Table of Contents
Comparison of Custodial vs Non-Custodial Wallets

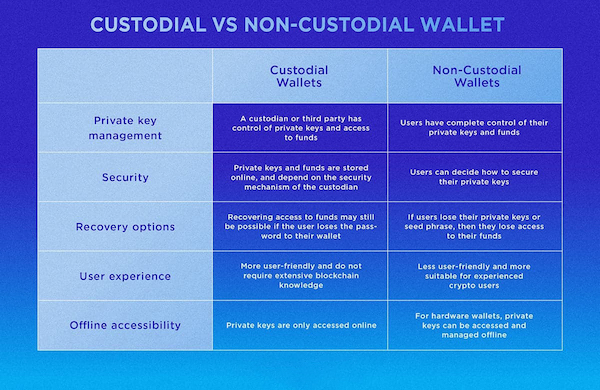
Custodial Wallets
To comprehend the functioning of a custodial wallet, it's essential to first grasp the operation of cryptocurrency wallets. Cryptocurrency wallets do not directly hold a user's funds; instead, they store the public key for transaction setup and the private key for transaction authorization.
As the name implies, a custodial wallet involves a third party assuming responsibility for safeguarding users' private keys. This third party gains complete control over the cryptocurrency assets, managing the user's wallet key, executing transaction signatures, and safeguarding the user's cryptocurrency holdings.
- Typically, custodial wallets are offered by cryptocurrency exchanges or specialized custodial wallet providers through mobile or web applications. Once users log into their wallet accounts, they utilize the provider's interface to oversee their assets and conduct transactions.
- This arrangement necessitates users placing trust in the service provider to securely store their tokens and implement robust security measures to thwart unauthorized access. These security measures may encompass two-factor authentication (2FA), email confirmation, and biometric authentication methods such as facial recognition or fingerprint verification.
Non-Custodial Wallets
A non-custodial wallet, also known as a self-custody wallet, places the full responsibility of managing cryptocurrency funds squarely on the owner. In this setup, the user exercises complete authority over their crypto holdings, administers their private key, and conducts transactions autonomously.
- Non-custodial wallets manifest in various forms. Browser-based wallets function as browser extensions, permitting users to input their private keys and initiate transactions. Mobile wallets take the form of downloadable mobile applications. In contrast, hardware wallets are tangible devices, often regarded as the most secure option due to their offline accessibility.
- Non-custodial wallets furnish users with a seed phrase. When establishing the wallet, users are prompted to record and safeguard a set of 12 randomly generated words, referred to as a 'recovery,' 'seed,' or 'mnemonic' phrase. This phrase serves as the foundation for generating public and private keys, also functioning as a backup and recovery mechanism in the event of users losing access to their original device. Possession of the seed phrase equates to full control over the funds held within a user's wallet. Should the seed phrase be misplaced, users forfeit access to their funds.
- Users assume the responsibility for managing and executing each transaction. Private keys are indispensable for sending funds and completing various transactions. Depending on the specific non-custodial wallet in use, transactions can occur in real-time on the blockchain or be signed offline and subsequently uploaded to the blockchain for confirmation.
Wallet Overview
A digital wallet is a virtual container that allows users to store their cryptocurrencies and interact with blockchain-based platforms. These wallets consist of a combination of public and private keys, enabling users to make secure transactions and access their holdings. In the Web3 ecosystem, where decentralization is a core principle, the choice between custodial and non-custodial wallets becomes critical.
The Importance of Wallets for Web3 Developers
Web3 developers play a crucial role in creating and maintaining decentralized applications. These developers often deal with cryptocurrencies and need reliable wallets to streamline their workflow. Wallets offer a convenient gateway for developers to manage funds, interact with smart contracts, and test their dApps on different blockchain networks. Whether it's deploying a new smart contract or testing blockchain integrations, a wallet is an essential tool for every Web3 developer.
Wallet Providers
Numerous wallet providers compete in the market, catering to the diverse needs of users. Some popular names include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Coinbase Wallet, Ledger, and Trezor, among others. These providers offer various wallet types, each with its unique features and services.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Custodial and Non-Custodial Wallets

The battle between custodial vs non-custodial wallets continues to shape the landscape of Web3. Each type of wallet comes with its own set of merits and caters to distinct user preferences. Custodial wallets provide ease of use and customer support, while non-custodial wallets offer security and decentralization. For Web3 developers, the choice depends on the specific needs of their projects and their stance on financial autonomy.
As the Web3 space continues to evolve, the development of innovative wallet solutions will undoubtedly progress. Whether you opt for custodial convenience or embrace the principles of non-custodial wallets, remember to prioritize security and stay aligned with the decentralized vision that Web3 brings to the world of cryptocurrencies and dApps.






