Have you ever imagined being part of shaping the future of a blockchain project you love? No longer are decisions made top-down. With the emergence of Governance Tokens, power has been decentralized to the community. Let's explore how Governance Tokens are revolutionizing our interaction with the decentralized world, bringing transparency, fairness, and a voice to everyone in the Web3 era.
Table of Contents
What is a governance token?
A Governance Token is a type of cryptocurrency that enables holders to participate directly in the on-chain governance of a blockchain project. Typically, each governance token held represents a vote for upcoming proposals, though there are other methods as well. Holders of governance tokens can use them to approve or reject changes to a decentralized application (dApp) or blockchain during periodic voting phases. Many dApps also allow token holders to propose initiatives and vote on them.

While governance tokens are not exclusively for decentralized finance (DeFi), they are most prevalent in this sector. Most decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and leading cryptocurrency lending platforms utilize governance tokens to empower community members in project management decisions.
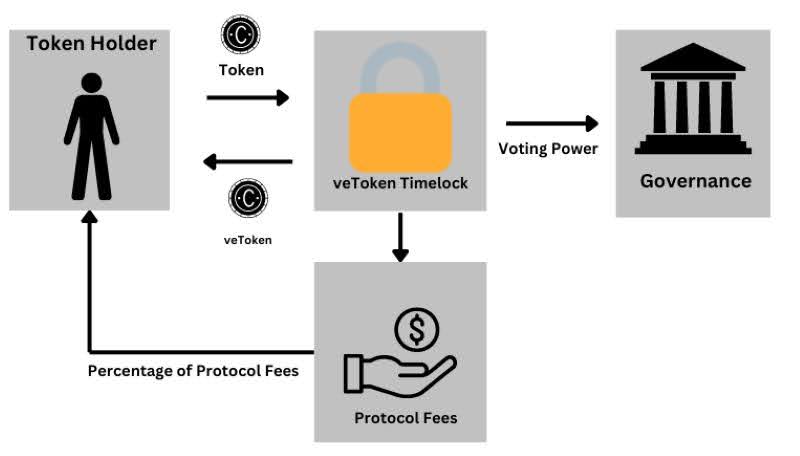
How Governance Tokens Work?
Governance Tokens operate by allowing holders to participate in the governance of blockchain protocols and dApps through Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs).
DAOs are organizational structures governed by a set of agreed-upon rules encoded as smart contracts. Smart contracts enable these rules to be automatically enforced on the blockchain network. This automation removes the need for a central authority or third-party intermediary.
The rules of smart contracts are validated and maintained by a computer algorithm known as a consensus mechanism. The consensus mechanism ensures agreement among all participants in a decentralized manner, without relying on a centralized intermediary to achieve consensus across the network.
The goal of a DAO is to create an autonomous, self-sustaining organization capable of making decisions and executing transactions without the need for interference from any centralized entity.
Smart contracts are also used in governance to ensure that votes are accurately recorded and that the outcomes of decisions are implemented after votes are cast. This is all achieved through publicly available parameters on the blockchain network, rather than the private decisions of a single centralized entity.
For example, a governance proposal might involve deciding whether to burn (permanently remove from circulation) a certain amount of the protocol's native tokens. In such a case, a smart contract would be created to automatically burn the tokens if a majority of token holders vote in favor of the proposal.
In this scenario, both the parameters of the voting process and the execution of the voting outcomes can be managed in a decentralized manner because all information is transparently maintained on the blockchain.
Governance tokens vs. utility tokens
Governance tokens and utility tokens share several common characteristics, leading some to use these terms interchangeably. However, there is a crucial difference between governance tokens and utility tokens, which lies in voting rights.
To qualify as a governance token, holders must have the ability to vote. Utility tokens, on the other hand, can serve various purposes within a blockchain ecosystem, including voting. Therefore, all governance tokens are utility tokens, but not all utility tokens are governance tokens.

