Blockchain Interoperability is a crucial concept in the blockchain industry, enabling seamless communication and data exchange between different blockchain networks. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with blockchain systems, making it easier to integrate and utilize various blockchain platforms. In this article, we will explore the importance of blockchain interoperability and the various approaches and solutions being developed to achieve it.
Table of Contents
What is blockchain interoperability?
The term blockchain interoperability has been increasingly mentioned recently. It refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to seamlessly interact with each other, allowing for the exchange of data and transfer of assets without the need for intermediaries or central authorities. Therefore, blockchain projects aim to implement interoperability into their platforms to create an ecosystem where different blockchains can communicate effectively with each other. The vision for enterprise blockchains with interoperability capabilities includes integrating with existing systems, initiating transactions across different networks, conducting transactions across chains, and facilitating easy transitions between different underlying platforms.
The Importance of Blockchain Interoperability
Blockchain interoperability is essential for several reasons:
Cross-Chain Functionality: Interoperability enables the development of cross-chain decentralized applications (dApps) that can function across multiple blockchains, rather than being isolated on a single network.
Asset Portability: Interoperability protocols allow users to transfer digital assets, such as tokens and NFTs, between different blockchain networks, increasing the utility and liquidity of these assets.
Ecosystem Integration: Interoperability facilitates the integration of blockchain-based systems with traditional IT infrastructure, enabling seamless data exchange and interaction between decentralized and centralized environments.
Scalability and Specialization: By allowing blockchains to focus on their unique strengths and specialize in specific use cases, interoperability enables a more scalable and efficient blockchain ecosystem.
.jpg)
The challenge of blockchain interoperability
Cross-chain interoperability solutions are not without challenges. Many prioritize "speed of development" over security. Cross-chain bridges, in particular, are vulnerable because they provide two entry points that hackers can exploit through any vulnerabilities. Security and integrity of these cross-chain bridges, complexity, autonomy, and incurred costs are some of the challenges and trade-offs associated with cross-chain interoperability solutions.
Addressing security issues: Ensuring the security and integrity of transactions across cross-chain bridges is a significant challenge. The bridges themselves serve as critical communication links between two networks. Any weaknesses or vulnerabilities in such a system could have serious consequences for the entire ecosystem. These solutions have the potential to increase the likelihood of attacks and pose new governance challenges between different blockchain networks.
Different trust models: Blockchains vary in their levels of trust and security. Each blockchain ledger has a different trust model—some are supported by hundreds of miners, while others have minimal support. Transferring information from less trustworthy ledgers to more secure ones can expose stronger blockchains to manipulation and compromise by external actors.
Manipulation: Transferring data or digital assets from less secure to more secure blockchains can also make the latter vulnerable to manipulation. If a bridge is compromised, malicious actors can access sensitive information or assets.
Hacks: Security risks associated with holding assets across multiple blockchains can be substantial, opening doors to hacks and potential loss of funds. Hackers consistently probe existing blockchain bridges and often succeed in finding vulnerabilities. Many of these hacks stem from multi-signature security setups or delegated proof-of-stake mechanisms, which are considered more centralized and vulnerable.
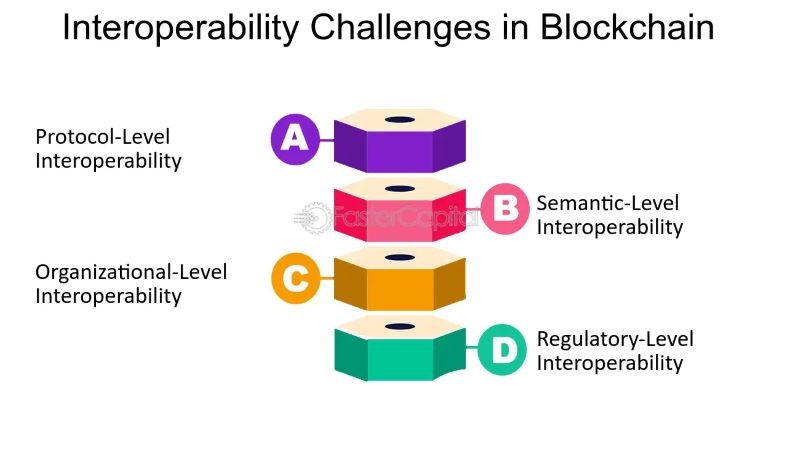
Technical complexity: Different blockchains may have different security solutions, consensus algorithms, and programming languages, which can add technical complexity. This complexity can increase difficulties in development, deployment, and maintenance of DAOs, while also affecting usability, accessibility, and security. Another barrier to blockchain interoperability is compatibility. Connecting interoperable blockchains will be easier than non-compatible ones.
Validity issues: Another significant challenge is the issue of validity—ensuring that funds will be available on the destination chain after they are committed to the source chain. Without validation, a transaction reversed on the source chain, such as a block reorganization, can cause issues on the destination chain—e.g., tokens being stuck unsupported. Without assurance of validity, bridges between two chains can also collapse.
Sovereignty and autonomy: Furthermore, interoperability solutions may impact the sovereignty and autonomy of DAOs by depending on or influencing decisions of other systems or entities. This could lead to conflicts with their values or objectives and impact their cohesion, trust, and reputation.
Looking ahead: Blockchain interoperability is a crucial component of blockchain's future. Despite the various challenges of current solutions, especially those using bridges, newer and more innovative blockchain interoperability solutions are emerging, holding promise for the future of blockchain interoperability.
