The demand for secure and customizable blockchain solutions is burgeoning. Private blockchain solutions emerge as a transformative force, offering businesses unparalleled control and security over their data and transactions. As industries seek innovative ways to safeguard sensitive information and streamline operations, private blockchains stand out as a beacon of trust and efficiency. This article explores the pivotal role of private blockchain solutions in empowering enterprises to navigate the complexities of modern business with confidence and resilience.
Table of Contents
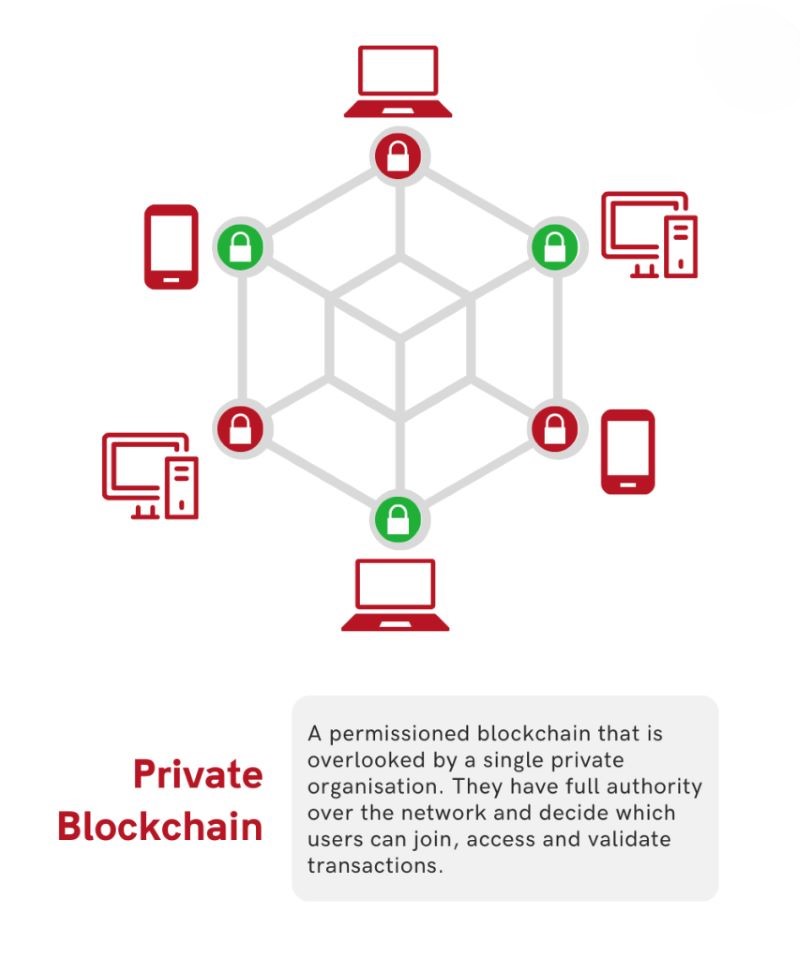
Understanding Private Blockchain Solutions
Key Characteristics of Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are characterized by several key features that distinguish them from public blockchains:
- Permissioned Access: Private blockchains restrict access to participants who have been granted permission. This contrasts with public blockchains where anyone can join and participate.
- Controlled Consensus: Consensus mechanisms in private blockchains are designed to be controlled and efficient, often relying on known entities (nodes) to validate transactions. This ensures faster transaction speeds and lower energy consumption compared to public blockchains.
- Customizable Governance: Governance structures in private blockchains can be tailored to fit the needs of the participating entities. This flexibility allows organizations to define rules for transaction validation, membership management, and dispute resolution.
Architecture and Components of Private Blockchains
The technical architecture of private blockchains typically includes the following components:
- Nodes: Participants in the network that maintain copies of the blockchain ledger and execute consensus protocols. Nodes can be organized into different roles based on their functions within the network.
- Consensus Algorithms: Algorithms used to achieve agreement among nodes on the validity of transactions. Examples include Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), Proof of Authority (PoA), and Raft consensus.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with predefined rules encoded within the blockchain. They automate processes and enforce agreements without requiring intermediaries.
- Data Storage: Private blockchains utilize various methods for storing data, including traditional databases and distributed storage solutions like IPFS (InterPlanetary File System).
