Explore the groundbreaking potential of Directed Acyclic Graphs in financial technology. Discover how this innovative approach is revolutionizing transaction settlement and reshaping the future of blockchain architecture.
Table of Contents
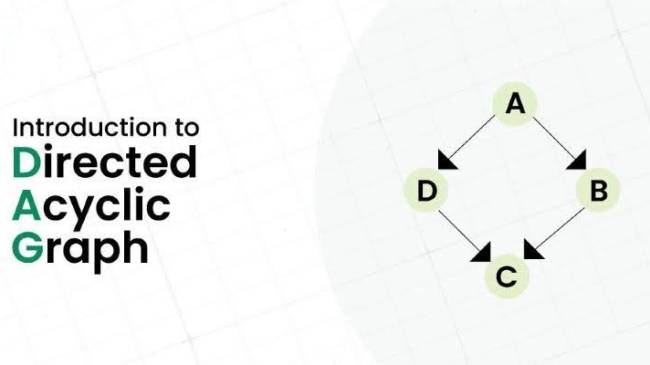
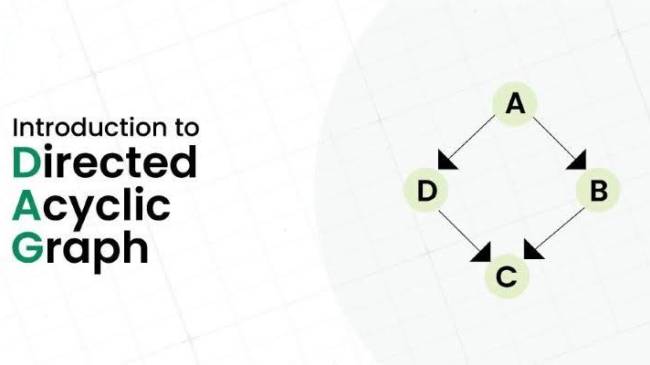
What are Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs)?
Definition of DAGs
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) are a novel data structure that is gaining traction as an alternative to traditional blockchains in the realm of financial technology. Unlike the linear, block-based structure of blockchains, DAGs offer a unique topology that resembles a web or tangle of interconnected transactions.
Structure of DAGs
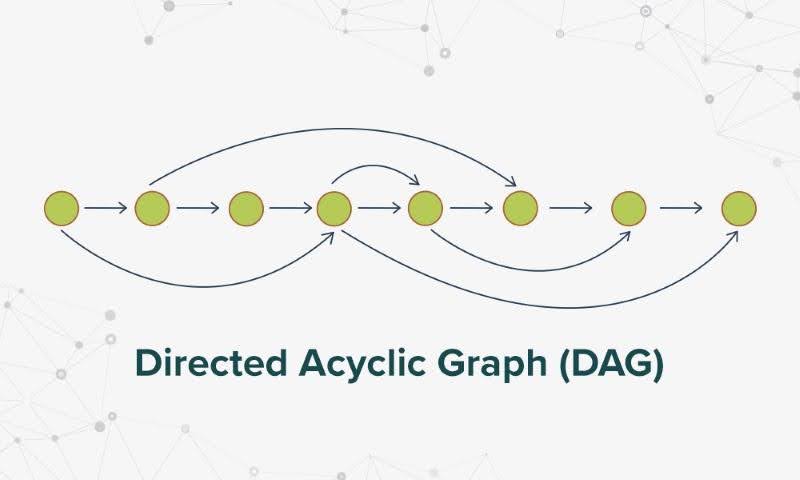
In DAGs, each transaction is represented as a vertex, and each edge represents a reference or validation of previous transactions. Instead of forming a linear chain of blocks, transactions in DAGs are interwoven, creating a complex network of dependencies. This structure allows for parallel processing of transactions, which can significantly improve scalability and transaction speed compared to traditional blockchains.
Consensus Mechanisms in DAGs
One of the most significant differences between DAGs and traditional blockchains is the way they achieve consensus. In a blockchain, miners or validators compete to create new blocks and add them to the chain, with the longest chain being considered the valid one. However, DAGs do not rely on miners or block producers. Instead, they employ alternative consensus mechanisms, such as:
- Tip Selection: New transactions are attached to the "tips" of the DAG, which are the most recent unconfirmed transactions. This creates a continuous process of validation, where each new transaction confirms the validity of the previous transactions it references.
- Weighted Random Walks: This algorithm involves traversing the DAG randomly, with the probability of selecting a particular path being proportional to the weight or cumulative value of the transactions along that path. This helps to ensure that the most "heavily referenced" transactions are considered valid.
Advantages of directed acyclic graphs in Financial Technology
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) are poised to revolutionize financial technology by addressing several key limitations of traditional blockchain architectures. Their unique structure and consensus mechanisms offer a range of advantages that could significantly enhance the efficiency, speed, and accessibility of financial transactions.
Unparalleled Scalability
One of the most significant advantages of DAGs in financial technology is their exceptional scalability. Unlike blockchains, which are limited by block size and confirmation times, DAGs can handle a much higher throughput of transactions. This is because transactions are validated concurrently, rather than sequentially, allowing for parallel processing and drastically increasing the network's capacity. For financial applications that require high transaction volumes, such as payment systems or decentralized exchanges, DAGs offer a promising solution to the scalability bottleneck.
