Dive into the world of Parachain Development and discover how this innovative approach propels scalability in blockchain networks. Explore key strategies, benefits, and real-world applications driving the evolution of decentralized technology
Table of Contents
- What are Parachains?
- The Scalability Bottleneck in Traditional Blockchains
- Parachain Development: A Solution to Scalability Challenges
- Parachain Development Process
- Real-World Examples of Parachain Scalability
- Why should we build on Parachain?
- Challenges of Parachain Development
- The Future of Parachain Development: A Glimpse into the Next Frontier
What are Parachains?
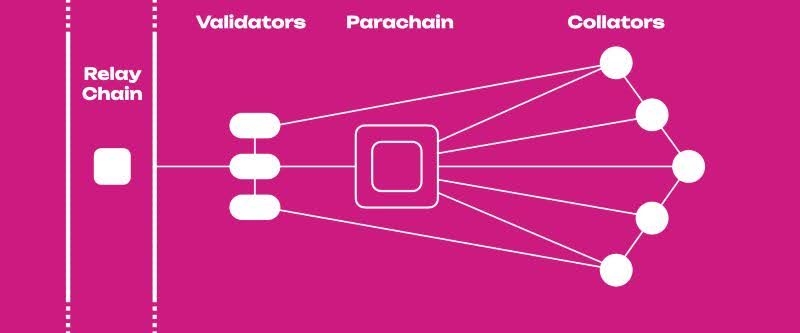
Parachains are specialized and customizable blockchains that operate independently within a larger, interconnected network known as a multichain ecosystem. Think of them as self-governing states within a federation, each with its unique laws and governance structure, all connected through a shared framework. In the blockchain context, this "federation" typically refers to a relay chain like Polkadot or Kusama.
Architecture of a Parachain
Each parachain connects to the relay chain, which serves as the central hub responsible for shared security, consensus, and cross-chain communication. While leveraging the robust security of the relay chain, parachains maintain their sovereignty and execute unique runtime logic tailored to specific use cases. This setup allows parachains to operate independently while benefiting from shared infrastructure.
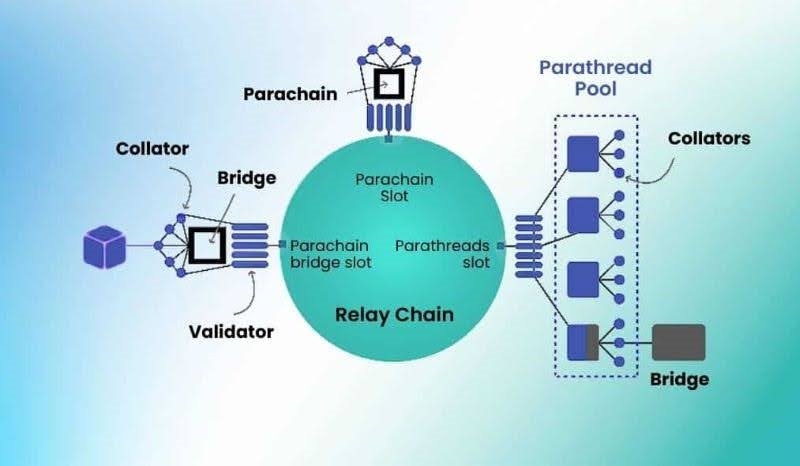
Parachain Consensus Mechanisms
Parachains leverage the security and consensus mechanisms of their connected relay chains, rather than having independent mechanisms of their own. This arrangement ensures that all parachains benefit from the robust security and decentralization provided by the relay chain's validators.
Typically, relay chains like those in the Polkadot ecosystem employ Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS), where token holders nominate validators to secure the network and validate transactions across all connected parachains. This shared security model guarantees consistent protection and integrity throughout the network.
While parachains rely on the relay chain for overarching security, they can implement their own block production mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Authority (PoA) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS), to manage transaction sequencing within their blocks. For instance, a parachain might opt for PoA, involving trusted authorities in block production for efficiency, albeit with reduced decentralization. Alternatively, variants like Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) enable token holders to delegate block production to elected representatives.
The choice of consensus mechanism for a parachain hinges on its specific requirements and operational objectives. However, all parachains ultimately finalize their transactions and secure their data through coordination with the relay chain's consensus, ensuring the overall security and validity of the entire network.
The Scalability Bottleneck in Traditional Blockchains
Traditional blockchain networks, while groundbreaking in their design, often struggle with scalability limitations. Scalability refers to their capacity to efficiently handle a high volume of transactions. As user numbers and application demands grow, these blockchains can become congested, resulting in slower transaction speeds and high transaction fees.
