of the most popular and widely used dApps in the industry.
Pancake Swap is a dApp that operates on the Binance Smart Chain ecosystem and allows the swapping of BEP 20 tokens. It has gained recognition for its user-friendly interface and low transaction fees, which are only 0.2% for makers and takers. Additionally, it supports multiple crypto wallets, making it more accessible for users.
1 Inch is another dApp that has seen tremendous growth and development since its inception. It started as an Ethereum-based decentralized exchange but has now expanded to become a multi-network trading DEX. Users can leverage the liquidity of a variety of decentralized exchanges that operate on different blockchains, which has made it a popular choice for traders.
Chainlink is a middleware software that is widely used for providing tamper-proof inputs, outputs, and computations for Oracle networks. It is a popular choice for developers and businesses that require reliable data sources. Currently, Google is testing Chainlink for use in their BigQuery PaaS data warehouse.
TraceDonate is a unique decentralized application that focuses on creating trust and transparency in the donation process. The app is designed for charities, donors, and beneficiaries to come together on a single platform, where donors can track how their donations are being utilized. Funds are stored in digital wallets, ensuring that donations reach the intended beneficiaries.
Aave is one of the most popular DeFi-based liquidity protocols that are open-source and provide complete transparency to its users. Users can stake, borrow, lend, and earn interest on deposits. As a decentralized platform, Aave ensures anonymity for both borrowers and lenders, making it a popular choice among DeFi enthusiasts.
Top Security Tips for DApp Users
Unfortunately, the world of cryptocurrency and decentralized applications is fraught with scams and fraudulent activities. However, by taking certain precautions, you can protect yourself from losing your funds to these scams.
Confirm the DApp you want to use is legitimate and reputable
One of the most important steps you can take is to ensure that the DApp you want to use is legitimate and reputable. To do this, you can check out databases like DAppRadar.com and DApp.com, which provide data related to popular DApps on the market. By reviewing the DApp’s on-chain data graphs, you can determine if there have been sudden drops in users, volume, or market cap, which could indicate a problem with the DApp.
In addition, it is important to check the DApp creators’ communication channels, such as Telegram, Twitter, or other social media links, to ensure that what they are saying makes sense. Active communication from the creators, especially if the DApp is new, is a good sign. You should also read the available reviews and only use DApps with a solid track record and a good reputation.
Furthermore, it is crucial to ensure that the DApp’s code has been audited by a qualified smart contract auditor, such as CertiK. If the smart contract has not been through auditing, there is a possibility of fatal bugs that could compromise your assets.
By taking these steps and being vigilant, you can reduce the risk of falling victim to fraudulent DApps and scams in the crypto markets. Remember to always do your due diligence and stay informed to protect your investments.
Use a VPN for public Wi-Fi networks
Accessing the internet through public Wi-Fi networks can put your personal information at risk, as hackers may intercept and access your internet traffic, including sensitive information such as login credentials. In order to avoid the possibility of such a breach, it is advisable to use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) when accessing Web 3.0 applications through public Wi-Fi networks.

Make sure you’re visiting the correct URL
In addition, it is important to be vigilant about the URLs of websites and decentralized applications (DApps) you visit, particularly when using the internet in public spaces. Cybercriminals have been known to create fake DApps that closely resemble legitimate ones, using similar URLs with only small differences that may not be immediately apparent.
This type of scam is known as phishing, and it can be difficult to detect. To safeguard against phishing attacks, it is recommended to double-check URLs carefully and ensure that you are visiting the correct website or DApp. By taking these precautions, you can help to protect your assets and personal information from cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in public Wi-Fi networks.
The Future of dApps
Decentralized applications (dApps) are a recent technological advancement in the blockchain space that has been rapidly growing and evolving. As they continue to expand, they are increasingly being integrated into a variety of industries, offering multiple benefits and becoming a lucrative choice for companies.
Given the widespread adoption of blockchain solutions across various sectors, it is not surprising that the popularity of dApps is also on the rise. In the near future, there are two changes that are likely to occur within the dApp ecosystem. Firstly, it is anticipated that stablecoins will become more prevalent. These cryptocurrencies are designed to address the issue of high price volatility that plagues other cryptocurrencies. They can be pegged to fiat currencies, precious metals, or even other cryptocurrencies, and use innovative mechanisms to maintain price stability. With more stablecoins in circulation, developers will likely create a greater number of dApps centered around these stablecoins.
Secondly, we may also see the use of innovative price-stabilizing mechanisms. This is particularly relevant for stablecoins, but can also be applied to other types of cryptocurrencies. Price stability is crucial for the mass adoption of cryptocurrencies, and innovative mechanisms that address this issue could greatly increase their appeal to investors.
Overall, the continued growth and evolution of dApps are poised to have a significant impact on the blockchain ecosystem. With their numerous benefits and increasing adoption, dApps are set to become an integral part of various industries and offer promising opportunities for developers and investors alike.
As the world becomes more interconnected and digital, Dapps are likely to play an increasingly important role in the future of technology. Whether you're a developer, investor, or simply curious about this exciting new area of innovation, there's no better time to learn about what is a dApp and how it works. With their potential to transform industries and disrupt traditional business models, Dapps are sure to be a major force in the years to come. Follow Unicorn Ultra to update more knowledge about blockchain