Popular Private Blockchain Platforms
Several prominent platforms have emerged for building and deploying private blockchain solutions:
- Hyperledger Fabric: Developed by the Linux Foundation, Fabric supports modular architecture, allowing organizations to customize their blockchain networks with features like permissioned membership, private transactions, and pluggable consensus.
- Corda: Created by R3, Corda is designed specifically for businesses. It emphasizes privacy and scalability, enabling firms to transact directly and privately using smart contracts that do not require global consensus.
- Quorum: Built on Ethereum, Quorum offers enterprise-focused enhancements such as privacy features (using private transactions and private contracts), network permissioning, and a consensus algorithm tailored for consortium chains.
Benefits of Private Blockchain Solutions for Businesses
Enhanced Security and Privacy:
Private blockchains excel in offering heightened security and privacy. By design, they feature permissioned access and controlled participation. This ensures that only authorized entities can interact with the blockchain, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches. The controlled access mechanism enhances data privacy, making private blockchains suitable for handling sensitive information securely.
Improved Efficiency and Transparency:
Private blockchains contribute to operational efficiency by automating processes and reducing paperwork. Smart contracts, embedded within private blockchains, streamline business operations by executing predefined actions automatically. This automation not only saves time but also minimizes errors and administrative overhead. Moreover, the immutable nature of blockchain records enhances transparency across business processes, providing stakeholders with a clear, auditable trail of transactions and agreements.
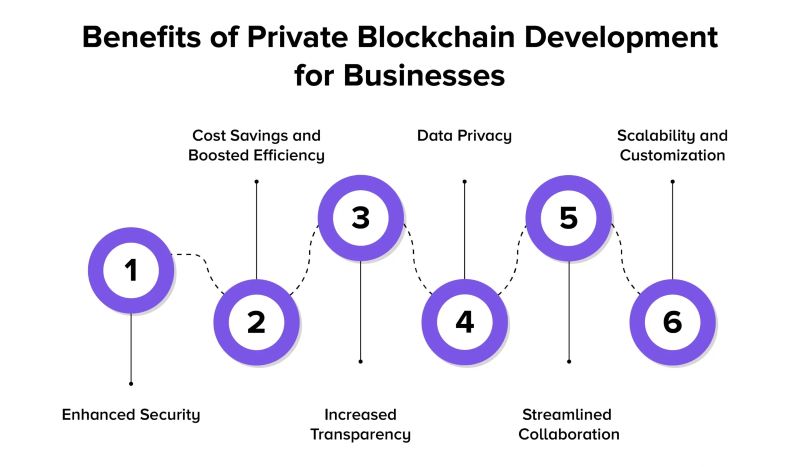
Cost Reduction:
Businesses benefit from cost savings through private blockchains in several ways. Automation enabled by smart contracts reduces the need for manual intervention, thereby lowering operational costs. Private blockchains also eliminate intermediaries in transactions, facilitating direct peer-to-peer interactions and reducing associated fees. Additionally, improved supply chain management within private blockchains optimizes inventory handling and reduces costs related to fraud and inefficiencies.
Enhanced Trust and Collaboration:
Private blockchains foster trust and collaboration among business partners by providing a shared ledger that is tamper-proof and transparent. Participants can access the same set of records, ensuring consistency and reducing disputes. This shared infrastructure promotes trust as all stakeholders have visibility into the transactions and activities recorded on the blockchain. Efficient dispute resolution further strengthens collaboration, enabling smoother interactions and agreements.
Regulatory Compliance:
Private blockchains aid businesses in adhering to regulatory requirements and industry standards, particularly concerning data privacy and security. The controlled access and encryption mechanisms inherent in private blockchains help organizations manage and protect sensitive data in compliance with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA. The auditability of blockchain records simplifies regulatory audits, ensuring that businesses can demonstrate compliance efficiently.