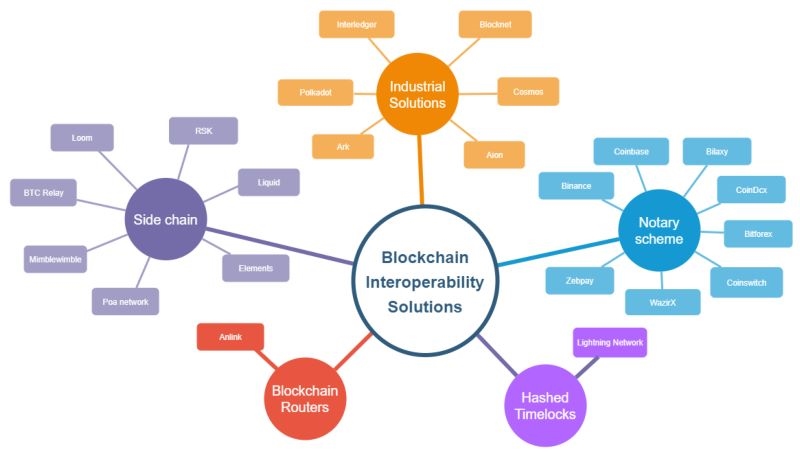
Approaches to Blockchain Interoperability
There are several approaches and technologies used to achieve blockchain interoperability, including:
Layer 2 Protocols: These protocols, such as Cosmos' Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) and Polkadots Cross-Chain Messaging, operate on top of base-layer blockchains to facilitate cross-chain communication and asset transfers.
Atomic Swaps: Atomic swaps enable the direct exchange of digital assets between different blockchain networks without the need for a centralized intermediary.
Cross-Chain Bridges: Bridges connect two or more blockchain networks, allowing the transfer of data and assets between them. Examples include Binance Bridge, Multichain Bridge, and Avalanche Bridge.
Decentralized Oracles: Oracles, such as Chainlink, can be used to securely relay data between blockchains, enabling cross-chain smart contract functionality and interoperability.
Key Blockchain Interoperability Projects
Blockchain interoperability is crucial for the seamless integration and communication between different blockchain networks, paving the way for a more connected and efficient decentralized ecosystem. Several prominent projects are at the forefront of this effort:
Polkadot
Polkadot is a multi-chain network designed to enable cross-chain communication and the creation of specialized, interoperable blockchains known as parachains. By facilitating the transfer of data and assets across different blockchains, Polkadot enhances scalability and innovation within the decentralized space, allowing for the seamless operation of diverse blockchain applications.
Cosmos
Cosmos is an ecosystem of interconnected blockchains that utilizes the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol to enable cross-chain interactions. The Cosmos network aims to create an "Internet of Blockchains," allowing different blockchain networks to interoperate while maintaining their sovereignty and security. This fosters a more integrated and cooperative blockchain environment.

Chainlink
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that provides secure and reliable data feeds, enabling cross-chain smart contract functionality. By connecting smart contracts to real-world data and external APIs, Chainlink enhances the capabilities of blockchain applications across various networks, ensuring accurate and trustworthy data flow between chains.
Wanchain
Wanchain focuses on cross-chain asset transfers and decentralized finance (DeFi) applications across different blockchain networks. By creating a decentralized infrastructure for seamless asset exchange and interoperability, Wanchain bridges the gap between isolated blockchain systems, promoting a more unified and versatile blockchain ecosystem.
Axelar
Axelar is a universal interoperability network that facilitates secure and seamless communication between any blockchain or Web3 application. Axelar's protocol connects various blockchains and enables the transfer of assets and data, promoting a more cohesive and integrated decentralized ecosystem.
The Significance of Interoperability in Web3
Interoperability is key to the future of Web3, as it allows diverse blockchain networks to communicate and work together. This interconnectedness leads to:
Enhanced User Experience: Users can seamlessly interact with multiple blockchain networks without needing to understand the complexities behind each one.
Greater Innovation: Developers can build more complex and feature-rich applications by
leveraging the strengths of different blockchains.
Increased Efficiency: Cross-chain transactions reduce bottlenecks and improve the speed and cost-effectiveness of blockchain operations.
Widespread Adoption: By creating a more accessible and cohesive ecosystem, interoperability drives broader acceptance and use of blockchain technologies.
The ability to interact between blockchains is not merely a technological term but a pivotal key to unlocking the true potential of Web3 and the decentralized ecosystem. By breaking down barriers between blockchain networks, we are moving closer to a world where decentralized applications (dApps) operate seamlessly across multiple platforms, digital assets are freely transferred, and data is securely shared.
Projects like U2U Network, with its advanced Modular Layer-1 Network and DePIN Subnets technology, are striving to build a reliable Web3 ecosystem where blockchain interoperability is supported and encouraged. Despite the challenges ahead, the future of blockchain interoperability is highly promising. With continuous developments in solutions such as cross-chain bridges, sidechains, and interoperability protocols, we can envision an expanding and efficient blockchain ecosystem.
Blockchain interoperability - the key to unlocking the true potential of Web3. Alongside pioneering projects like U2U Network, we are moving closer to a future where decentralized applications can operate seamlessly across multiple platforms, digital assets can be freely transferred, and data can be securely shared. This is not just a technological advancement but a paradigm shift towards a more decentralized and transparent world.





.png)