For instance, the Bitcoin blockchain, renowned for its robust security, operates with a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism that restricts its transaction processing capability to a few transactions per second. Similarly, Ethereum, despite its extensive decentralized application (dApp) ecosystem, faces scalability challenges, particularly during peak usage periods.
These constraints impede the broader adoption of blockchain technology in real-world applications that demand high transaction throughput and low latency, such as decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and gaming. The sluggish transaction speeds and elevated fees associated with congested networks create suboptimal user experiences and restrict blockchain's potential use cases.
Parachain Development: A Solution to Scalability Challenges
Parachain development emerges as a promising solution to alleviate the scalability limitations of traditional blockchains. By adopting a multichain architecture, parachains facilitate parallel transaction processing across interconnected blockchains. This approach substantially enhances the overall network throughput, enabling faster and more cost-effective transactions.
Unlike conventional blockchains that centralize transaction validation on a single chain, parachains distribute transaction processing across multiple specialized chains. Each parachain is optimized for specific applications, enhancing not only scalability but also the adaptability and customization capabilities of the blockchain ecosystem.
Parachain Development Process
Creating a parachain involves a complex process that demands technical proficiency, strategic foresight, and community involvement. The journey typically unfolds through several pivotal stages:
- Conceptualization and Design: Begin by clearly defining the parachain's objectives, intended audience, and unique value propositions. Identify the specific challenges it aims to address and outline its key features, including governance models, tokenomics, and architectural considerations.
- Substrate Framework: Leveraging Substrate, developed by Parity Technologies, is pivotal. This framework offers a modular toolkit that streamlines parachain development. It provides essential components like consensus mechanisms, networking capabilities, and runtime modules, empowering developers to focus on implementing bespoke parachain logic efficiently.
- Parachain Slot Acquisition: Securing a parachain slot on the relay chain is essential for operational deployment. Typically obtained through competitive parachain auctions, this process involves bidding native tokens or crowdloaned funds. Winning a slot grants access to the relay chain's shared security and interoperability features, crucial for network integration.
- Parathread Deployment (Optional): For projects requiring flexibility or cost-effectiveness, parathreads offer an alternative. These allow temporary participation in the relay chain's security and interoperability without occupying a dedicated slot, catering well to projects in developmental phases or with varying resource needs.
- Development and Deployment: Post-slot acquisition, focus shifts to developing and deploying the parachain's custom runtime logic. This phase includes smart contract development, governance framework establishment, and potential integration with other parachains or external networks, ensuring seamless functionality within the broader ecosystem.
- Community Building and Engagement: Vital to long-term success is fostering a robust community around the parachain. Engage developers, validators, and users who resonate with the project's vision through social media, forums, and targeted events. Cultivating an active ecosystem bolsters support, innovation, and sustained growth.
Real-World Examples of Parachain Scalability
Several parachain projects exemplify the transformative impact of this technology, addressing blockchain scalability challenges and expanding the horizons of decentralized applications (dApps).
Moonbeam: Moonbeam stands out as a prominent parachain on Polkadot, offering full compatibility with Ethereum. This integration allows seamless deployment of existing Ethereum smart contracts and dApps on Polkadot, attracting a vibrant ecosystem. Popular DeFi platforms like SushiSwap and Curve Finance have migrated to Moonbeam, benefiting from enhanced scalability through Polkadot's parachain architecture. Transactions on Moonbeam are faster and cheaper compared to Ethereum's mainnet, highlighting its scalability advantages.
Acala: Focused on decentralized finance (DeFi), Acala is another notable parachain on Polkadot, providing a comprehensive suite of financial services including stablecoins and decentralized exchanges (DEXs). Acala's unique architecture integrates stablecoin issuance with a DEX, garnering significant interest from the DeFi community. Leveraging Polkadot's shared security and interoperability, Acala ensures scalability and security for its DeFi applications, empowering global access to financial services.
Astar: Astar serves as a versatile smart contract hub on Polkadot, supporting both the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and WebAssembly (WASM). This flexibility makes Astar a preferred platform for developers across various sectors, including DeFi, NFTs, and gaming. By utilizing Polkadot's parachain infrastructure, Astar achieves impressive scalability, accommodating a growing array of dApps and users within its thriving ecosystem.
Parachain Scalability in Action: These examples vividly demonstrate how parachains are revolutionizing blockchain applications. In DeFi, platforms like Moonbeam and Acala facilitate faster, more cost-effective transactions, enhancing accessibility on a global scale. In the realm of NFTs, parachains facilitate the creation and exchange of unique digital assets with minimal transaction fees. Moreover, in gaming, parachains empower the development of next-generation blockchain games with enhanced scalability and seamless interoperability.
Why should we build on Parachain?
