The debate between multichain and crosschain technologies has ignited a lively discussion within the blockchain community. While both approaches aim to achieve interoperability, they differ in their underlying architectures and mechanisms. Multichain solutions focus on building interconnected networks with shared security and communication protocols, while cross chain technologies enable direct communication and asset transfers between independent blockchains. U2U Network, recognizing the strengths and weaknesses of both approaches, is forging a path toward a hybrid solution that leverages the best of both worlds.
Table of Contents
Multichain Technologies
Multichain: Think of multichain as a network of high-speed rail lines connecting different cities. Each city (representing a blockchain) has its own unique features, but they are all interconnected to allow passengers (digital assets) to move seamlessly between them.
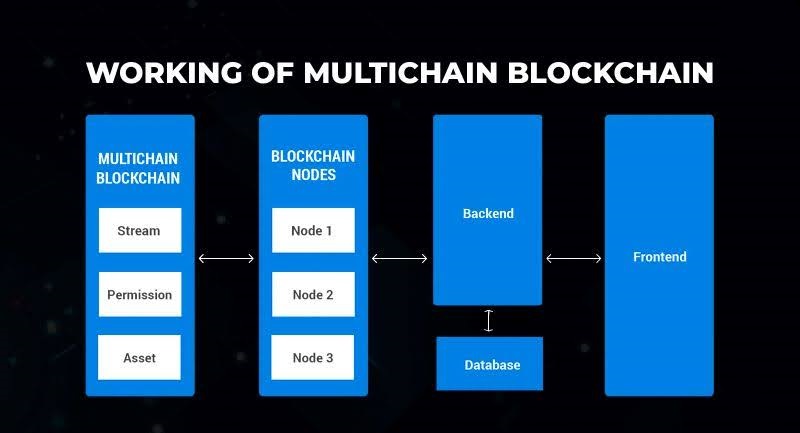
How Multichain Works
At its core, a multichain network relies on a few key components:
- Relay Chains: These act as the backbone of the multichain system, providing shared security and facilitating communication between different blockchains within the network.
- Parachains: These are independent, customizable blockchains that connect to the relay chain, leveraging its security while maintaining their own sovereignty and specialization.
- Bridges: These protocols enable the transfer of assets and data between the multichain network and external blockchains, expanding the reach and interoperability of the system.
Key Characteristics of Multichain
- Scalability: By distributing the computational load across multiple chains, multichain architectures offer improved scalability compared to single-chain systems. This allows for faster transaction processing and reduced network congestion.
- Flexibility: Multichain networks allow for the creation of specialized parachains tailored to specific use cases, fostering innovation and adaptability within the ecosystem.
- Interoperability: The primary goal of multichain is to enable seamless communication and asset transfer between different blockchains, unlocking new possibilities for decentralized applications and cross-chain collaboration.
Advantages of Multichain
- Enhanced Scalability: The ability to process transactions across multiple chains significantly improves scalability and reduces the risk of bottlenecks.
- Increased Flexibility: Customizable parachains allow for a wide range of use cases, from decentralized finance (DeFi) to supply chain management.
- Improved Interoperability: Multichain networks foster a more connected blockchain ecosystem, enabling cross-chain communication and collaboration.
- Reduced Network Congestion: By distributing the workload across multiple chains, multichain architectures can mitigate network congestion and maintain high transaction throughput.
Disadvantages of Multichain
- Management Complexities: The interconnected nature of multichain networks can introduce complexities in terms of governance, coordination, and maintenance.
- Potential Security Concerns: While relay chains provide shared security, the overall security of a multichain network can be influenced by the security of individual parachains and bridges.
- Interchain Communication Challenges: Establishing efficient and secure communication channels between different blockchains within a multichain network can be a technical challenge.
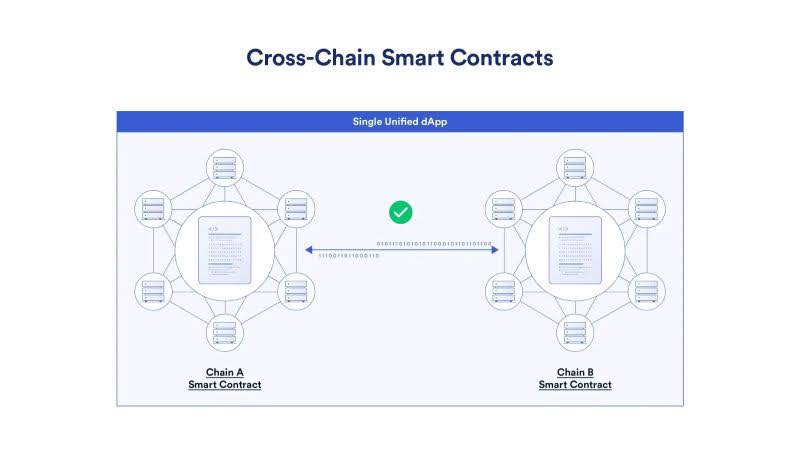
Cross Chain Technologies
Crosschain: Crosschain is like bridges connecting separate islands (different blockchains). These bridges enable people (digital assets) to move back and forth between the islands directly and conveniently.
How Cross Chain Works
Cross Chain communication relies on various mechanisms, each with its unique approach:
- Atomic Swaps: This mechanism enables the direct exchange of cryptocurrencies between two different blockchains without the need for intermediaries. It relies on smart contracts and cryptographic techniques to ensure that the exchange is either fully executed or not at all, eliminating the risk of counterparty default.
- Relays: These protocols facilitate cross-chain communication by relaying messages and data between different blockchains. Relays can be centralized or decentralized, with varying degrees of security and trust assumptions.