Near-Instantaneous Speed
DAGs also excel in terms of transaction speed. Since transactions can be confirmed almost instantly upon submission, users can enjoy a near-real-time experience. This is a significant improvement over traditional blockchains, where transaction confirmation times can range from minutes to hours. In the fast-paced world of finance, where time is often of the essence, the speed of DAG-based transactions can be a game-changer.
Cost-Effective Transactions
Another key advantage of DAGs is their potential for significantly lower transaction fees. Traditional blockchains rely on miners to validate transactions, who are rewarded with transaction fees for their efforts. However, DAGs eliminate the need for miners, allowing for near-zero or even zero transaction fees. This makes DAGs an attractive option for financial applications that involve frequent, low-value transactions, such as micropayments or remittances.
Micropayments Made Possible
The low transaction fees associated with DAGs open up new possibilities for micropayments and other low-value transactions. On traditional blockchains, the high fees often make these types of transactions economically unfeasible. However, with DAGs, even the smallest transactions can be processed quickly and cheaply, unlocking new opportunities for financial inclusion and innovation.
Energy Efficiency
Finally, DAGs are inherently more energy-efficient than Proof-of-Work (PoW) based blockchains. PoW requires miners to expend significant computational power to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions. This process consumes a tremendous amount of energy, raising concerns about the environmental impact of blockchain technology. DAGs, on the other hand, do not rely on mining, making them a more sustainable and environmentally friendly option.
Use Cases of Directed acyclic graphs in Financial Technology
The unique characteristics of Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) make them well-suited for a variety of applications in the financial technology sector. Here are some of the most promising use cases:
Revolutionizing Remittances
Cross-border payments have long been plagued by slow processing times, high fees, and complex intermediaries. DAG-based systems have the potential to revolutionize remittances by offering near-instantaneous transactions at a fraction of the cost. The absence of miners and the ability to process transactions in parallel can significantly reduce friction and increase accessibility, particularly for underserved populations in developing countries.
Enhancing Supply Chain Transparency
Supply chains are often complex and opaque, making it difficult to track the origin and movement of goods. DAGs can provide a transparent and immutable record of every transaction and movement within a supply chain, reducing the risk of fraud and counterfeit goods. This enhanced traceability can improve supply chain efficiency, ensure product authenticity, and build trust between stakeholders.
Streamlining Trade Finance
Trade finance processes are notoriously cumbersome, involving a multitude of documents and manual approvals. DAGs can automate and streamline these processes, reducing paperwork and minimizing the risk of errors or delays. Smart contracts built on DAG-based platforms can automatically execute upon fulfillment of predetermined conditions, accelerating trade settlements and improving liquidity for businesses.
Other Potential Applications in Financial Technology
The versatility of DAGs opens up a wide range of other potential applications in financial technology. Some examples include:
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): DAG-based DEXs can offer faster and cheaper trading than traditional exchanges, with the potential to handle high volumes of transactions without congestion.
- Prediction Markets: DAGs can be used to create decentralized prediction markets, where users can bet on the outcome of future events. The fast confirmation times and low fees of DAGs make them well-suited for this type of application.
- Identity Management: DAGs can provide a secure and decentralized way to manage digital identities, protecting user privacy and reducing the risk of identity theft.
U2U Network and DAG Technology
U2U Network is a pioneering project that has recognized the potential of Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) to revolutionize the financial technology landscape. Embracing a DAG-based architecture, U2U Network is building a high-performance blockchain platform that aims to address the scalability, speed, and cost challenges that have long plagued traditional blockchain systems.
U2U Network's DAG-Based Architecture
U2U Network's core infrastructure is built upon a DAG architecture, enabling it to achieve unparalleled scalability and transaction speed. By leveraging the unique properties of DAGs, such as parallel transaction processing and the absence of miners, U2U Network can handle a massive volume of transactions with near-instantaneous confirmation times and minimal fees.
U2U Subnet: A Scalable and Customizable Solution
One of the key innovations of U2U Network is its subnet technology, which allows for the creation of customized sub-networks within the U2U ecosystem. These subnets can be tailored to specific use cases, such as decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, or gaming. By utilizing a DAG-based architecture, U2U subnets can achieve high throughput and low latency, making them ideal for applications that require fast and efficient transaction processing.
Benefits for U2U Users and Partners
The integration of DAG technology into U2U Network offers a wide range of benefits for both users and partners:
- Faster and Cheaper Transactions: U2U Network's DAG-based architecture enables near-instant transaction confirmations and significantly lower fees compared to traditional blockchain networks. This makes it an attractive option for users who need to send or receive money quickly and affordably.
- Improved Scalability: U2U subnets can scale horizontally to accommodate a growing number of users and applications, ensuring that the network can handle high transaction volumes without sacrificing performance.
- Enhanced Security: DAGs are inherently more resistant to certain types of attacks, such as double-spending, due to their unique structure and consensus mechanisms.
- Greater Flexibility: U2U subnets can be customized to meet the specific needs of different applications, providing developers with greater flexibility and control over their blockchain environments.
U2U Network leads in blockchain innovation, dedicated to utilizing advanced technologies like DAGs to revolutionize the financial landscape. With a commitment to DAG architecture and its own subnet system, U2U is paving the way for faster, more cost-effective, and accessible financial transactions. The network's emphasis on scalability, efficiency, and user-friendly solutions aligns perfectly with DAGs' potential to transform sectors such as remittances, trade finance, decentralized exchanges, and identity management. As U2U Network continues to implement DAG-based solutions, it stands ready to significantly influence the future of finance, fostering inclusivity, transparency, and efficiency across the board.




.png)