Building on a parachain presents compelling advantages for blockchain projects and developers, offering unparalleled scalability, interoperability, and innovation potential. Here's why you should consider leveraging a parachain for your blockchain application:
- Unleashed Scalability: Parachains resolve the scalability constraints of traditional blockchains by enabling concurrent transaction processing across multiple chains. This results in higher throughput, faster transaction speeds, and lower fees, enhancing the efficiency and accessibility of your decentralized application (dApp).
- Tailored Customization: Parachains are highly customizable, allowing you to tailor the blockchain environment precisely to your use case. You have full control over design aspects such as consensus mechanisms, governance models, and specific features, ensuring your dApp meets unique requirements effectively.
- Seamless Interoperability: Designed for seamless communication, parachains facilitate data sharing with other chains within the same ecosystem. This interoperability fosters interconnected dApps that leverage diverse blockchain strengths, enabling cross-chain collaboration and innovative solutions.
- Robust Shared Security: Connected to relay chains like Polkadot or Kusama, parachains inherit robust network security. This eliminates the need for individual security infrastructure development, saving time and resources while ensuring high-level protection for your dApp.
- Thriving Ecosystem: Parachain ecosystems are vibrant and rapidly expanding, attracting diverse projects and developers. Building on a parachain connects you with a dynamic community of peers, potential collaborators, and an expanding user base, fostering growth and adoption.
- Reduced Time to Market: Leveraging Substrate, the parachain development framework, offers a modular and flexible approach. This reduces development complexity and time, enabling quicker and more efficient dApp launches.
- Future-Proof Technology: Parachain technology represents the forefront of blockchain innovation, continuously evolving and improving. By building on a parachain, you invest in a future-proof technology poised to adapt to evolving blockchain landscapes and user needs.
Challenges of Parachain Development
Challenges in parachain development present significant hurdles despite their potential to enhance blockchain scalability. These challenges must be navigated effectively to ensure the sustainability and success of parachain projects.
Parachain Slot Auctions and Costs: Securing a parachain slot through competitive auctions on networks like Polkadot or Kusama requires substantial capital. High bidding costs can exclude smaller projects with limited resources, potentially concentrating influence among well-funded entities.
Technical Complexity: Developing a parachain demands expertise in frameworks like Substrate and deep knowledge of blockchain architecture, consensus mechanisms, and smart contract deployment. This complexity can deter smaller teams or less technically adept projects from entering the parachain ecosystem.
Governance and Security: Each parachain operates autonomously, necessitating the establishment of robust governance models and security protocols. Challenges include designing effective decision-making processes, managing token distribution, and mitigating vulnerabilities inherent in decentralized systems.
Interoperability Challenges: While designed for interoperability, ensuring seamless communication and asset transfers between different parachains remains complex. Unique architectures and protocols among parachains require sophisticated bridges and interfaces to facilitate efficient cross-chain interactions.
Centralization Risks: The relay chain, central to providing shared security and consensus for all parachains, poses risks of centralization. Concentration of power among a few validators on the relay chain may raise concerns about potential censorship and control over the network's operations.
The Future of Parachain Development: A Glimpse into the Next Frontier
The potential of parachain technology is just beginning to be realized. As the technology matures and the ecosystem expands, parachains are expected to play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of blockchain.
One of the most promising trends is the use of parachains to build Web3 applications. Web3 envisions a decentralized internet where users have more control over their data and interactions. Parachains, with their scalability, interoperability, and customizability, provide an ideal foundation for building the infrastructure and applications that will power the Web3 revolution.
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is another area where parachains are poised to make a significant impact. The scalability and interoperability of parachains can enable the creation of more complex and sophisticated DeFi applications, such as decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, and insurance protocols.

Furthermore, parachains are also being explored for enterprise use cases. Their ability to provide customizable and scalable blockchain solutions makes them attractive for businesses looking to leverage blockchain technology for supply chain management, identity verification, and other applications.
As the parachain ecosystem continues to evolve, even more innovative use cases are expected to emerge. With their ability to unlock the full potential of blockchain technology, parachains are set to play a crucial role in shaping the future of decentralized applications and the broader adoption of blockchain in various industries.
U2U Network stands at the forefront of blockchain innovation, leveraging parachain development to tackle scalability challenges head-on. By integrating parachain technology into its platform, U2U Network enhances its capabilities while driving forward the broader blockchain ecosystem. This proactive stance underscores U2U Network's commitment to a future where blockchain is both secure and highly scalable, essential for widespread adoption across industries. As parachains evolve, U2U Network's leadership positions it as a pivotal force in shaping the future of blockchain scalability, paving the way for transformative applications across diverse sectors.





.png)