- Bridges: These platforms act as intermediaries between blockchains, facilitating the transfer of assets and data across different networks. Bridges can be trusted or trustless, depending on whether they rely on a central authority or utilize decentralized mechanisms for verification and validation.
Advantages of Cross Chain
- Direct Interoperability: Cross Chain technology enables direct communication and asset transfer between different blockchains, simplifying the process compared to multichain solutions.
- Reduced Complexity: By focusing on bridging individual blockchains rather than building an interconnected network, cross chain solutions can be less complex to implement and maintain.
- Increased Accessibility: Cross Chain bridges can open up new markets and opportunities for blockchain projects by enabling access to a wider range of users and assets across different networks.
Disadvantages of Cross Chain
- Security Risks: Cross Chain bridges can be vulnerable to attacks and exploits, as they often hold significant amounts of assets and can become a central point of failure.
- Reliance on Third Parties: Some cross chain solutions rely on centralized entities or trusted intermediaries, which can introduce counterparty risk and compromise the decentralization ethos of blockchain.
- Interoperability Challenges: Ensuring seamless and secure communication between different blockchains with varying architectures and protocols can be technically challenging.
Differences between Multichain vs cross chain technologies
To better understand the strengths and weaknesses of each approach, let's compare multichain and cross chain technologies across several key dimensions:
|
Feature |
Multichain |
Cross Chain |
|
Scalability |
High (due to distributed workload across multiple chains) |
Moderate (depends on the specific bridge or protocol) |
|
Security |
Moderate (shared security of relay chain, but can vary) |
Moderate (can be vulnerable to attacks on bridges) |
|
Security |
High (customizable parachains for various use cases) |
Moderate (limited by the specific bridge or protocol) |
|
Complexity |
High (requires complex architecture and coordination) |
Moderate (simpler implementation compared to multichain) |
|
Interoperability |
High (seamless communication within the network) |
Moderate (depends on the number and quality of bridges) |
Multichain vs crosschain technologies Applications
Multichain
- DeFi Ecosystems: The scalability and flexibility of multichain architectures make them ideal for building complex DeFi ecosystems with multiple interconnected applications and assets.
- Enterprise Solutions: Multichain can be used to create private or consortium blockchains for specific industries or use cases, leveraging the interoperability and customization capabilities of the technology.
- Web3 Infrastructure: Multichain can serve as the foundation for a more scalable and interoperable Web3 infrastructure, supporting a wide range of decentralized applications and services.
Cross Chain
- Asset Swaps and Transfers: Cross Chain bridges are primarily used for swapping or transferring assets between different blockchains, providing liquidity and access to a wider range of markets.
- Cross-chain DeFi: Cross Chain technology enables the creation of cross-chain DeFi applications, allowing users to access liquidity and participate in financial activities across multiple blockchain networks.
- Oracle Integration: Cross Chain protocols can be used to integrate oracles into blockchain applications, providing access to real-world data and enabling a wider range of use cases for smart contracts.
The Future of Blockchain Interoperability
The future of blockchain interoperability is moving towards a hybrid approach that combines the strengths of both multi chain and cross chain technologies. While multichain architectures excel in scalability and flexibility within a single network, cross chain interoperability facilitates smooth communication and asset transfers across distinct blockchain networks.
Increasingly, projects are adopting hybrid models. They utilize multichain architectures to develop specialized blockchains tailored for specific purposes, integrating these chains with other independent blockchains through cross chain bridges and protocols. This approach blends the scalability and flexibility of multichain with the expansive interoperability capabilities of crosschain.
Moreover, advancements in technologies such as zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) and optimistic rollups are poised to enhance the security and efficiency of cross chain bridges, mitigating current challenges. As these technologies evolve, they promise a more seamless and secure cross chain experience, accelerating the adoption of blockchain across diverse industries.
U2U Network: Pioneering Cross Chain Interoperability
U2U Network is an ambitious project at the forefront of cross-chain innovation. Its core mission is to create a seamless and secure environment for the exchange of assets and information across various blockchain networks. U2U envisions a future where blockchain interoperability is not just a buzzword but a practical reality, empowering users with the ability to harness the unique strengths of different blockchain ecosystems.
U2U Network leverages cutting-edge cross-chain technology to bridge the gaps between disparate blockchains. By developing a robust and secure infrastructure for cross-chain communication, U2U enables the seamless transfer of assets and data between different networks. This approach not only enhances the liquidity and utility of digital assets but also opens up new possibilities for cross-chain collaboration and innovation.

The debate between multichain and cross chain technologies is not about choosing one over the other, but rather understanding and harnessing the strengths of each approach to foster a more interconnected and interoperable blockchain ecosystem. Multichain architectures excel in scalability and flexibility, allowing for specialized blockchains tailored to specific use cases. On the other hand, cross chain solutions provide a direct method to connect existing blockchains and facilitate seamless asset transfers.
U2U Network stands out in this evolving landscape with its focus on cross-chain interoperability. By pioneering innovative solutions that bridge different blockchain networks, U2U empowers users with enhanced flexibility, choice, and access to a diverse array of decentralized applications and services. Whether enabling cross-chain DEX aggregation, facilitating NFT marketplaces, or spearheading other groundbreaking initiatives, U2U showcases the transformative potential of cross-chain technology.
As blockchain technology matures, the significance of interoperability will continue to grow. Projects like U2U Network, committed to building a more connected and collaborative blockchain ecosystem, are leading the charge towards a future where blockchain's full potential can be realized. This future promises seamless interactions across multiple blockchains, unrestricted flow of assets between networks, and an environment where decentralized innovation thrives.





.png)