An excellent example of a utility token that is not a governance token is the Basic Attention Token (BAT) used within the Brave browser. BAT incentivizes advertisers and users on the Brave browser but does not grant holders special voting rights.
Technically speaking, a governance token is a type of utility token. However, unless a cryptocurrency allows holders to participate in DAO proposals (Decentralized Autonomous Organization), it cannot qualify as a governance token.
What are the advantages of governance tokens?
Governance Token transcends mere voting; it embodies a decentralization philosophy that disrupts traditional hierarchies. By distributing decision-making power among token holders, it promotes equity and inclusivity, reducing the risk of central control.
Transparency is pivotal in Governance Token. Every decision, vote, and outcome is permanently recorded on the blockchain, ensuring public scrutiny and eliminating hidden agendas. This transparency fosters accountable decision-making, conducted openly for the entire community.
The most profound impact of Governance Token lies in its ability to stimulate community engagement. With a stake in the project's success, token holders actively participate, shaping its trajectory. This ownership cultivates a dedicated community committed to long-term growth.

Active participation also aligns incentives: token holders prioritize community-wide benefits, ensuring decisions uphold sustainability over short-term gains. This alignment encourages decisions that safeguard the project's future.
Moreover, governance tokens fuel innovation by empowering communities to propose and vote on new ideas. This inclusive approach fosters experimentation, yielding innovative features and strategies that enrich the project.
In essence, governance token is revolutionary, reshaping organizational dynamics. By empowering individuals, ensuring transparency, and aligning incentives, it pioneers a decentralized, equitable, and innovative future.
What are the challenges of governance tokens?
Governance Token, while promising, faces several challenges that must be navigated to ensure its effectiveness and sustainability over the long term.
One significant challenge is voter apathy. Despite the opportunity to influence project direction, not all token holders actively participate in voting. This can lead to decisions being skewed by a small, potentially unrepresentative group, impacting the legitimacy of governance outcomes.

Another critical issue is the knowledge gap among token holders. Many may lack the technical expertise or deep understanding of project intricacies necessary to make well-informed decisions. This gap increases the risk of uninformed voting, potentially resulting in unintended consequences for the project.
Security is a paramount concern in governance token. Voting mechanisms, especially those conducted directly on the blockchain, are vulnerable to hacking and manipulation. Safeguarding these systems is essential to maintain trust and confidence in the governance process and protect the integrity of outcomes.
Legal ambiguity adds another layer of complexity. Regulatory frameworks around token-based governance are still evolving, leaving projects uncertain about compliance requirements. This regulatory uncertainty can deter potential participants and create operational challenges for projects operating across different jurisdictions.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of governance token - including decentralization, transparency, and community engagement - are substantial. As the ecosystem matures, addressing these challenges through improved participation incentives, educational initiatives, enhanced security measures, and clearer regulatory guidelines will be crucial. These efforts will strengthen governance tokens as a foundational pillar of Web3, driving innovation and empowering communities worldwide.
Governance tokens examples
There are dozens of governance tokens, but the most prominent ones are on the Ethereum blockchain. Here are some of the most mentioned DeFi protocols (at the time of writing) that provide DAO tokens:
Uniswap: Ethereum's decentralized exchange (DEX), Uniswap, airdropped its UNI token to all users of its platform in 2020. UNI token remains one of the top governance tokens available on most centralized cryptocurrency exchanges (CEX).
Aave: Developed in 2017, Aave is a leading decentralized lending platform on the Ethereum blockchain. Holders of AAVE governance tokens not only have voting rights but can also stake their AAVE to secure the dApp.
Maker: Maker Protocol is best known for issuing the algorithmic stablecoin DAI on the Ethereum blockchain. The governance token of Maker is MKR, used by holders to vote on adjustments to DAI issuance, collateral requirements, and protocol interest rates.
Compound: Compound's COMP token holds a significant position in cryptocurrency history. In the summer of 2020, the lending platform introduced the concept of governance tokens and liquidity mining with the issuance of COMP. COMP holders can propose and vote on proposals for the platform.
There have been criticisms that the voting power does not proportionately match the market capitalization of these tokens. In reality, their value stems from their ability to implement fee switches through governance.
Governance Tokens have emerged as a game-changer in the Web3 era, empowering users and reshaping the management and development of blockchain projects. By decentralizing decision-making, fostering community participation, and ensuring transparency, Governance Tokens are not just technical tools but symbols of innovation and progress in the decentralized world. As Web3 continues to evolve, Governance Tokens promise to play an increasingly significant role, opening new opportunities and promoting the sustainable growth of the entire blockchain ecosystem.





.png)