Use Cases of Private Blockchain Solutions
Private blockchain solutions are being increasingly utilized across diverse industries for their reliability, security, and efficiency. Here are some compelling use cases:
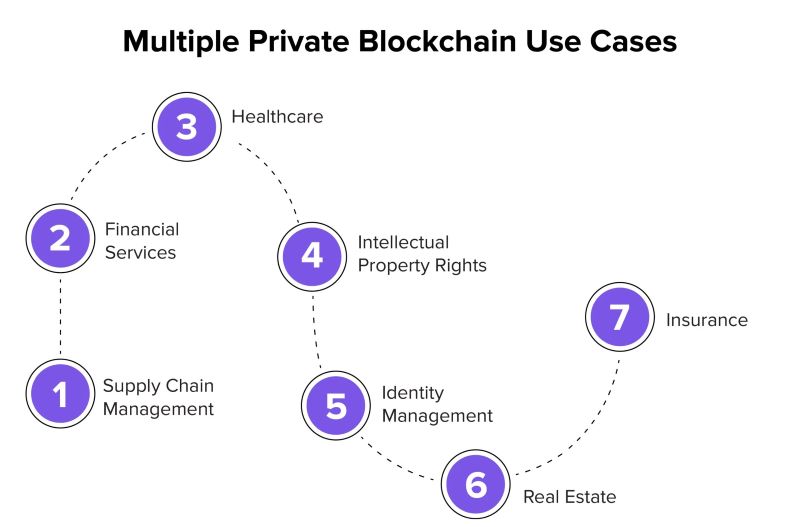
Supply Chain Management
Private blockchains revolutionize supply chain management by providing a transparent and immutable ledger for tracking products from source to destination. Each transaction along the supply chain, such as manufacturing, logistics, and retail, can be recorded securely. This enhances transparency and authenticity, allowing stakeholders to verify the origin, authenticity, and journey of goods. For example, companies can use private blockchains to track food products to ensure compliance with safety standards and to quickly identify and address issues like contamination or counterfeit products.
Financial Services
In the realm of financial services, private blockchains are transforming operations by offering faster, cheaper, and more secure transactions. Financial institutions can leverage private blockchains for instant settlement of transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries and minimizing transaction costs. Additionally, smart contracts enable automated execution of agreements, such as loan disbursements or insurance claims, improving efficiency and reducing processing times. These blockchain solutions also enhance security by providing a tamper-proof record of transactions, which helps mitigate fraud and enhances trust among participants.
Healthcare
Private blockchains are playing a crucial role in healthcare by securely storing and sharing patient data across healthcare providers while ensuring privacy and compliance with regulations like HIPAA. Blockchain technology enables interoperability among disparate systems, allowing healthcare professionals to access patient records securely and efficiently. Moreover, private blockchains facilitate the management of clinical trials by recording trial data transparently and securely, ensuring the integrity of research findings. This improves collaboration among researchers and accelerates medical advancements.
Government
Governments are exploring private blockchains for various applications such as secure identity management, voting systems, and land registry. Private blockchains offer a robust solution for managing identities securely, protecting personal information from unauthorized access while ensuring easy verification. In voting systems, blockchain technology can enhance transparency and trust by providing a tamper-proof record of votes, thereby reducing the risk of fraud and improving electoral integrity. Moreover, private blockchains can streamline land registry processes by recording property transactions immutably, reducing disputes and enhancing transparency in property ownership.
Challenges and Considerations for Implementing Private Blockchain Solutions
Scalability: Private blockchains often struggle with scalability as transaction volumes increase. Solutions like sharding and sidechains can alleviate these issues by distributing transaction processing across multiple nodes or utilizing off-chain processing for certain activities.
Interoperability: Achieving interoperability between different private blockchains and with public blockchains is essential for seamless data exchange and asset transfer across disparate networks. Establishing common standards and protocols facilitates compatibility and integration.
Governance: Clear governance models are necessary to ensure transparent decision-making and effective management within private blockchain networks. Consensus mechanisms and smart contracts can automate governance processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing the potential for disputes.
Cost and Complexity: Implementing private blockchain solutions involves substantial upfront costs for infrastructure setup, development, and integration. Ongoing operational costs include maintenance, security measures, and regulatory compliance efforts.

In conclusion, private blockchain solutions are proving to be a game-changer for businesses across various industries. By offering enhanced security, improved efficiency, cost reduction, and enhanced trust, private blockchains are enabling enterprises to streamline operations, unlock new revenue streams, and foster collaboration in a secure and transparent manner.
The ongoing advancements in private blockchain technology, such as improved scalability and interoperability, are further expanding the potential applications and benefits of these solutions. As businesses continue to explore and adopt private blockchains, we can expect to see a significant transformation in how industries operate and interact.
Private blockchain solutions are not just a burgeoning technology but a significant leap forward, unlocking a new era of security, efficiency, and customization for enterprises. With its exceptional benefits, private blockchain holds the promise of becoming a powerful tool, enabling businesses to optimize processes, enhance data security, and create distinctive value in today's competitive business environment.
In addition, you can follow the U2U Network website to get the latest information about Blockchain.





.png)
